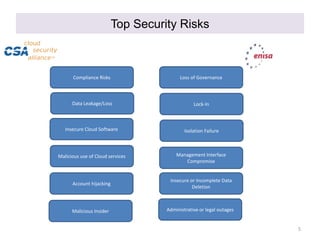
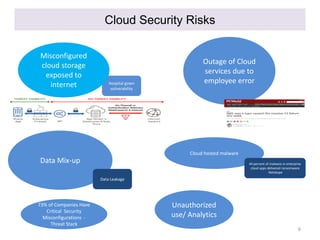
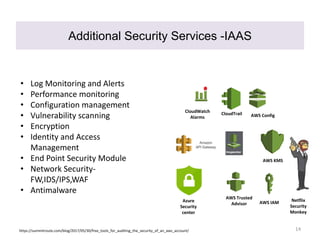
This document discusses cloud security governance and related challenges. It begins by outlining key cloud security concerns like lack of visibility, loss of control, and multi-tenancy issues. Major risks are then examined, such as data leakage, account hijacking, and insecure cloud software. The document also explores the shared responsibility model between cloud service providers and consumers. It notes that many breaches are due to customer misconfiguration rather than provider vulnerabilities. Finally, challenges in implementing cloud security governance are mentioned, such as cloud discovery, gaps in contracts, and rapidly changing cloud services and architectures.