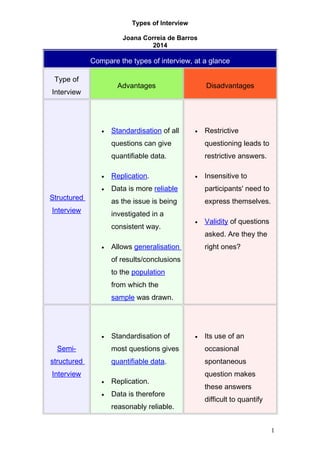
The document compares four types of interviews: structured, semi-structured, clinical, and unstructured. Structured interviews have standardized questions but restrictive answers, while semi-structured interviews standardize most questions but allow some flexibility. Clinical interviews are flexible but difficult to replicate, and unstructured interviews are natural but hard to generalize from. Overall, the document outlines the key advantages and disadvantages of each type of interview format.