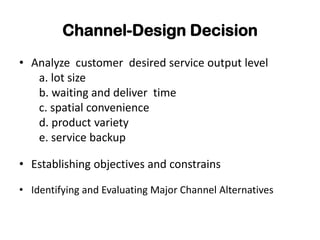
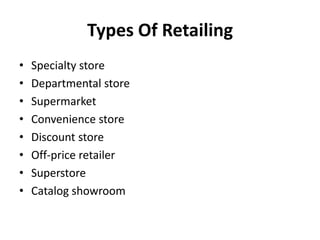
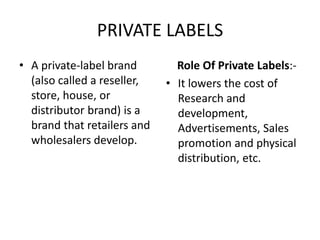
This document discusses key concepts related to marketing channels and logistics. It defines marketing channels as the set of interdependent organizations involved in making a product available for consumption. It also discusses types of retailers like specialty stores, department stores, and convenience stores. It covers wholesaling functions like selling, buying, warehousing, and risk bearing. The document emphasizes integrated logistics planning and objectives like minimizing total costs while meeting customer requirements.