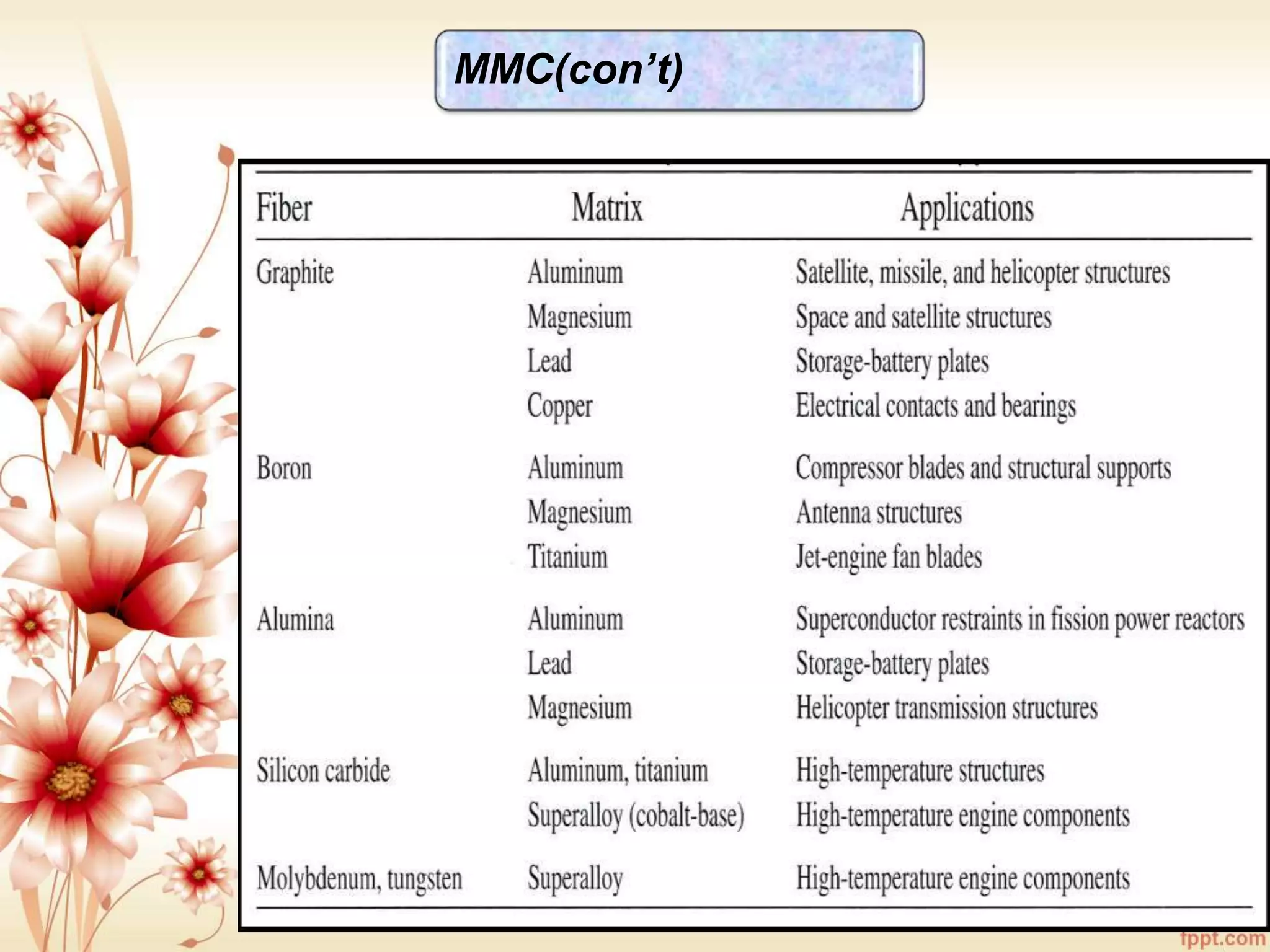
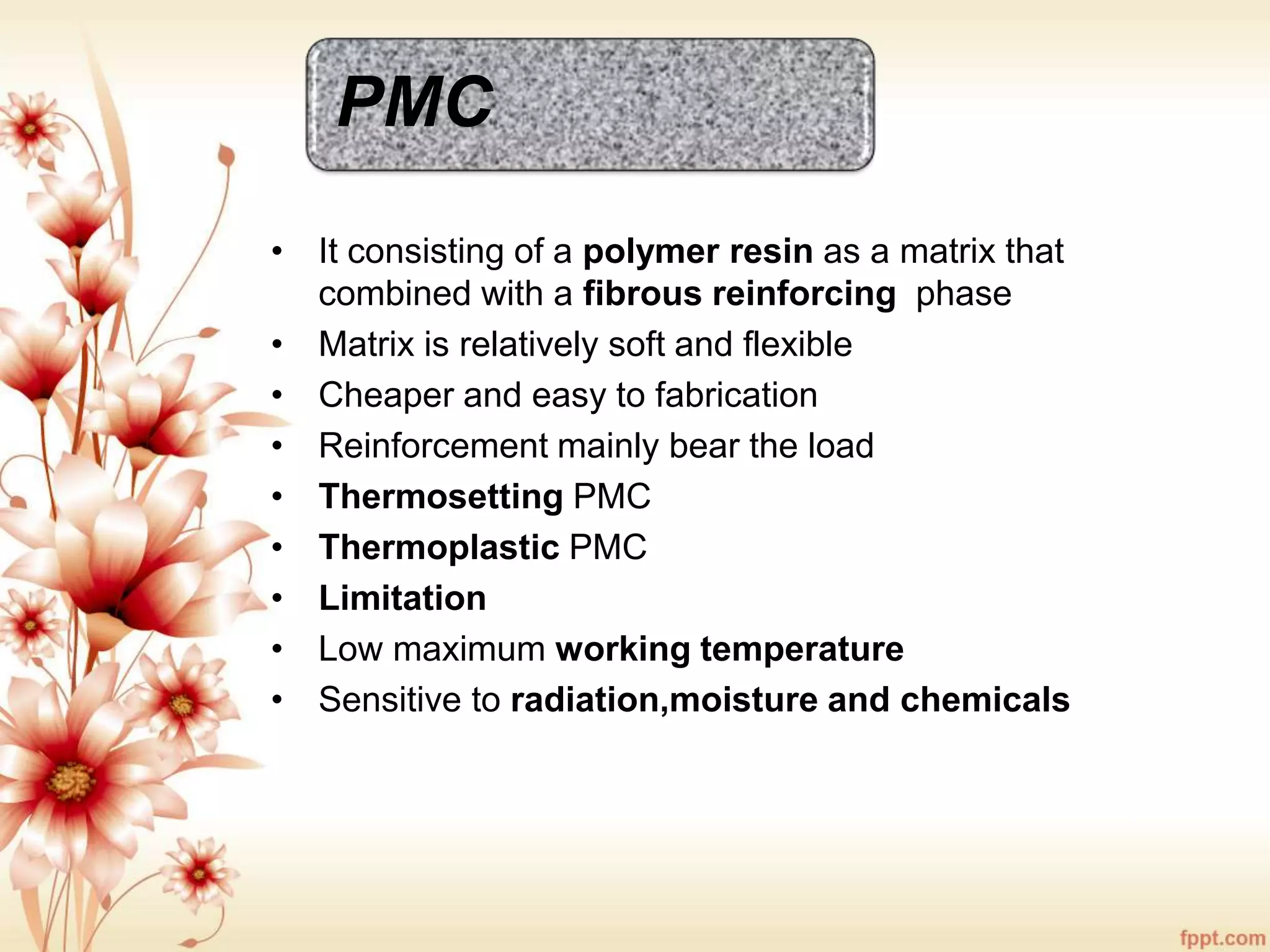
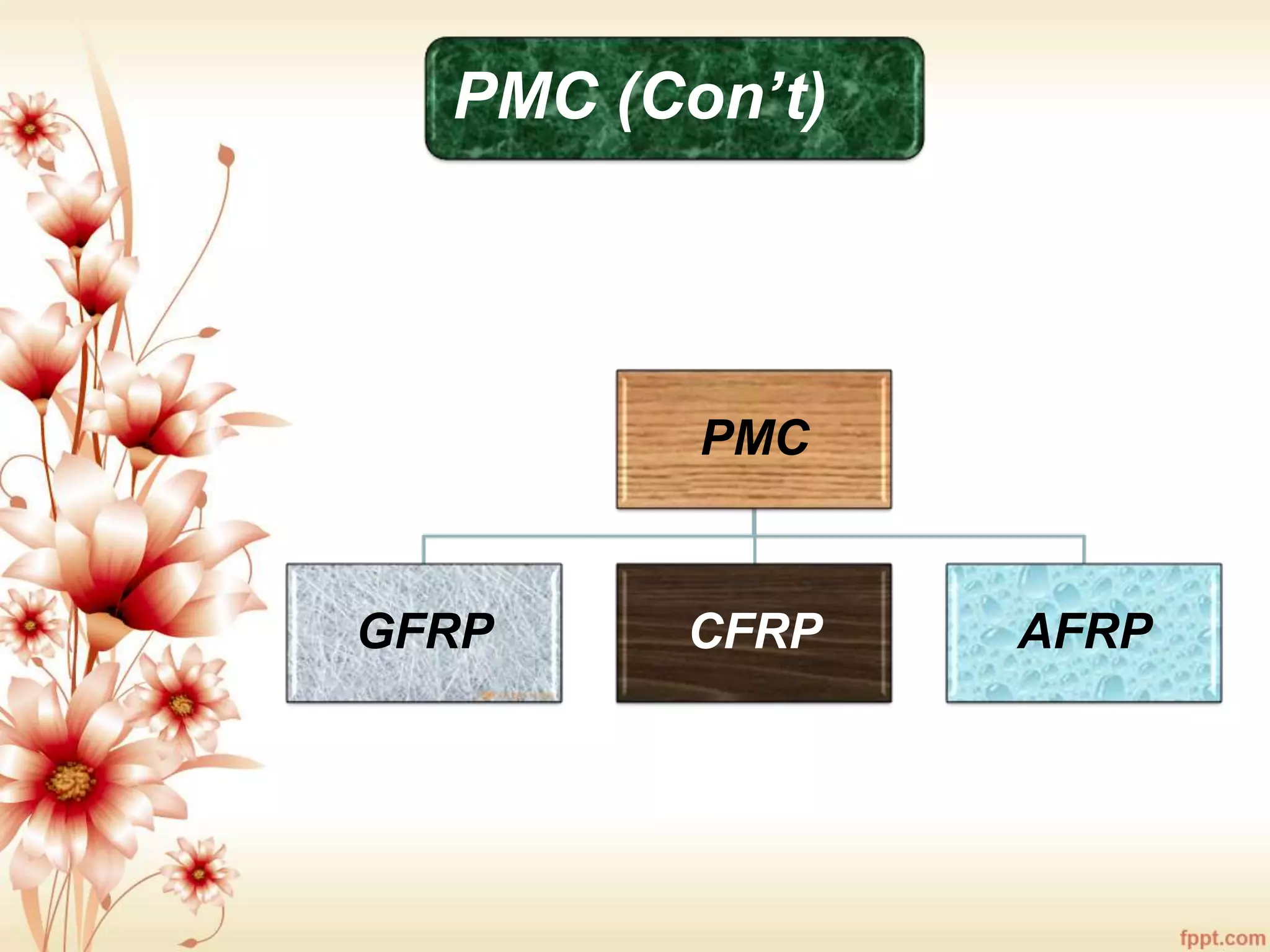
