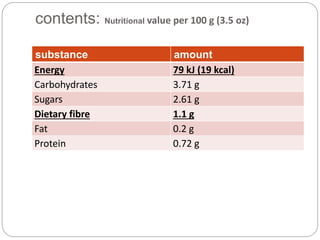
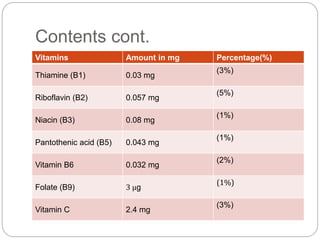
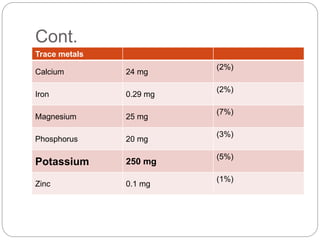
Coconut water is the clear liquid found inside young, green coconuts that are 5-7 months old. It is low in calories and rich in nutrients like vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. Coconut water has various health benefits such as hydration, anti-aging effects, and helping with digestion. While coconut water was used intravenously during World War II in emergencies, it is now commonly consumed as a refreshing drink. It can help with issues like diarrhea, dehydration, and high blood pressure, but should be used with caution during pregnancy, breastfeeding, or before/after surgery.