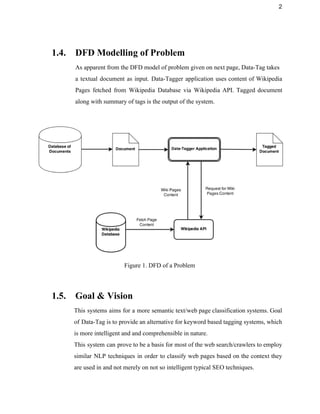
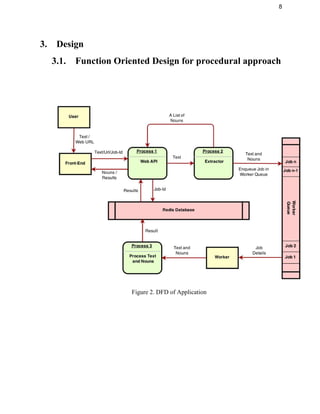
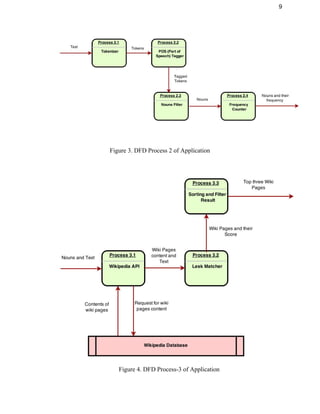
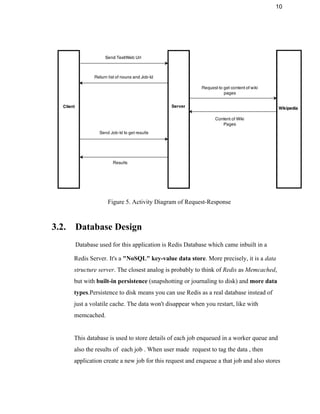
This document provides an overview of the Data Tag project, which aims to intelligently tag textual data and web pages based on their semantic context rather than just keywords. It begins with an introduction describing the purpose, system overview, and problem statement. It then discusses requirements such as user characteristics, functional requirements, dependencies, and constraints. The design section covers the functional design using data flow diagrams, database design using Redis, and GUI design. It also describes the coding, testing, installation, user instructions, future work, and provides a summary.