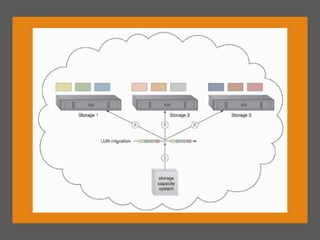
This document describes 10 cloud computing architectures:
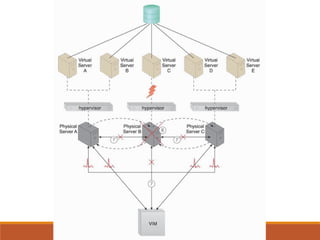
1) Hypervisor clustering protects VMs from hypervisor failures through live migration.
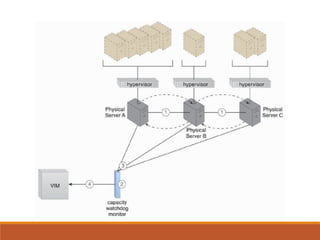
2) Load balancing distributes virtual server instances to prevent under/over-utilized servers.
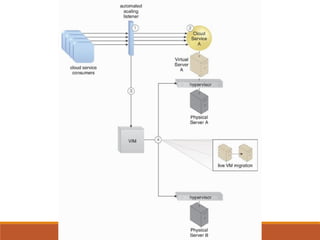
3) Non-disruptive relocation moves services without disruption through replication and live migration.
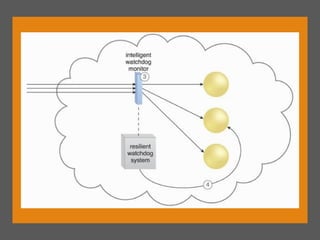
4) Zero downtime prevents failures through dynamic migration and failover across physical servers.
5) Cloud balancing distributes loads across multiple clouds for improved performance and reliability.