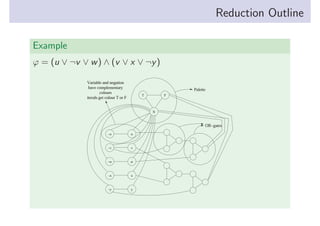
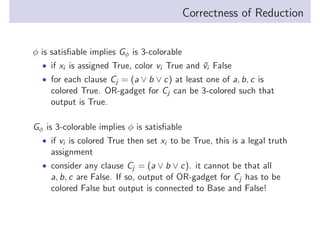
3-Coloring is NP-complete. The document shows that 3-SAT reduces to 3-Coloring in polynomial time, proving 3-Coloring is NP-hard. The reduction works by creating a graph where each variable gets two nodes and each clause gets an OR-gadget. If the graph is 3-colorable, it encodes a satisfying assignment, and vice versa.