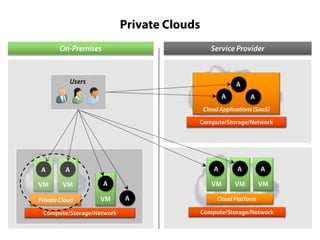
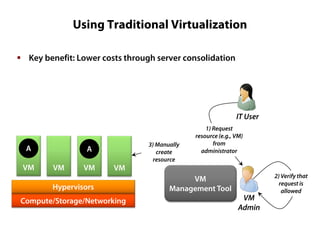
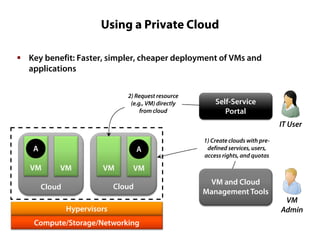
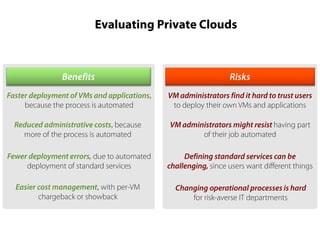
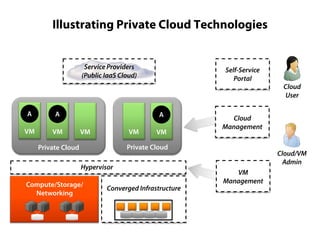
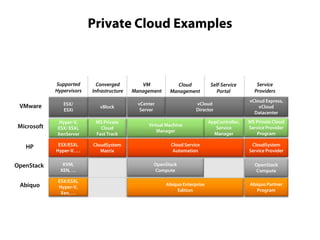
Private clouds provide infrastructure as a service (IaaS) within an organization's own data center. They automate the provisioning of virtual machines (VMs) through self-service portals, reducing costs and deployment times compared to traditional VM provisioning. Private clouds integrate hypervisors, storage, networking and management tools to deliver cloud services internally while addressing security and compliance needs. They are often combined with public cloud services to provide a hybrid cloud environment for additional flexibility and capacity.