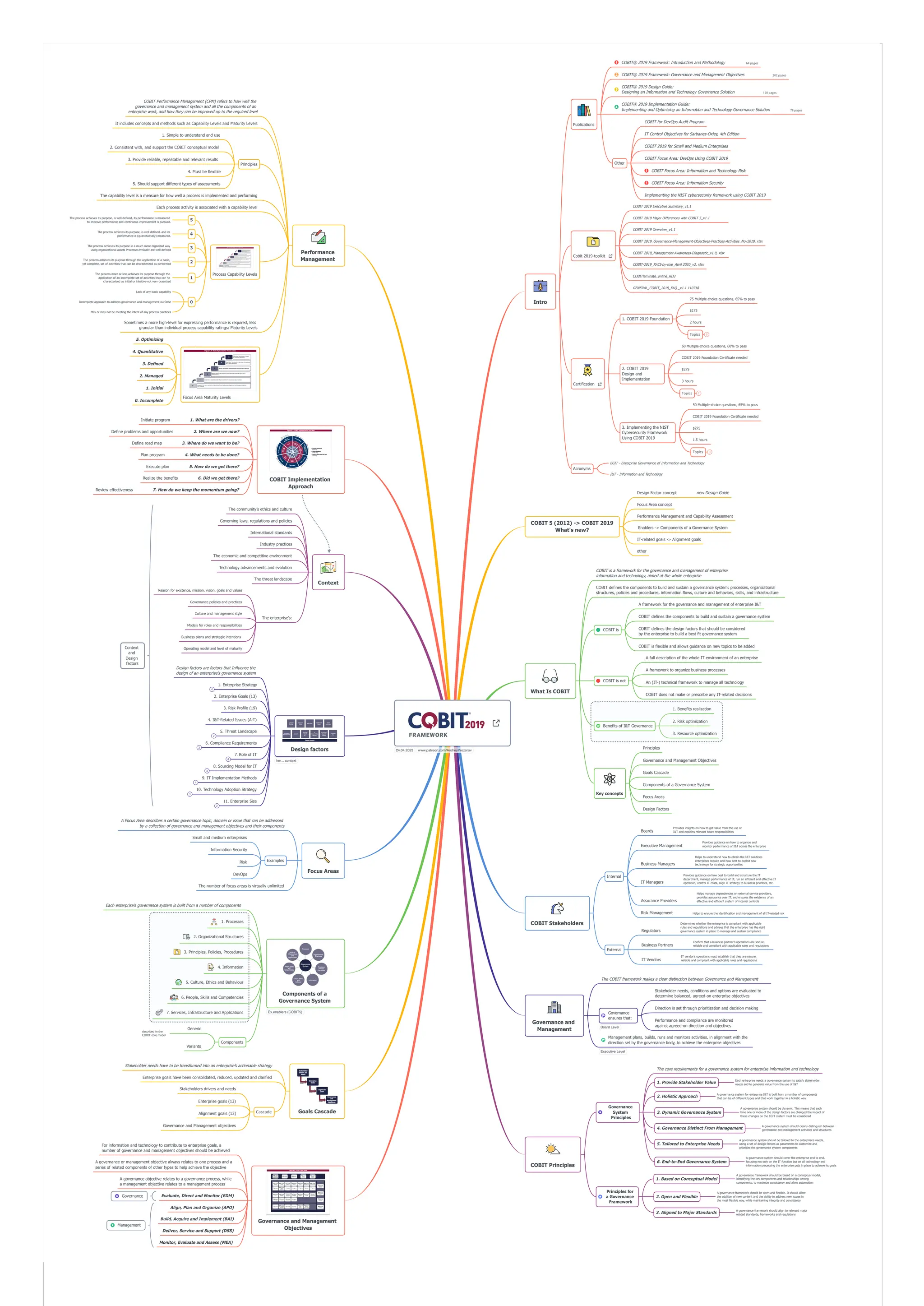
The document outlines the COBIT 2019 framework for governance and management of enterprise information and technology, highlighting its principles, components, and design factors necessary for effective implementation. It distinguishes between governance and management, detailing processes for evaluation, direction, and performance monitoring. Additionally, it provides certification information and emphasizes the importance of aligning the governance system with stakeholder needs and enterprise goals.