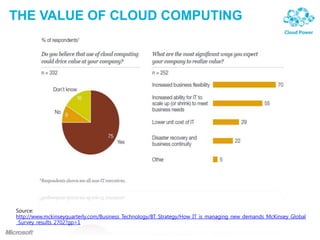
The document discusses the economics of cloud computing, highlighting key principles such as high availability, cost-effectiveness, and scalability. It underscores the benefits of multi-tenancy and demand-side economies of scale, emphasizing how Microsoft's cloud services reduce total cost of ownership while improving efficiency and sustainability. Additionally, it contrasts public and private cloud models and illustrates the evolution of technology through the 'horseless carriage syndrome' analogy.