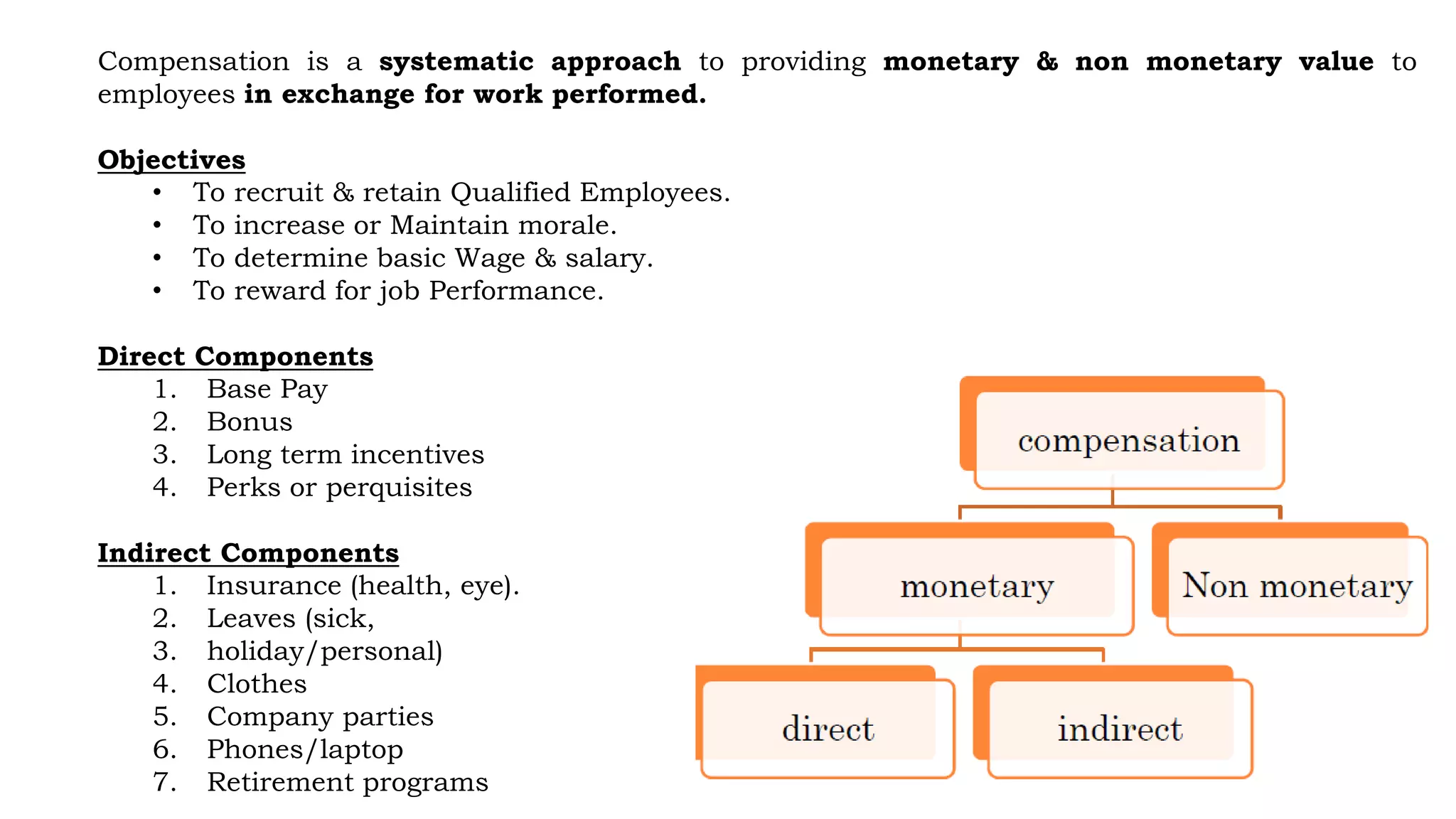
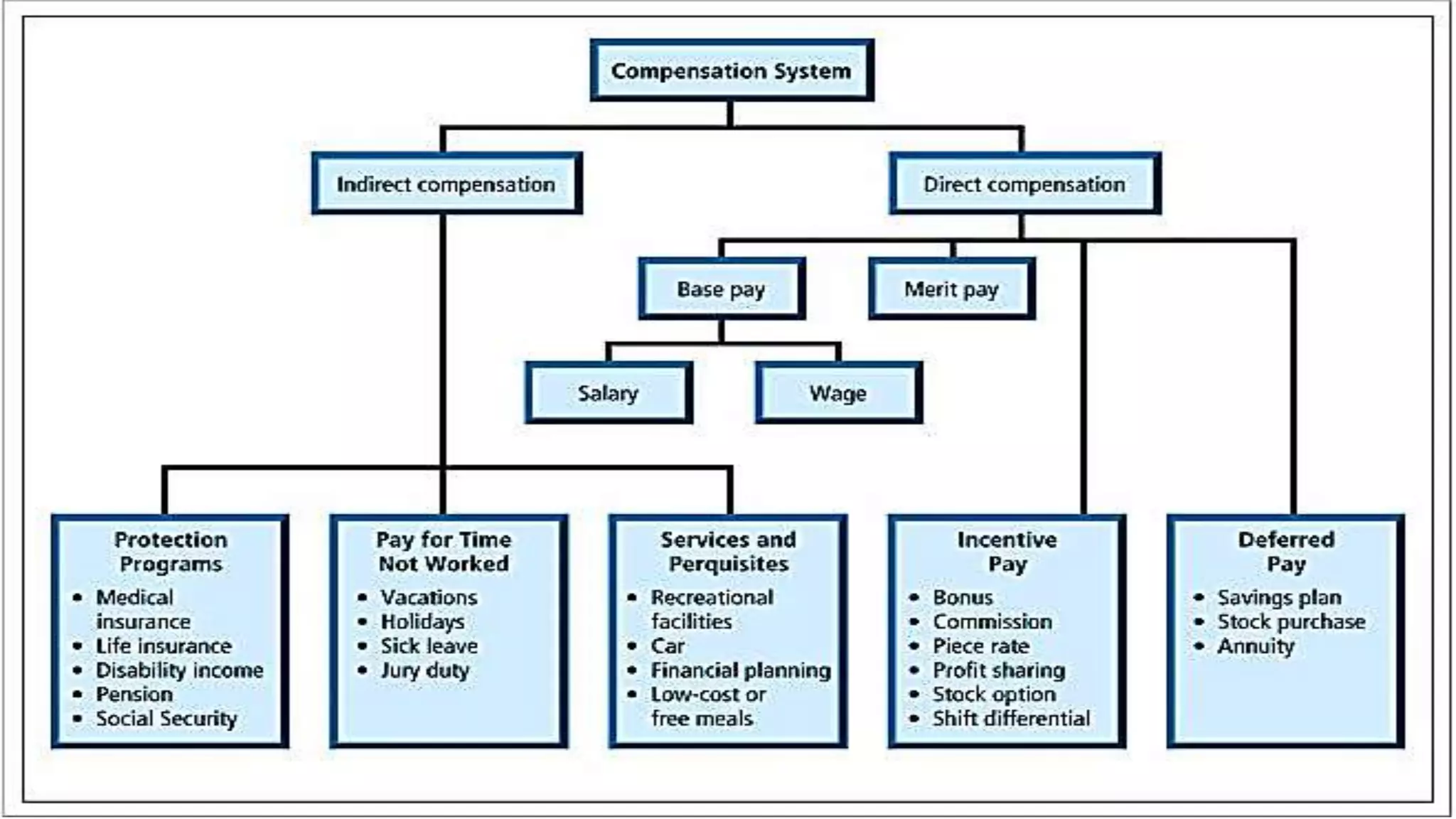
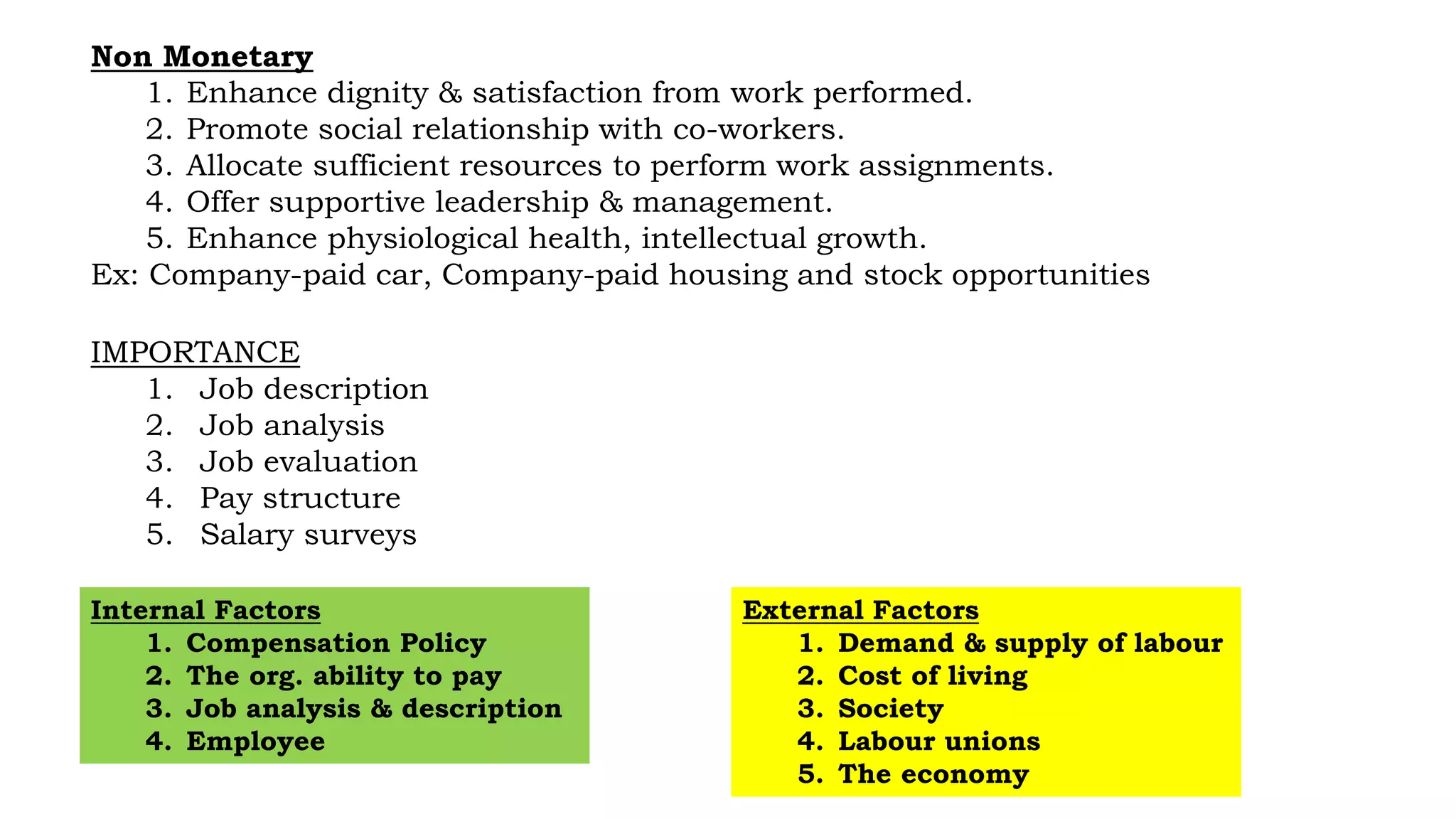
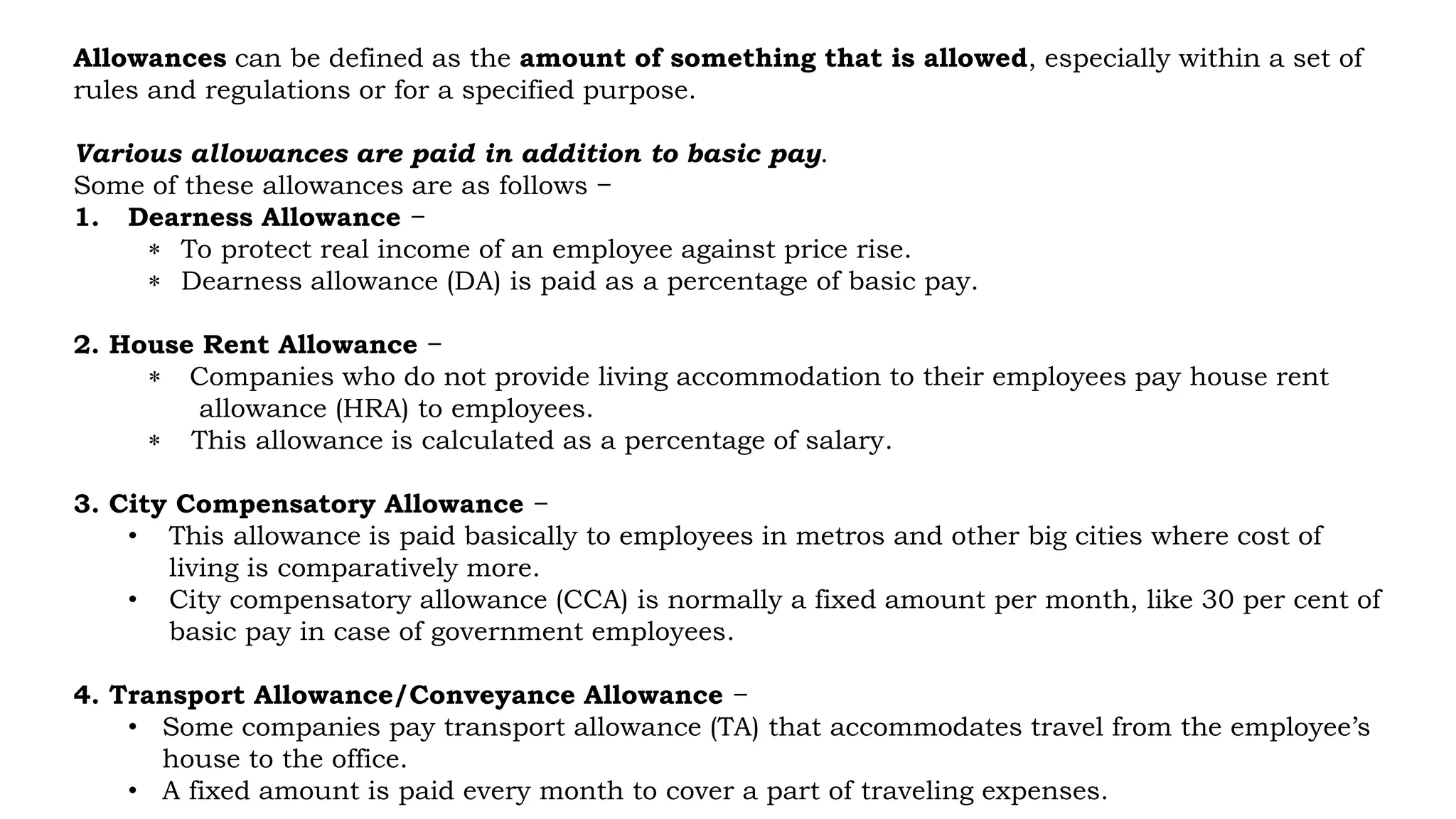
This document discusses compensation management and outlines its objectives, direct and indirect components, importance, and factors that influence compensation. Compensation is a systematic approach to providing monetary and non-monetary value to employees in exchange for work. The objectives of compensation include recruiting and retaining qualified employees, increasing or maintaining morale, determining basic wages and salaries, and rewarding job performance. Compensation consists of direct components like base pay, bonuses, and benefits, as well as indirect components like insurance, leaves, and retirement programs. Both internal factors like an organization's compensation policy and external factors like cost of living and the economy influence compensation.