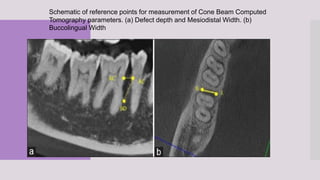
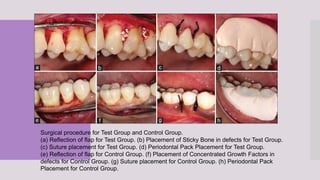
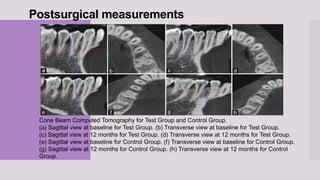
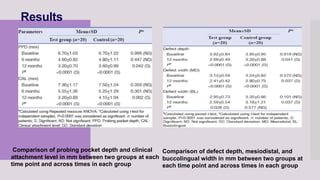
This randomized clinical trial compared the efficacy of sticky bone (an autologous fibrin glue-enriched bone graft matrix) and concentrated growth factor (CGF) in treating intrabony defects. 40 intrabony defects in 20 patients were randomly assigned to receive either sticky bone or CGF. Clinical parameters and cone-beam computed tomography scans found that sticky bone resulted in significantly greater clinical attachment level gain, probing pocket depth reduction, and defect depth reduction compared to CGF alone at 12 months. The study concluded that sticky bone is more effective than CGF for treating intrabony osseous defects.