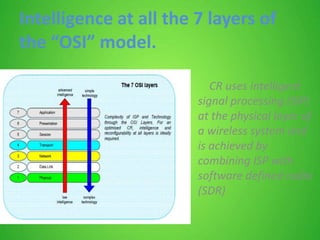
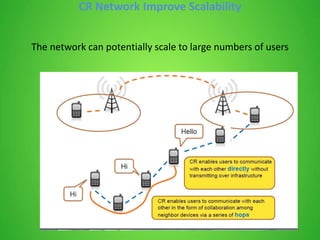
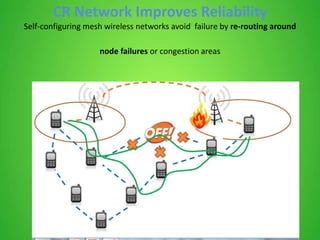
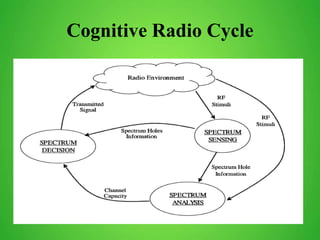
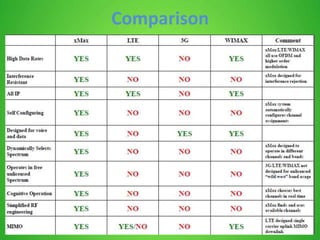
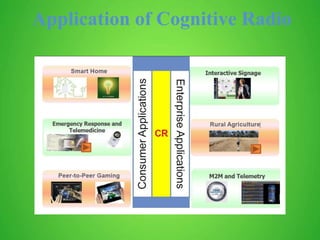
This document discusses cognitive radio sensor networks (CRSN). It defines cognitive radio as a radio that is aware of its surroundings and adapts intelligently. A CRSN allows radios to dynamically tune to different frequencies and protocols based on environmental conditions to improve accessibility, adaptability, scalability, reliability and interconnectivity. The document outlines the CRSN mechanism of sense, analyze, decide and tune in using sensing and reconfigurable antennas. It compares cognitive radios to conventional radios, highlighting cognitive radios' ability to identify unused spectrum and adapt to interference. Benefits of CRSN include meeting FCC regulations and maximizing throughput. Applications of cognitive radio include compact wireless access points.