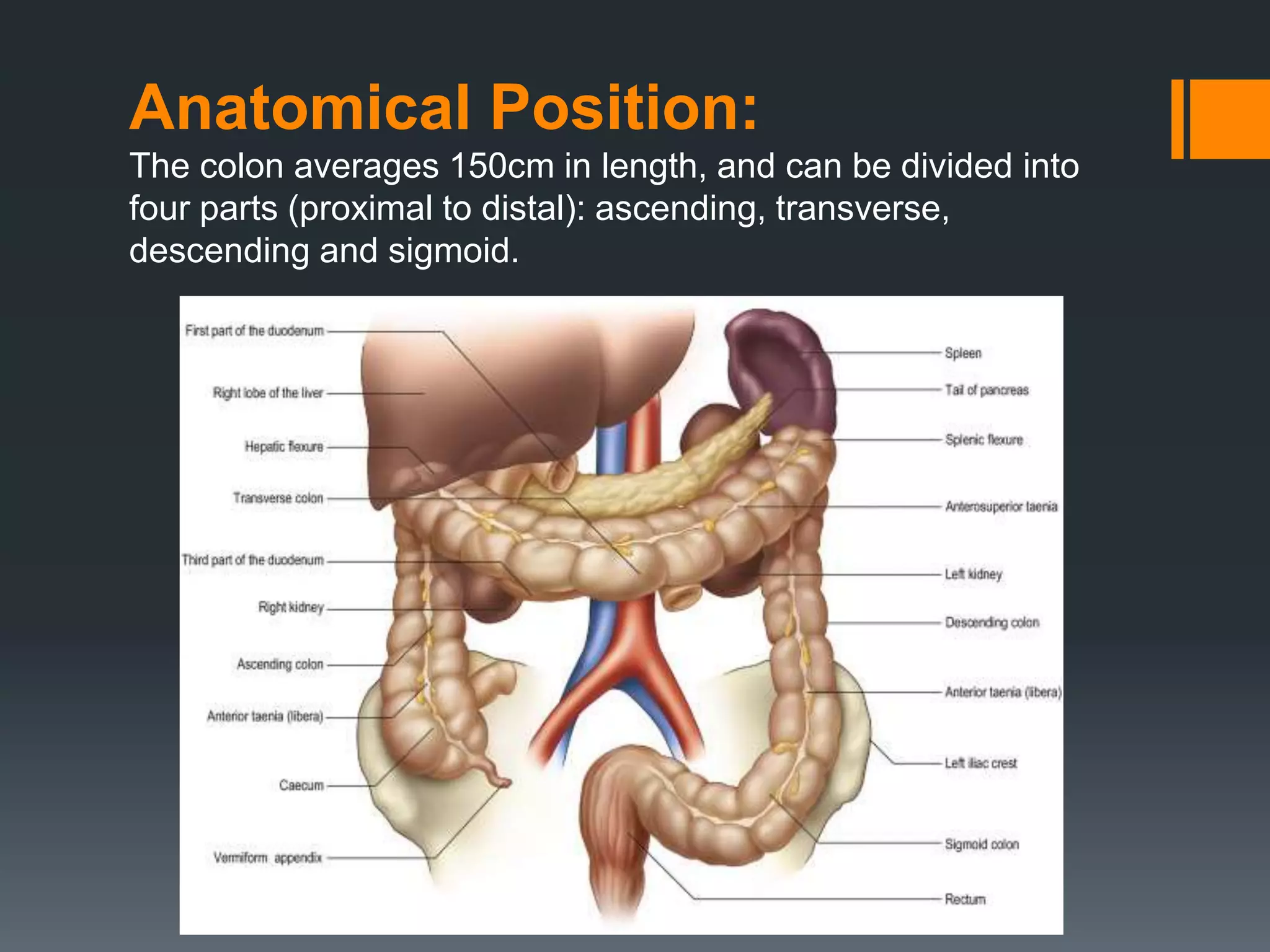
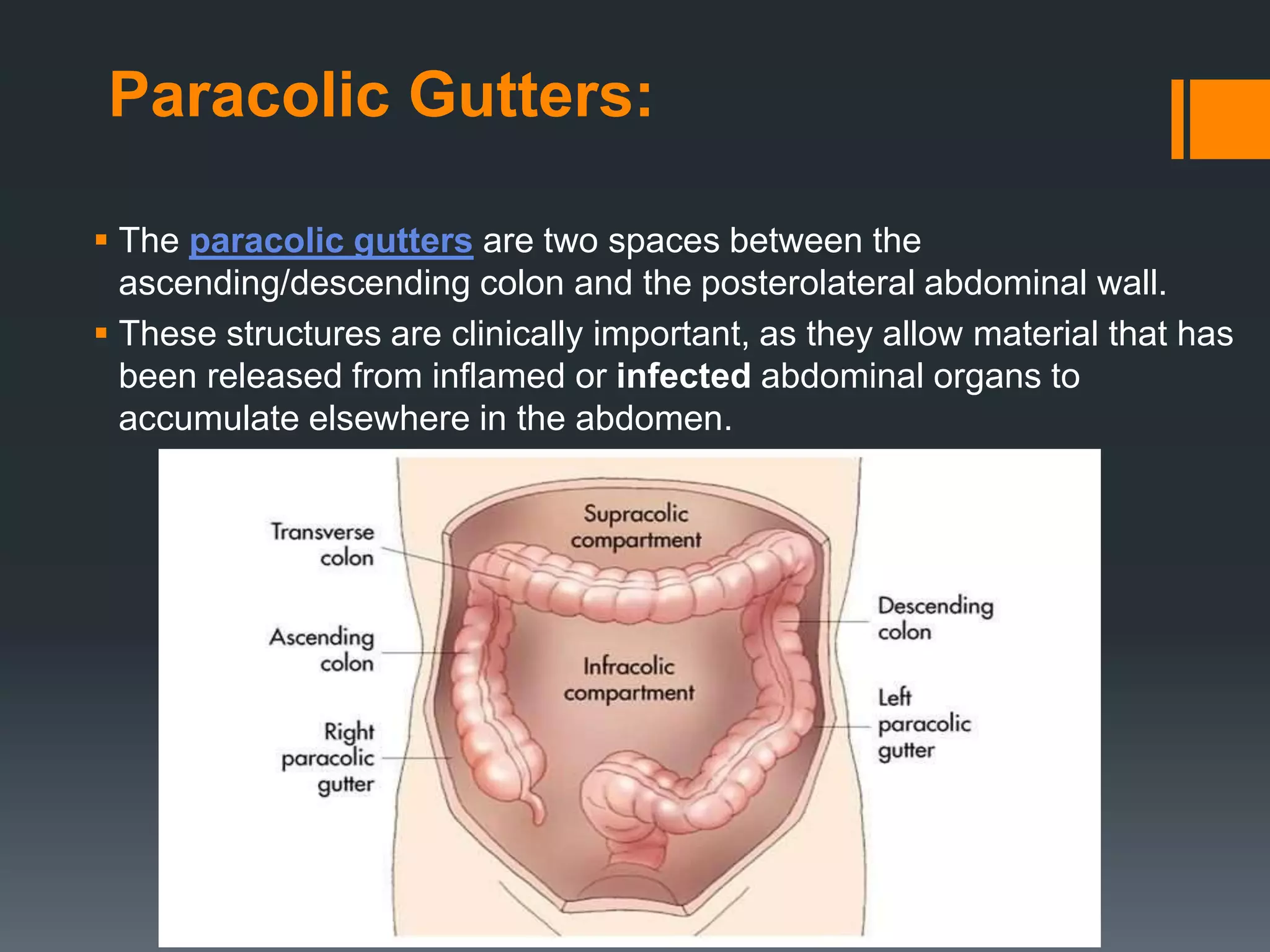
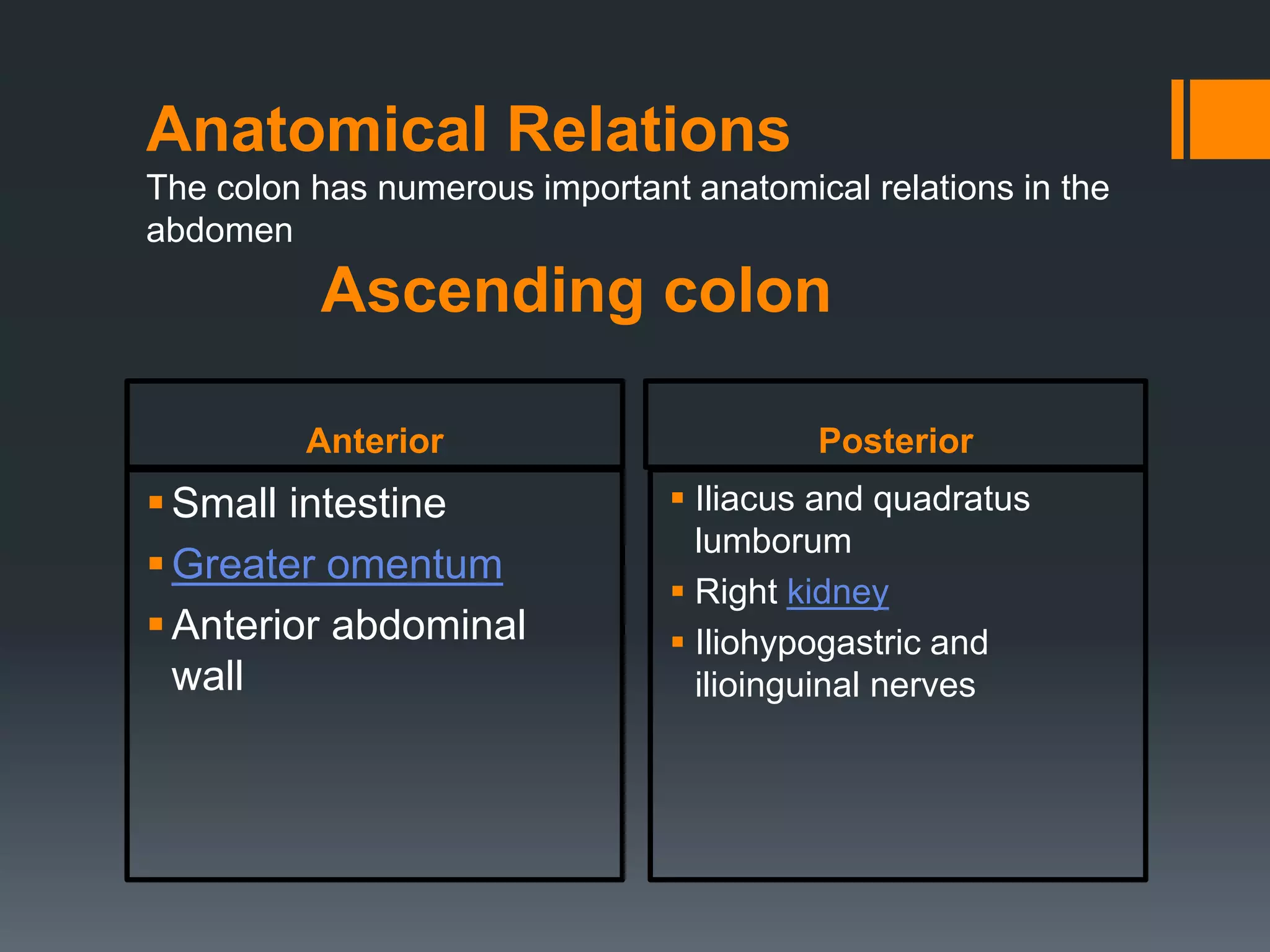
The large intestine extends from the small intestine to the anus. It is composed of the cecum, colon, and rectum. The colon can be divided into four parts - ascending, transverse, descending, and sigmoid. It absorbs water from digested food and forms feces. Diseases that can affect the large intestine include colorectal cancer, colonic polyps, ulcerative colitis, diverticulitis, and irritable bowel syndrome.