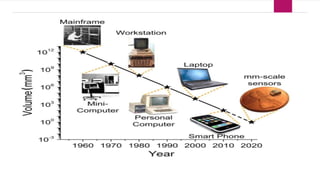
This document summarizes the evolution of communication from ancient times to modern times. It discusses early forms of communication like signs, smoke signals, and homing pigeons. It then covers the development of long-distance communication systems like mailing systems, telegraphs, telephones, radio, television, and computers. Finally, it mentions the invention of the World Wide Web in 1990 which led to what is recognized as the Internet today.












![Telephone
In 1876, Alexander Graham Bell was
the first to be granted a United
States patent for a device that produced
clearly intelligible replication of the
human voice at a second device.[2] This
instrument was further developed by
many others, and became rapidly
indispensable in business, government,
and in households.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation-230829143803-c60fe6f7/85/Evolution-Of-Communication-13-320.jpg)