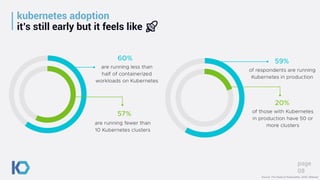
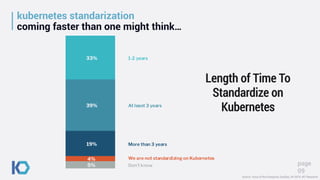
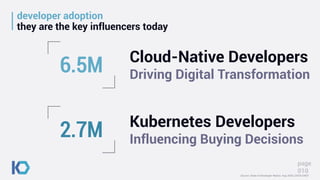
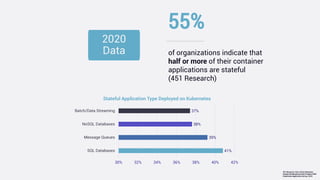
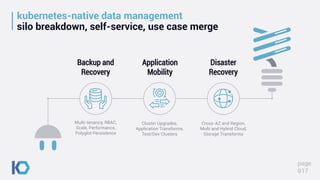
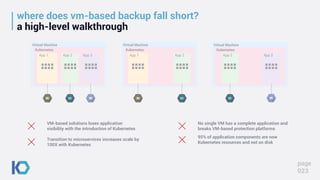
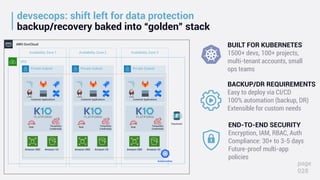
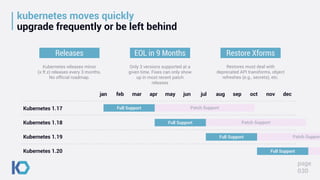
This document discusses data protection challenges in Kubernetes environments. It notes that traditional VM-based backup falls short for containerized applications due to lack of application visibility and scale. A Kubernetes-native approach is needed that focuses on complete application capture including resources and persistent state. It also discusses DevOps challenges around skills gaps and need for self-service, as well as concerns around Kubernetes upgrades, security, and ecosystem integration. The document promotes Kasten K10 as a solution built specifically for Kubernetes that provides ease of use, automation, security and support for applications across clusters and clouds.