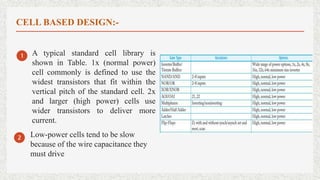
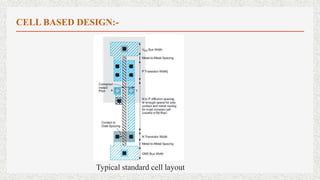
The document discusses three CMOS design methods: cell-based design, full custom design, and platform-based design. Cell-based design uses pre-designed standard cells from a library as building blocks and can deliver smaller, faster, and lower-power chips than FPGAs. Full custom design involves manually designing layouts at the transistor level, while cell-based design offers higher productivity through reuse of predesigned cells. Platform-based design uses common predesigned structures like buses and processors to implement a design through a high-level language.