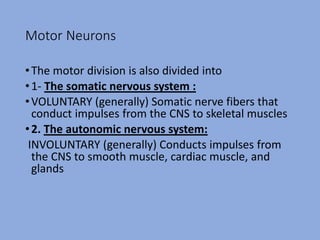
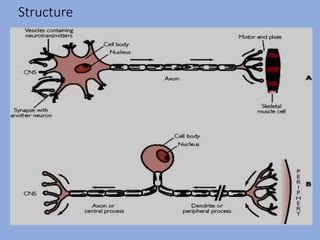
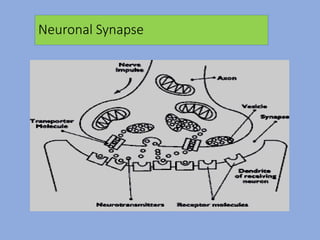
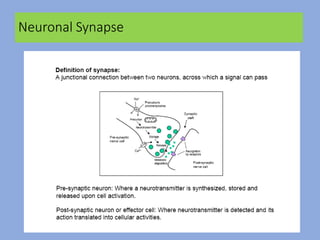
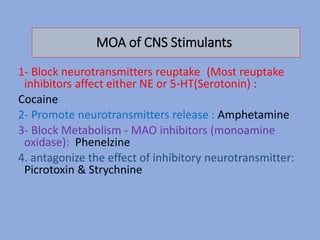
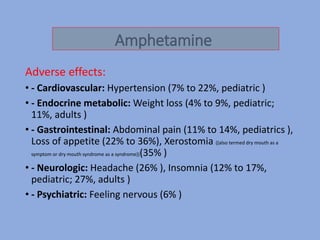
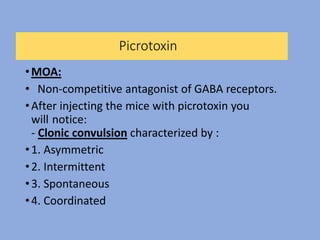
The document discusses the classification and functions of the nervous system, focusing on central and peripheral divisions, types of neurons, and neurotransmitters. It details CNS stimulants, their mechanisms of action, clinical uses, and adverse effects, while also describing the effects of specific substances like amphetamine, picrotoxin, and strychnine. Additionally, it touches on cognition enhancers and hallucinogens, listing various compounds with psychotropic properties.