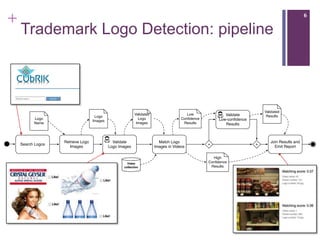
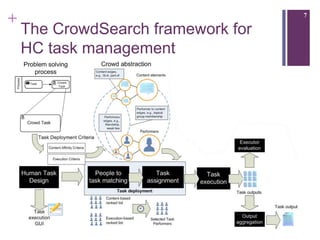
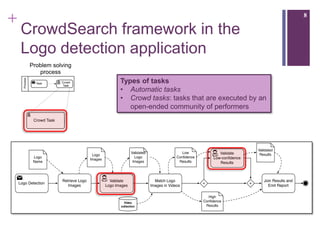
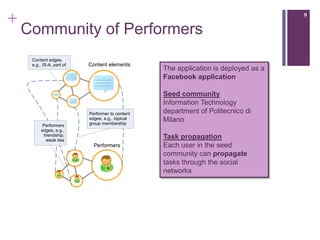
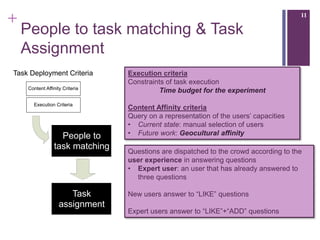
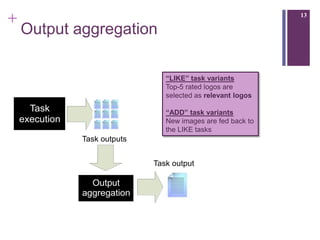
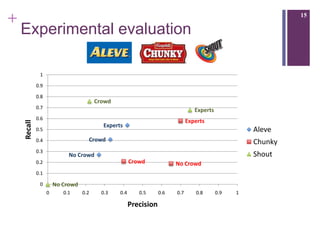
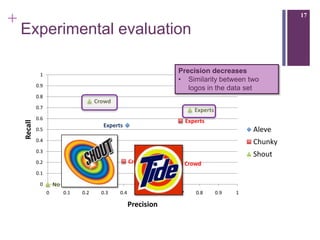
The document describes a framework called CUbRIK that uses human computation to improve multimedia search. It presents a case study on using the crowd to detect trademark logos in videos. Workers validate automatically detected logos and add new logos. The system matches tasks to workers based on their skills. An evaluation compares the logo detection accuracy of automatic methods, experts, and the crowd. While the crowd recall is higher, its precision is lower due to the workers' varied locations and expertise.