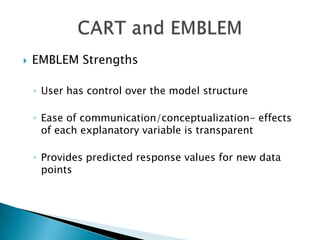
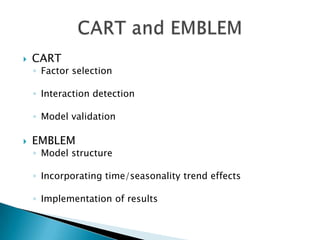
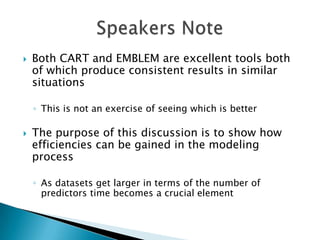
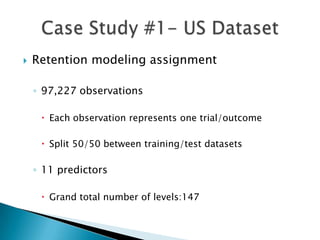
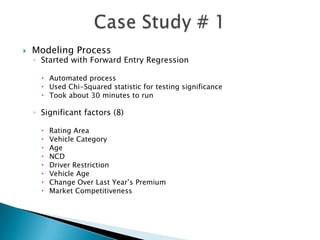
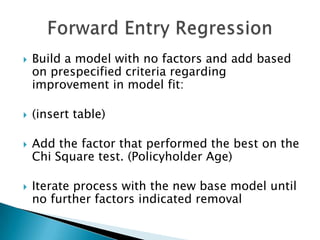
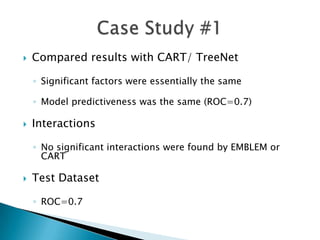
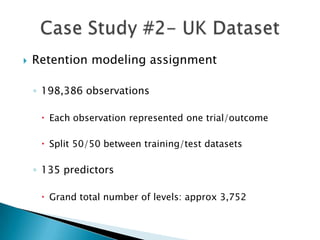
This document discusses how EMB America and Salford Systems can leverage their combined strengths in predictive modeling for the insurance industry. EMB specializes in insurance predictive modeling applications using their EMBLEM tool, while Salford Systems provides tree-based modeling techniques. The document outlines case studies where they have used both EMBLEM and CART (Classification and Regression Trees) models to identify important factors, interactions, and segments in large insurance datasets. Combining the approaches helped reduce modeling time and improve predictive performance for applications like customer retention modeling.