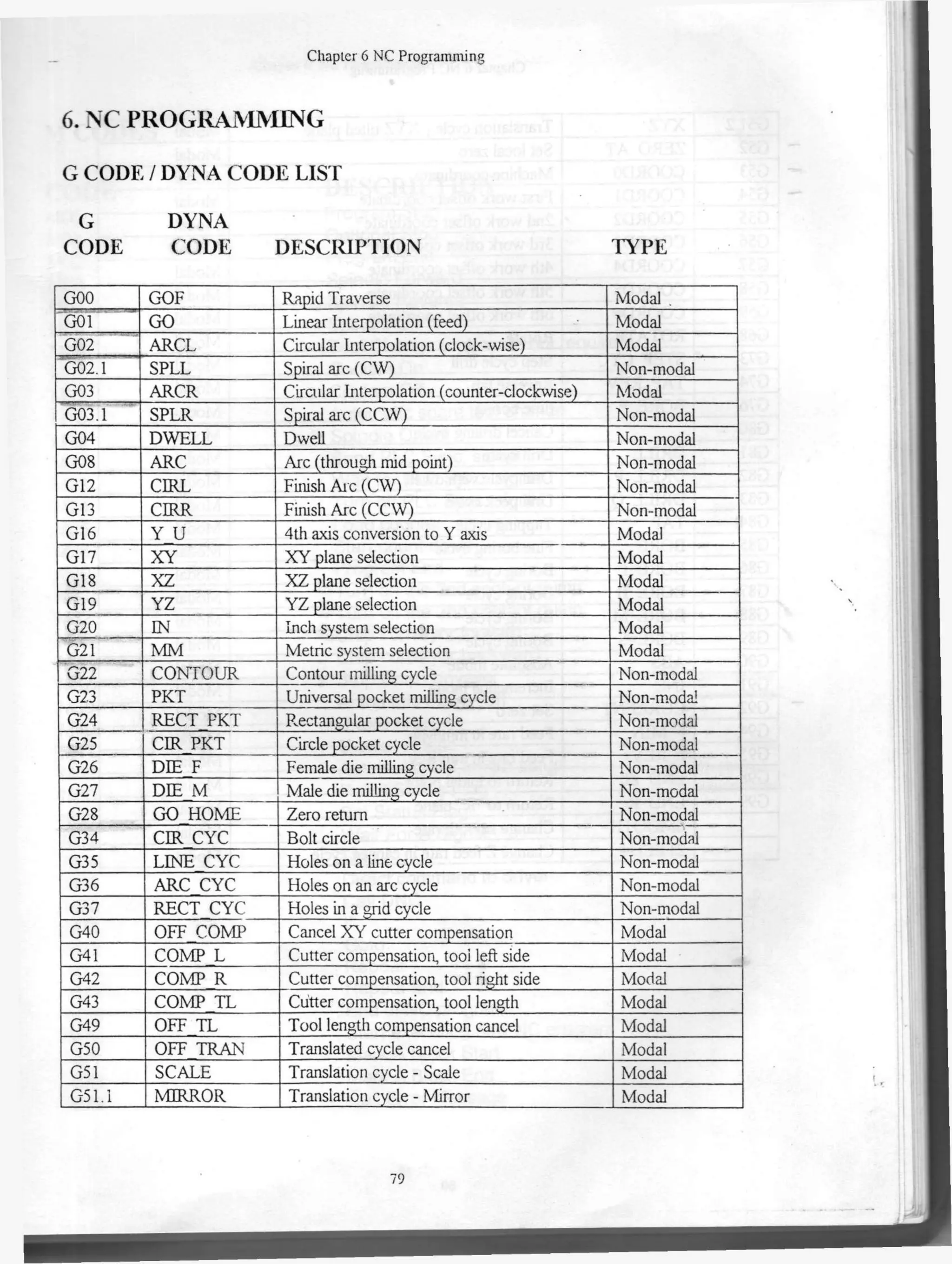
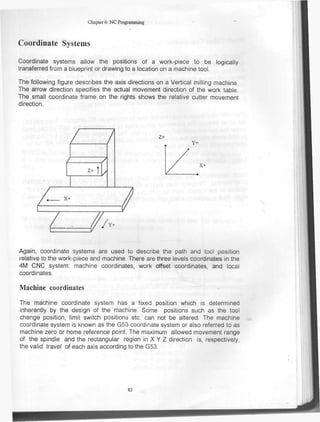
The document describes G and M codes used in NC programming. It lists G codes for linear and circular interpolation motions as well as codes for drilling cycles, coordinate systems, and tool compensation. It also lists M codes for controlling spindle direction, coolant, and program flow. Coordinate systems include machine coordinates defined by the machine's physical design, work offsets for part geometry, and local coordinates.