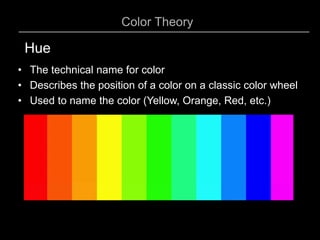
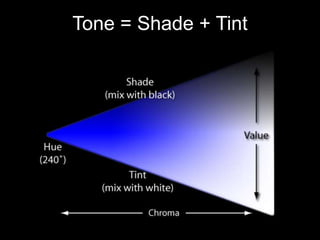
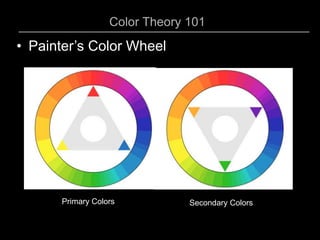
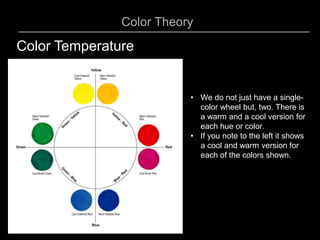
This document provides an overview of color theory and different color schemes. It begins by defining key color concepts like hue, saturation, tone, warm and cool colors. It then explains the traditional painter's color wheel and different color schemes including:
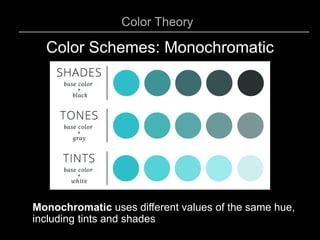
1) Monochromatic which uses different values of the same hue.
2) Analogous which uses colors adjacent on the color wheel.
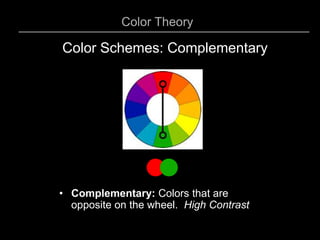
3) Complementary which uses colors opposite each other on the wheel for high contrast.
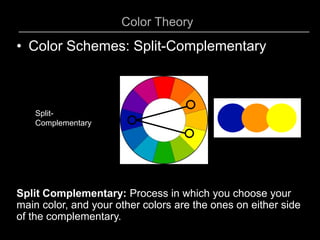
4) Split-complementary which uses a main color and the colors on either side of its complement.
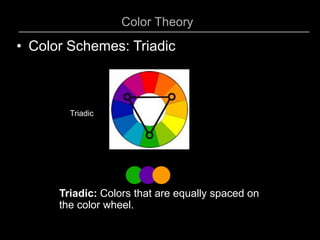
5) Triadic which uses three colors equally spaced around the color wheel.
Examples of each color scheme are