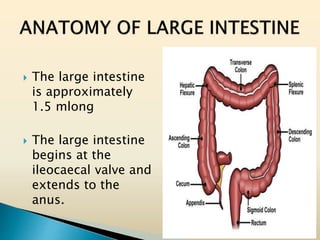
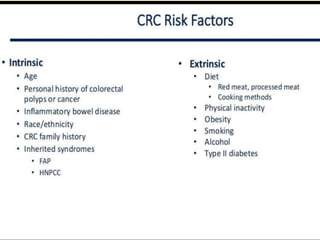
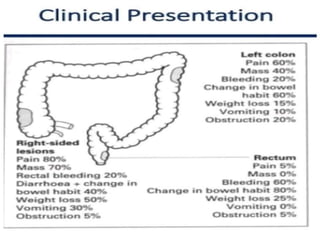
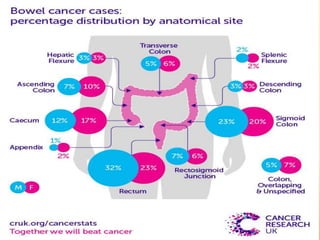
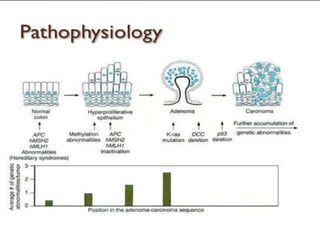
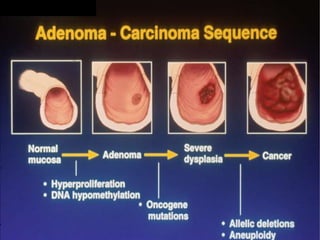
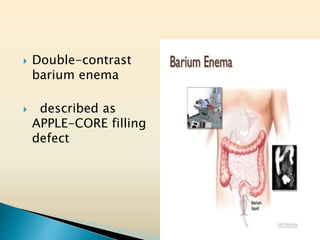
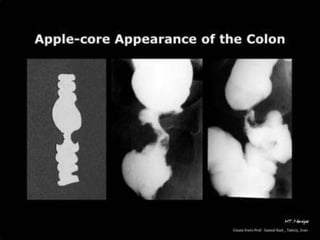
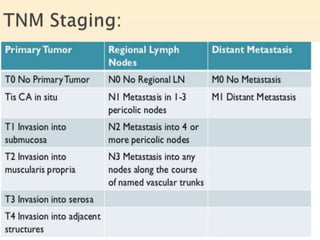
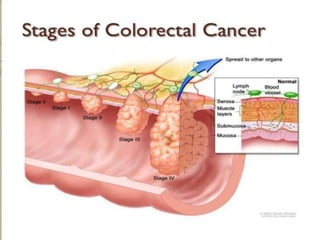
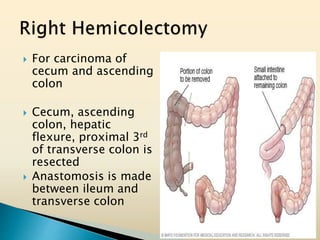
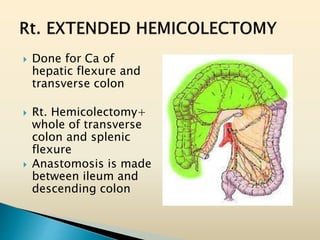
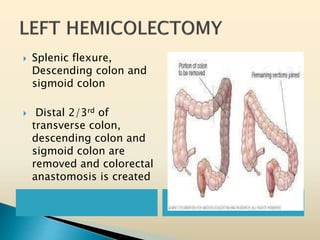
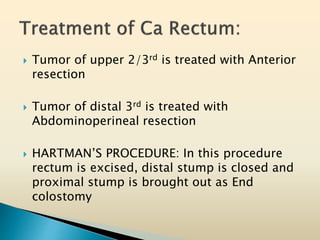
Tasleem Akhtar, a 50-year old female, presented with post-prandial vomiting, abdominal pain, and constipation. Imaging showed signs of intestinal obstruction. She underwent exploratory laparotomy, which found a stricture in the sigmoid colon due to a hard mass. A segment of the sigmoid colon was resected along with the mass. Histopathology revealed colorectal cancer. She was diagnosed with colorectal cancer affecting the sigmoid colon.