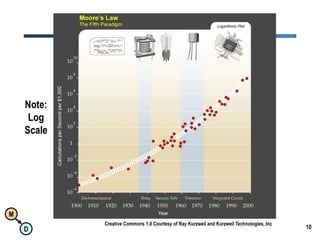
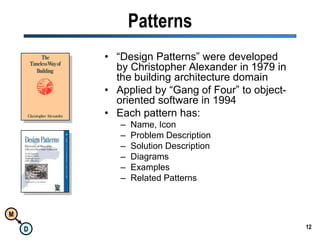
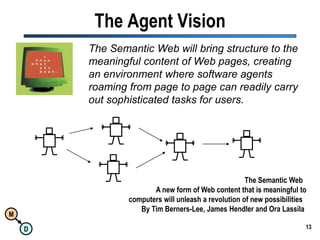
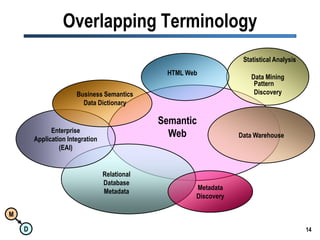
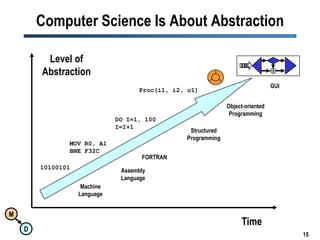
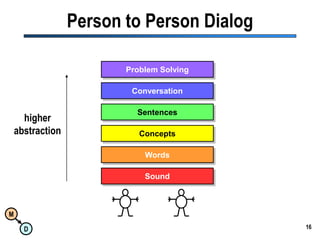
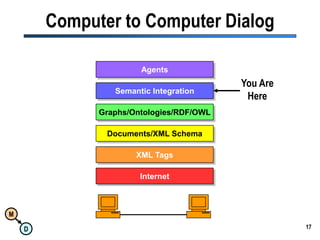
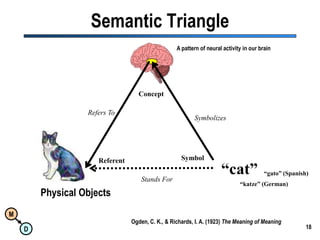
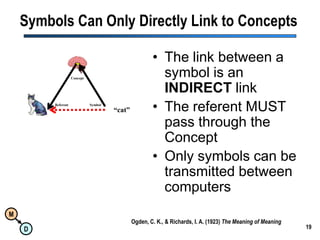
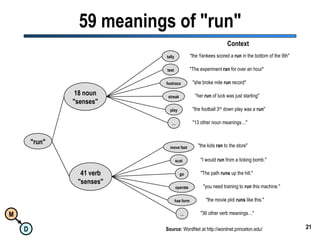
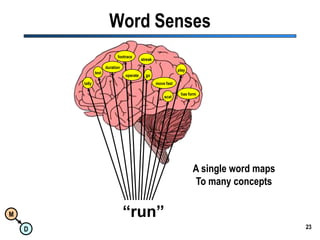
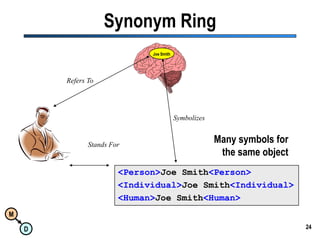
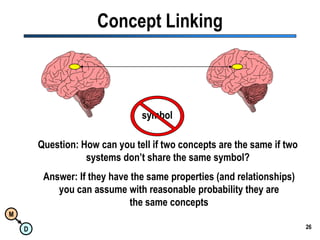
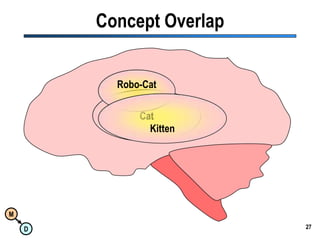
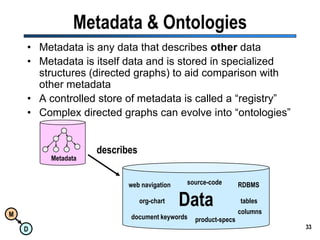
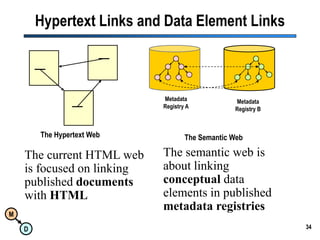
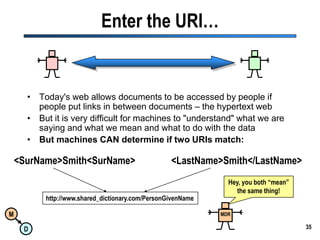
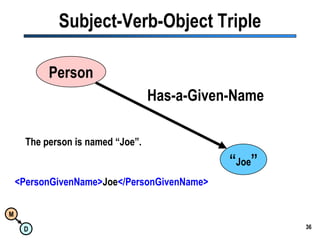
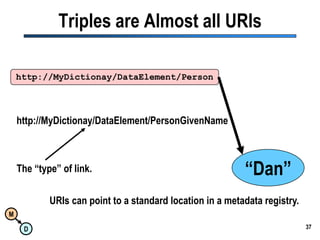
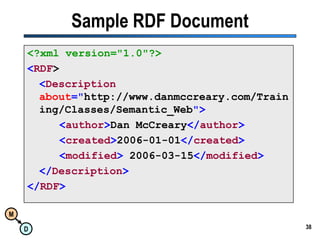
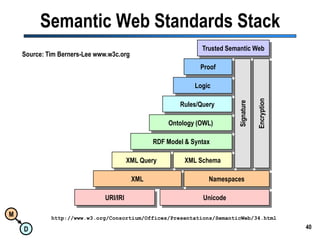