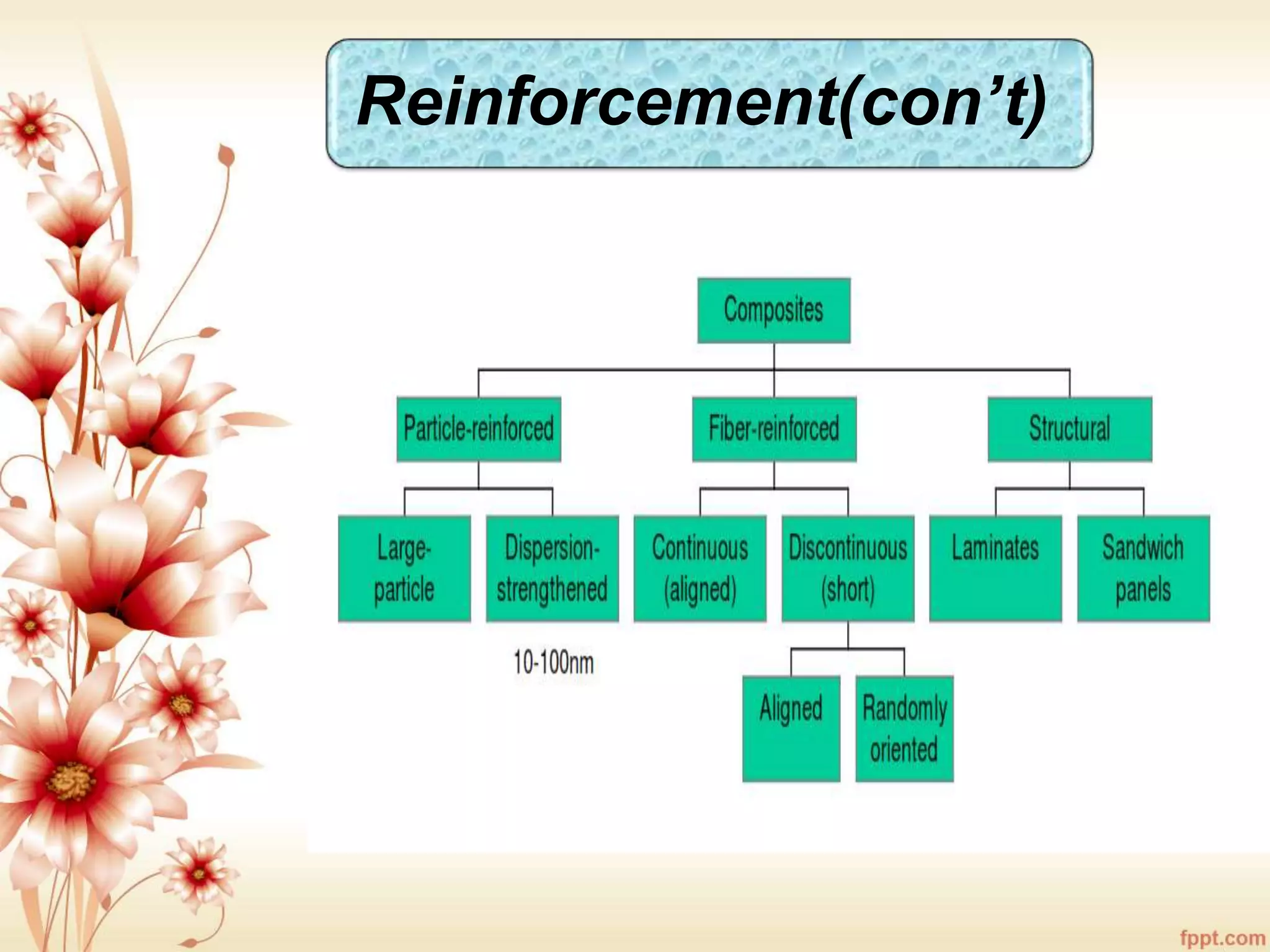
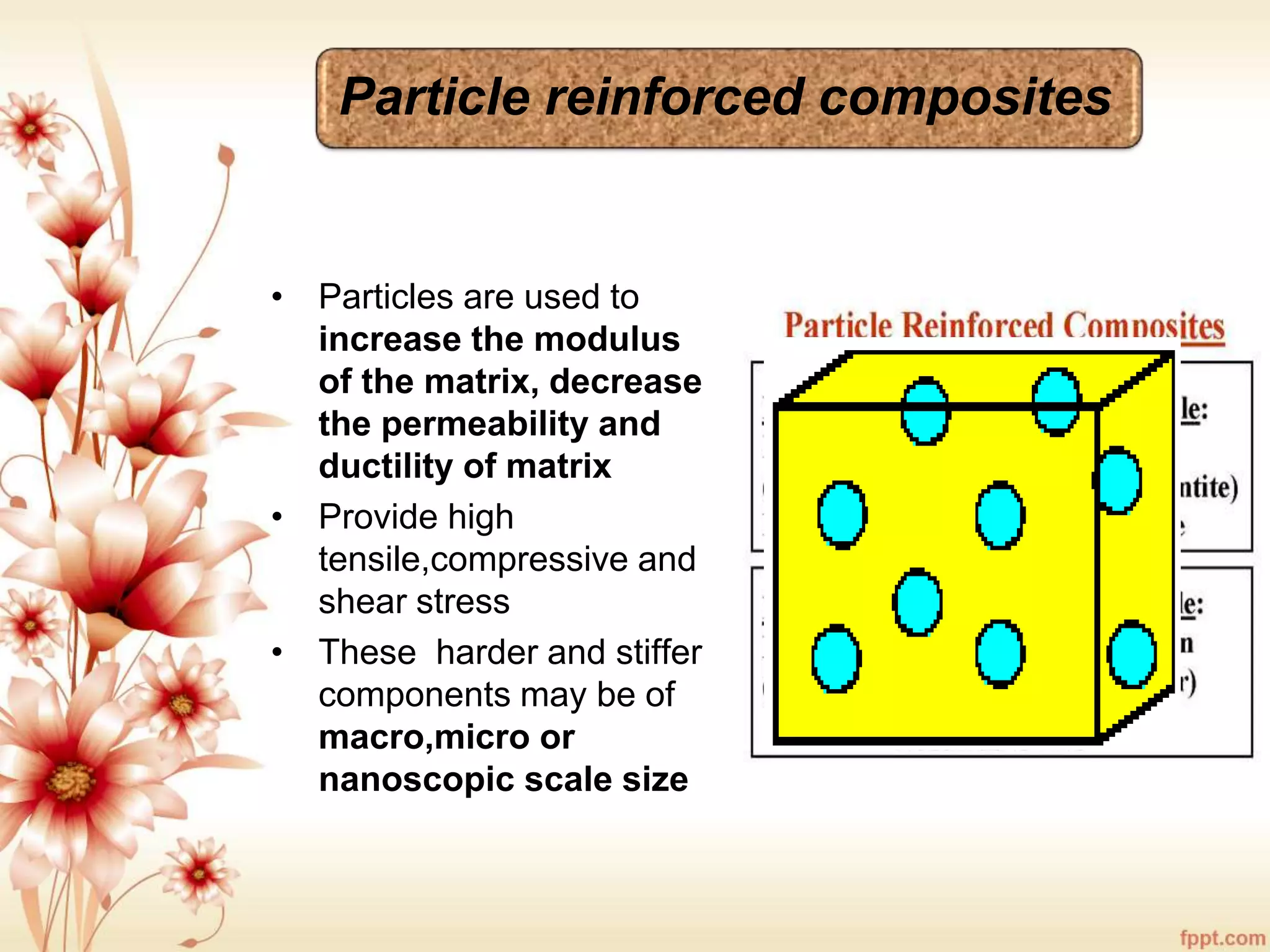
