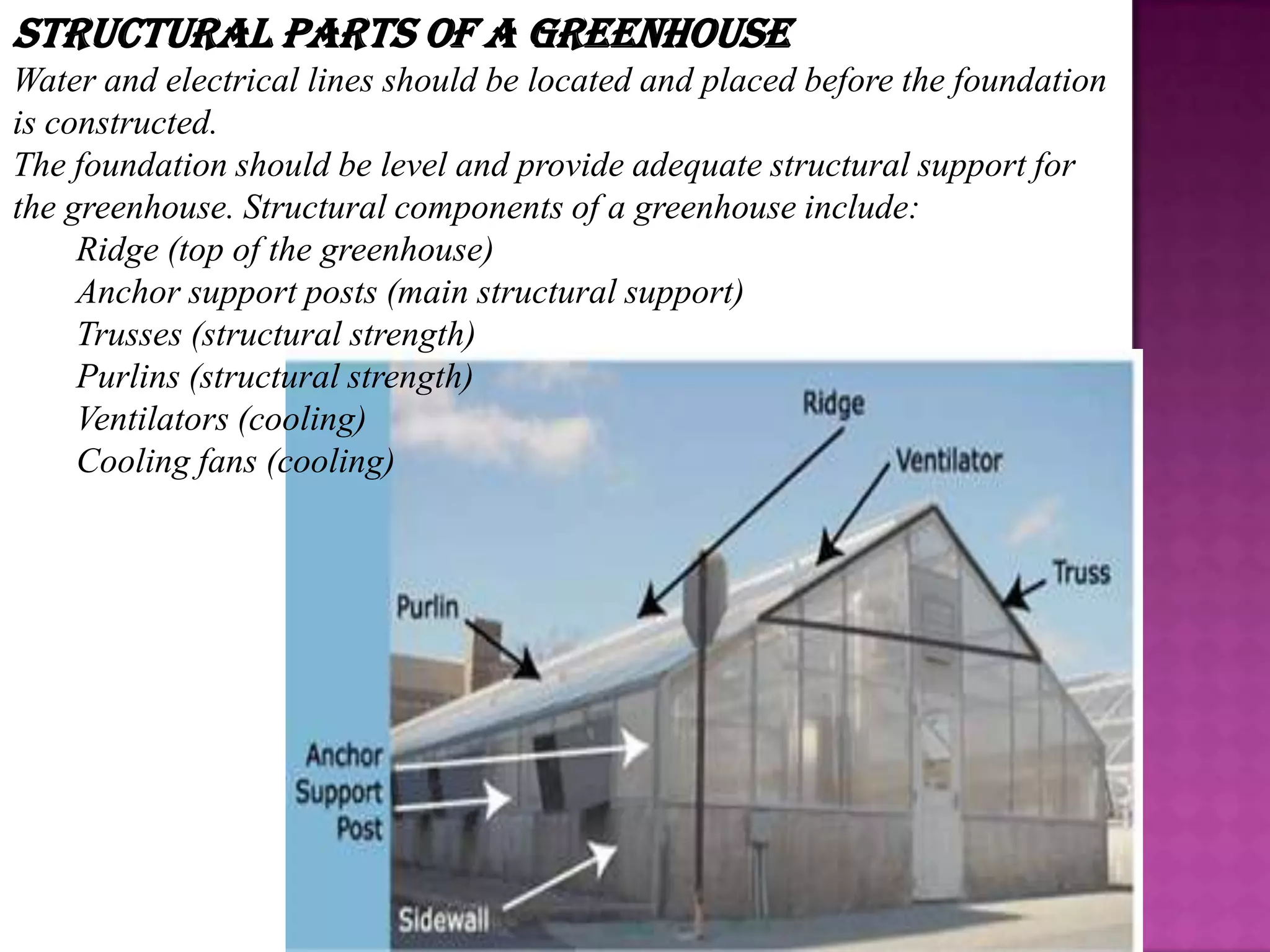
This document provides information about a presentation on greenhouses. It lists the presenters and then discusses what a greenhouse is, factors to consider in choosing a location, structural components, types of greenhouses, glazing materials, crops grown, ventilation needs, advantages of greenhouses, and the greenhouse effect. The main points are that a greenhouse is a framed structure that controls the environment for growing plants, important considerations include location factors and infrastructure needs, and greenhouses offer benefits like environmental control and uniform crop production.