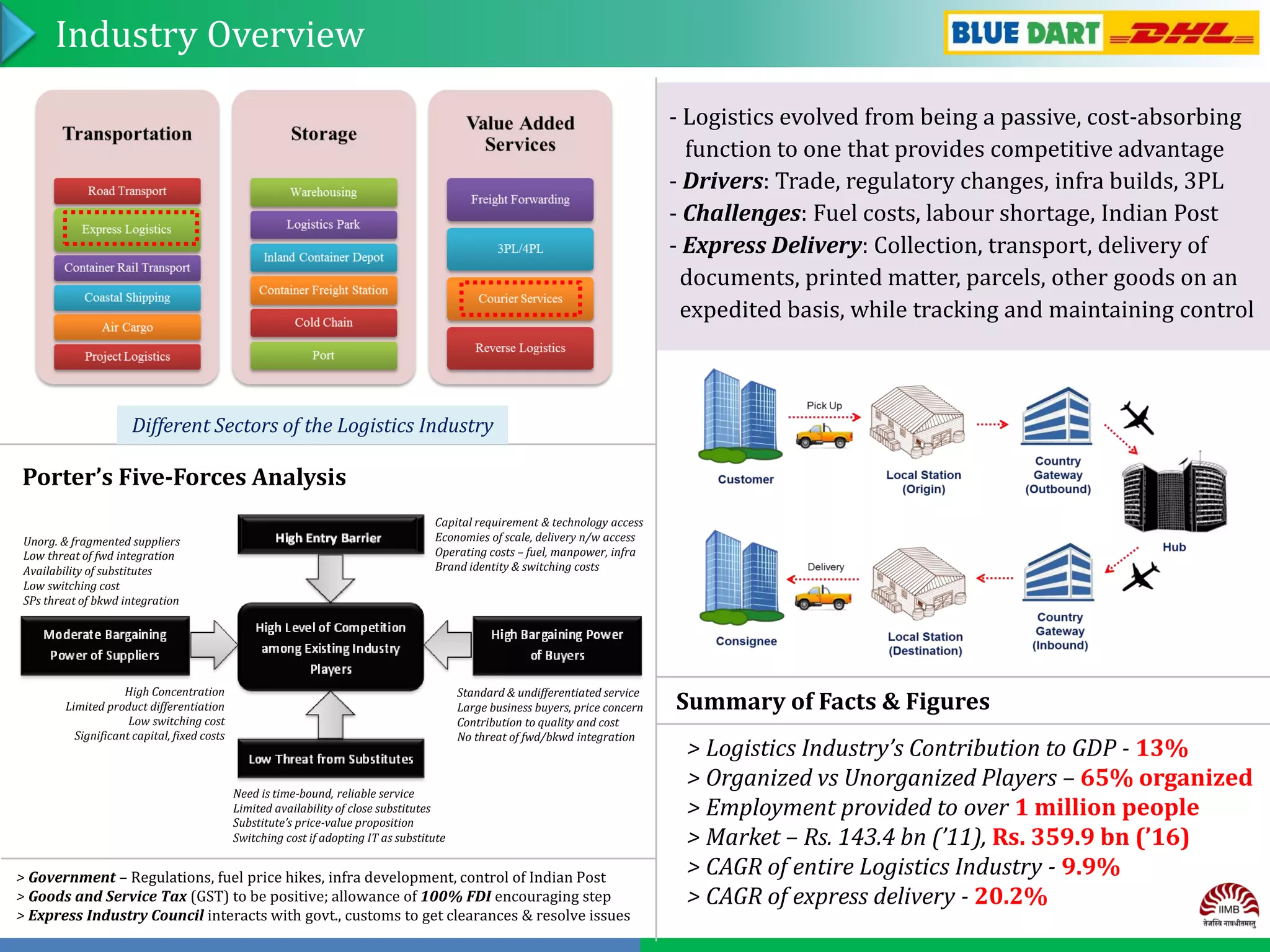
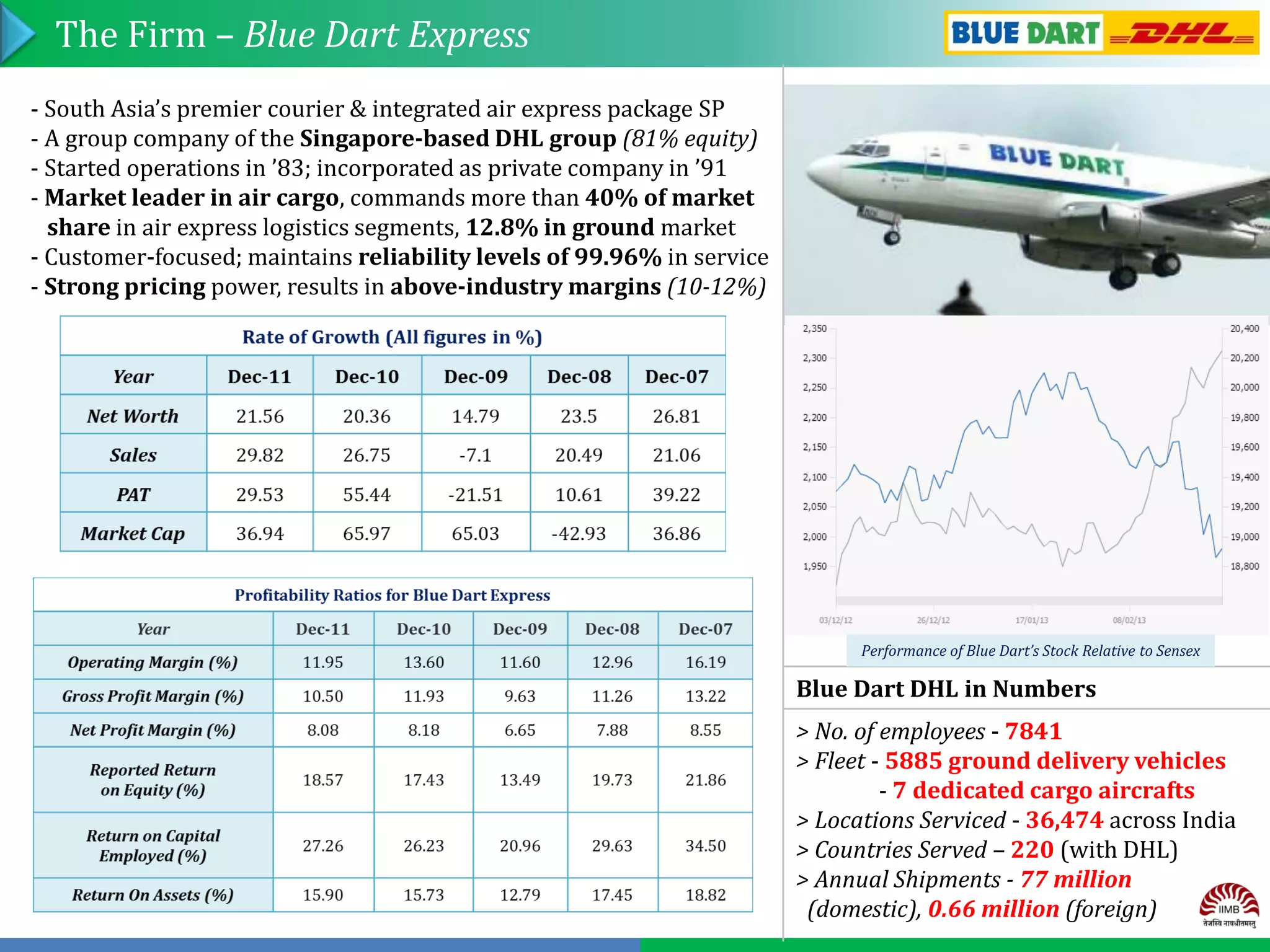
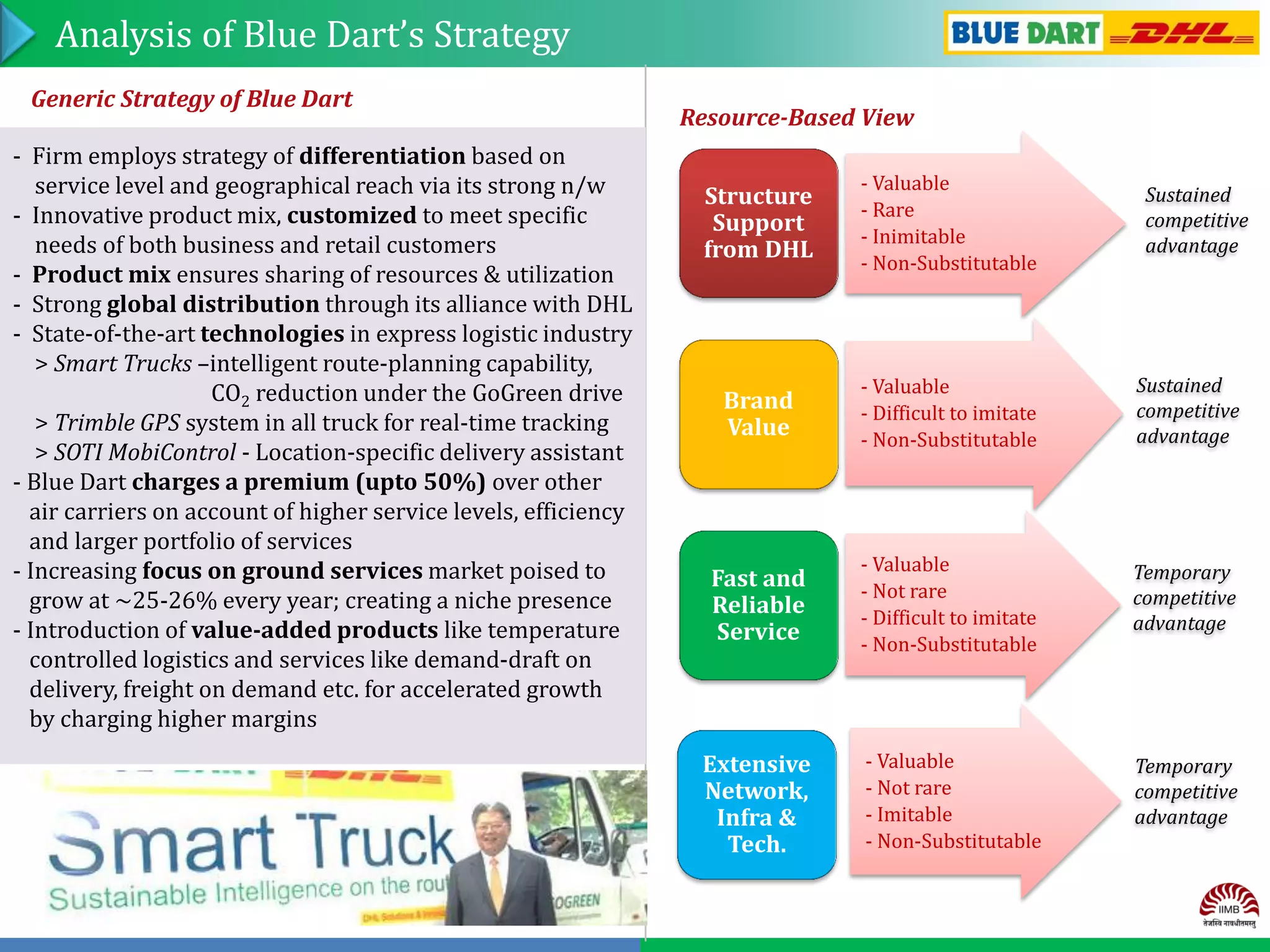
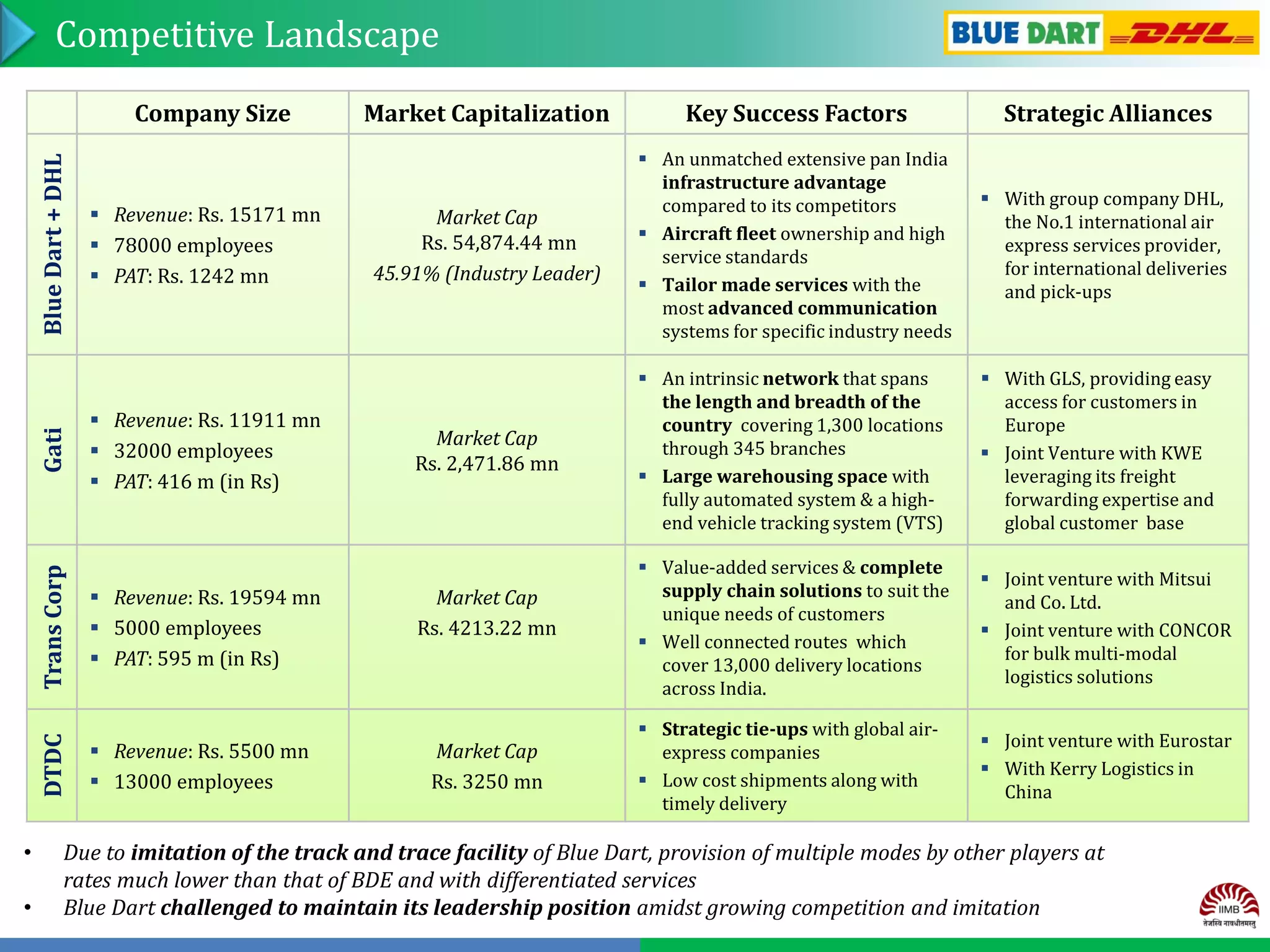
Group No. 13 analyzed the express delivery service industry in India. Blue Dart Express is the market leader with over 40% market share in air cargo. It has an extensive network across India and provides fast and reliable service. While Blue Dart has sustained competitive advantages through its brand, network, and alliance with DHL, competition is increasing from players like Gati and DTDC who are improving technology and expanding networks. To maintain leadership, Blue Dart should focus on customer service, expanding reach, adopting new technologies, and partnering with e-commerce companies.