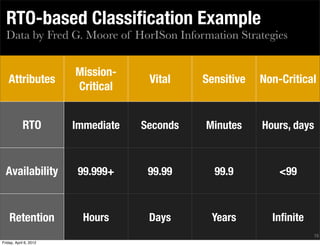
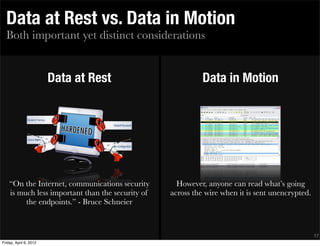
This document discusses virtualization, cloud computing, and data security. It begins by introducing the author and their background in security, privacy, and building virtual datacenters. It then discusses some key challenges around securing data in the cloud, including gracefully losing control while maintaining accountability. The rest of the document covers various aspects of cloud security such as access control, data classification, encryption of data at rest and in motion, and some of the unique security challenges presented by virtualization and moving data off-premise into the cloud.













![CA Office of HIPAA Implementation
Requires encryption to protect any data containing electronic
protected health information (EPHI).
‣ DATA AT REST
• Data at rest should be protected by one of the following:
- Encryption, or
- Firewalls with strict access controls that authenticate the identity of those
individuals accessing _____ [system/data].
• The use of password protection instead of encryption is not an
acceptable alternative to protecting EPHI.
• Systems that store or transmit personal information must have proper
security protection, such as antivirus software, with unneeded services or
ports turned off and subject to needed applications being properly
configured.
18
Friday, April 6, 2012](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/csa-q22012-120406120412-phpapp01/85/Cloud-Security-Alliance-Q2-2012-Atlanta-Meeting-18-320.jpg)
![CA Office of HIPAA Implementation
Requires encryption to protect any data containing electronic
protected health information (EPHI).
‣ TRANSMISSION SECURITY
• All emails with EPHI transmitted outside of State (or county) departments’
networks must be encrypted.
• Any EPHI transmitted through a public network to and from vendors,
customers, or entities doing business with ___ [name of the org in the State
of California, or a county] must be encrypted or be transmitted through an
encrypted tunnel. EPHI must be transmitted through a tunnel encrypted
with ___ [specify type of encryption to be used, such as virtual private
networks (VPN) or point-to-point tunnel protocols (PPTP) like Secure Shells
(SSH) and secure socket layers (SSL)].
• Transmitting EPHI through the use of web email programs is not allowed.
• Using chat programs or peer-to-peer file sharing programs is not allowed.
• Wireless (Wi-fi) transmissions must be encrypted using ___.
19
Friday, April 6, 2012](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/csa-q22012-120406120412-phpapp01/85/Cloud-Security-Alliance-Q2-2012-Atlanta-Meeting-19-320.jpg)








![VM Introspection
Inspecting a virtual machine from the outside (typically by way
of the hypervisor) for the purpose of analyzing [its behavior]
‣ Introspective firewalling
‣ Introspective malware detection
‣ Introspective DLP
‣ Traditionally, distinct products
• Catbird, Hytrust, Juniper, Reflex
Systems,Trend Micro, VMware, etc.
30
Friday, April 6, 2012](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/csa-q22012-120406120412-phpapp01/85/Cloud-Security-Alliance-Q2-2012-Atlanta-Meeting-30-320.jpg)