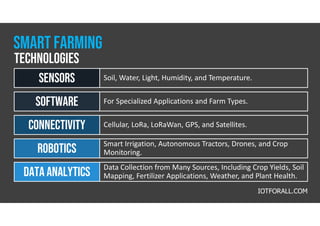
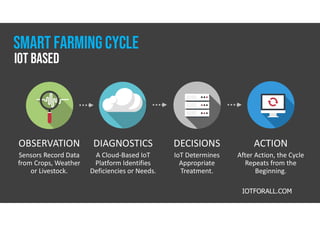
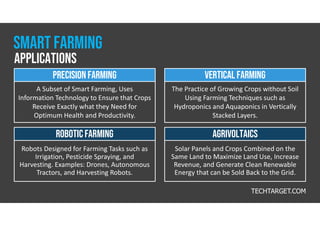
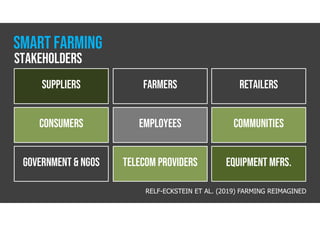
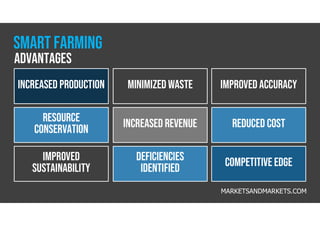
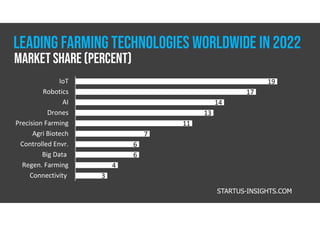
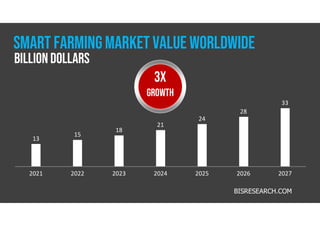
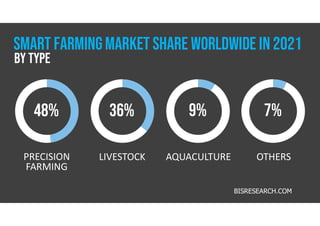
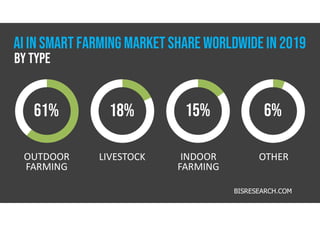
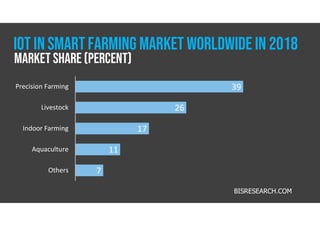
The document discusses smart farming, which leverages information and communication technologies to enhance agricultural productivity while minimizing environmental impact. It highlights advantages such as increased efficiency in resource use and crop production, along with challenges like poor connectivity and high equipment costs. The document also notes the growing market for smart farming technologies, which is expected to triple by 2027.