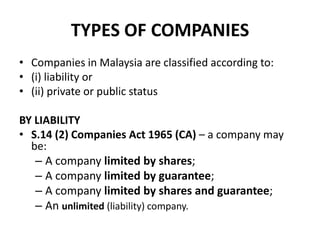
The document provides an overview of companies in Malaysia, detailing their definitions, classifications, and types based on liability and status. It explains different company forms such as companies limited by shares, by guarantee, and unlimited companies, along with regulations governing private and public companies. Additionally, it outlines the distinction between holding and subsidiary companies and the requirements for foreign companies operating in Malaysia.