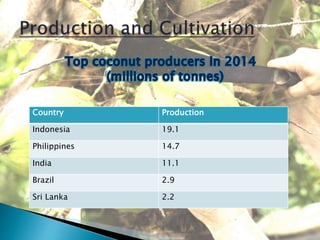
Coconut trees can grow up to 30 meters tall and produce their first fruit within 6 years. Coconuts have a variety of uses such as drinking water, cooking oil, materials for crafts and building. There are many health benefits to consuming coconut as well, such as aiding weight loss, reducing cholesterol, and promoting heart health. Major coconut producing countries include Indonesia, the Philippines, and India. Coconut trees require warm, humid climates and regular rainfall to thrive.