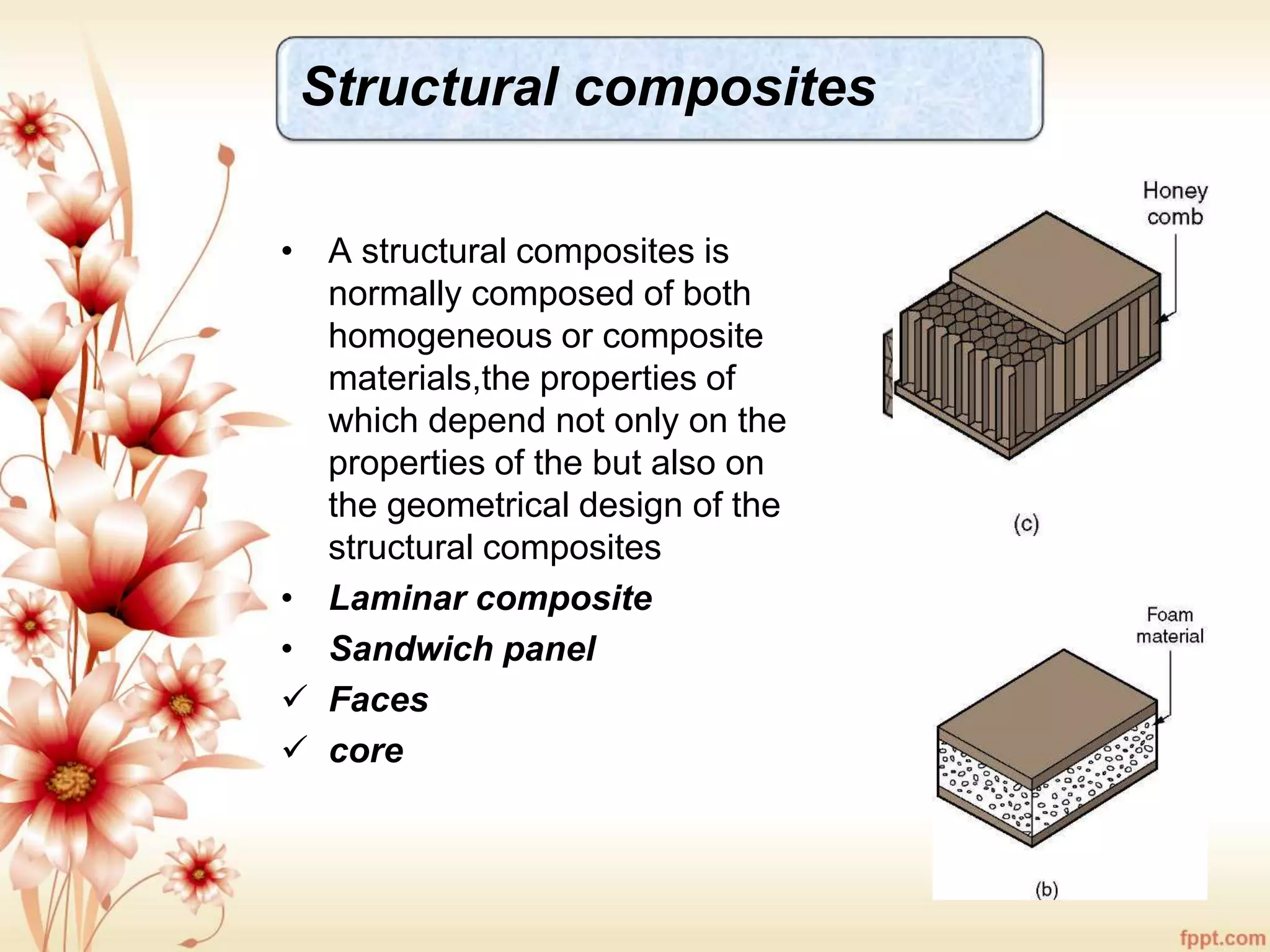
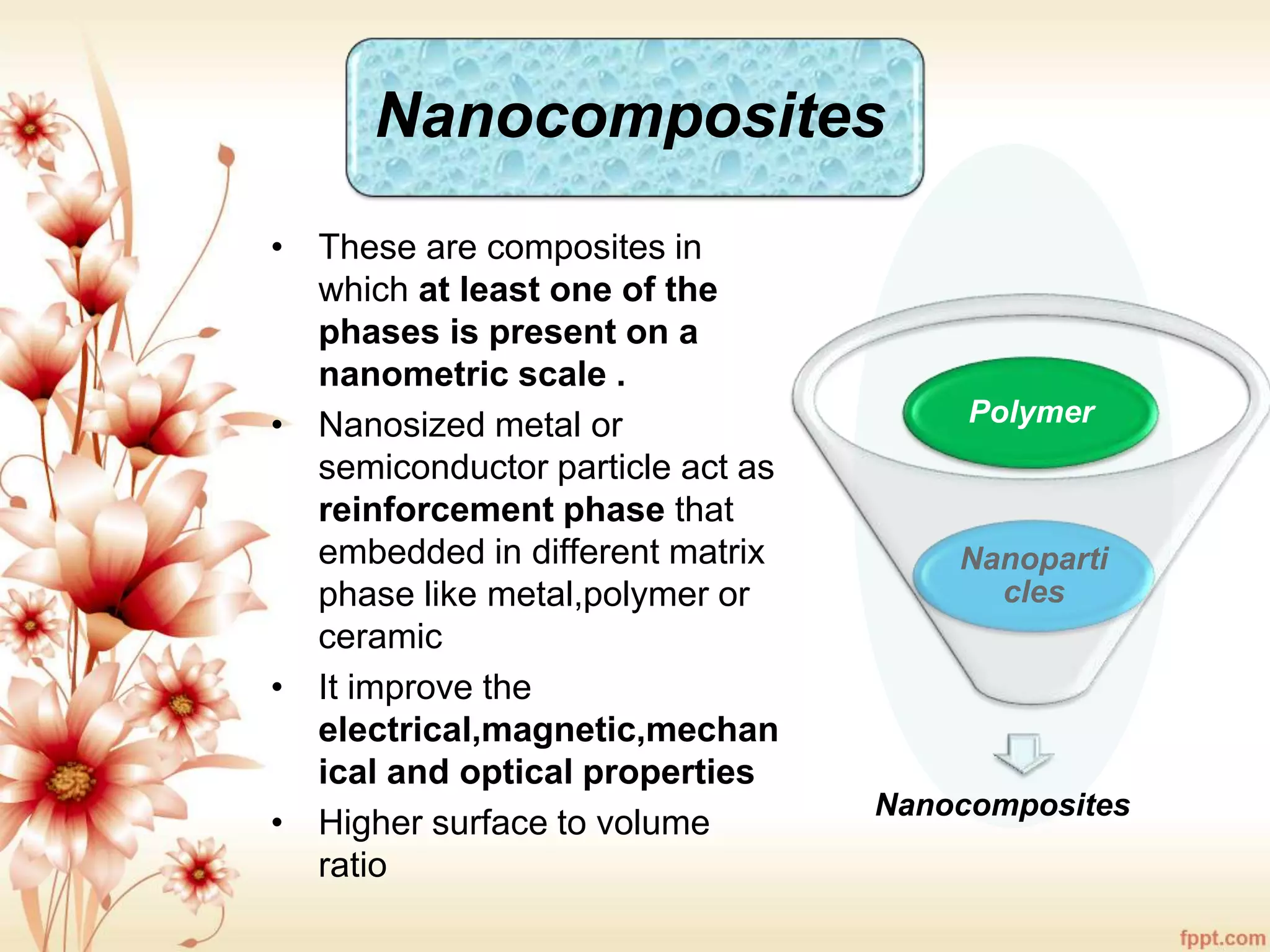
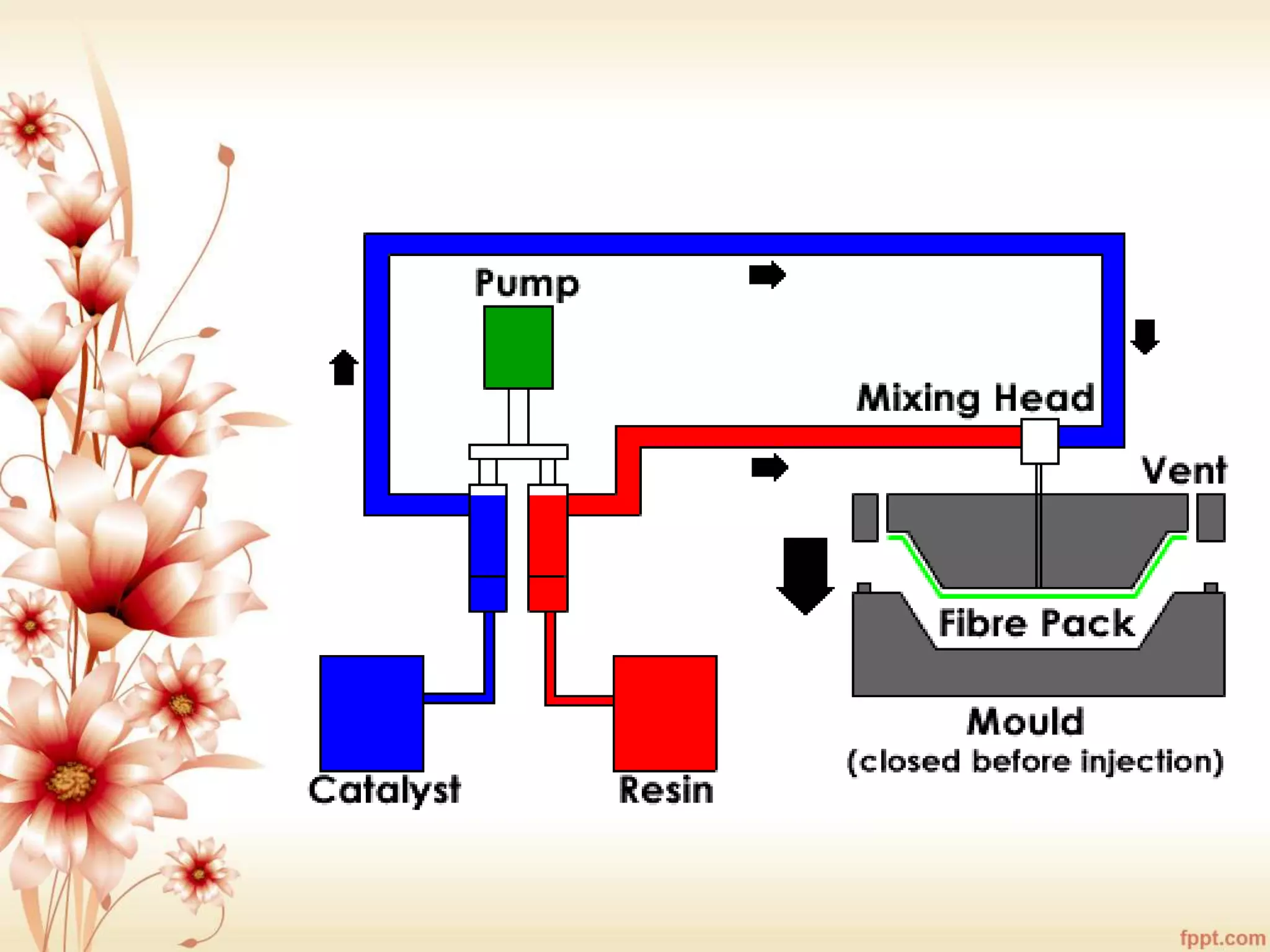
The document discusses the characteristics and advantages of composite materials, which combine different materials to enhance their properties. It highlights the roles of matrix and reinforcement phases in various types of composites, including metal, ceramic, and polymer matrix composites, as well as particle and fiber reinforced composites. The document also addresses the limitations and applications of these materials, emphasizing their diverse functionalities and tailored properties.