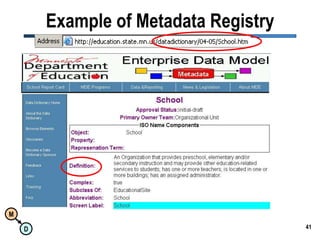
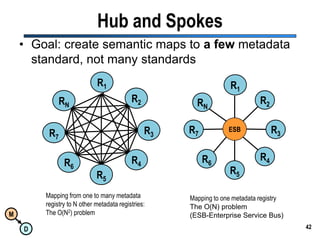
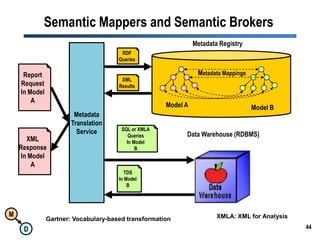
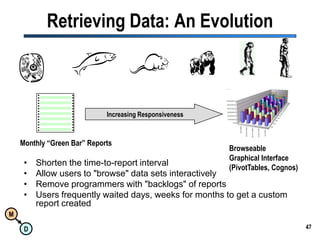
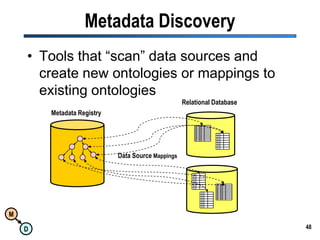
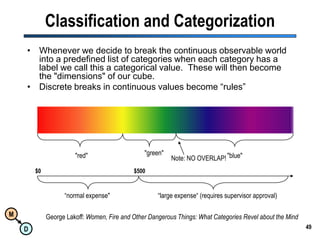
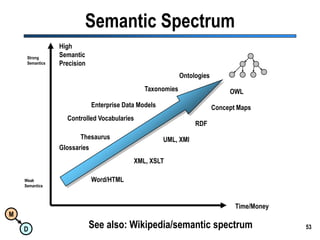
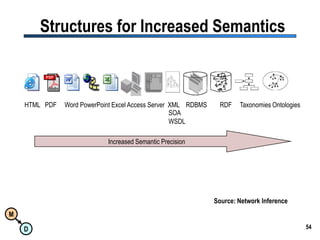
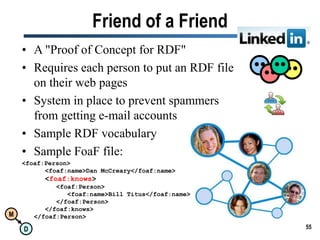
The document discusses the importance of semantic integration in computer systems and the role of the semantic web in improving data interoperability. It highlights the limitations of current data exchange methods and the need for semantics to facilitate more precise communication between computers. The presentation outlines various patterns used to enhance semantic technologies and suggests that addressing these issues could lead to significant advancements in data management and automation.