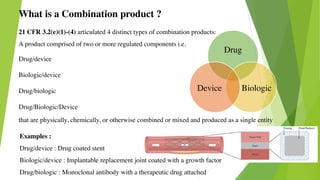
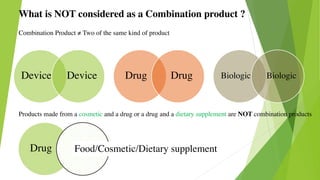
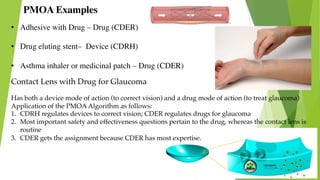
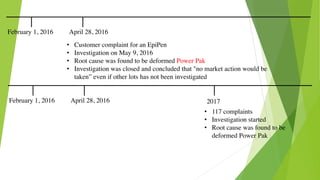
This document discusses regulatory aspects of drug-device combination products and provides examples of violations found in an FDA warning letter. It defines combination products and explains how the FDA determines the primary mode of action to assign the product to the appropriate FDA center for review. The warning letter outlines violations found at a manufacturer including failures to adequately investigate complaints, establish design controls and validation procedures, and perform required analyses of nonconformities and processes. Overall the document provides an overview of combination product regulation and examples of good manufacturing practice failures identified in an FDA inspection.