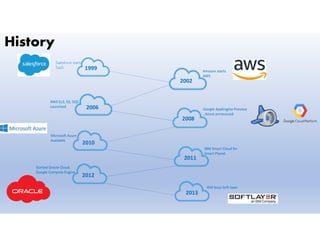
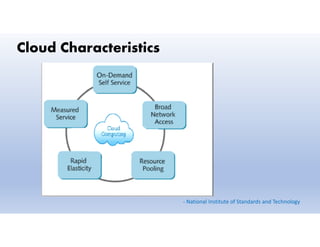
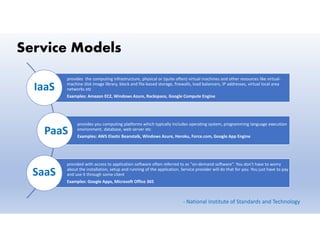
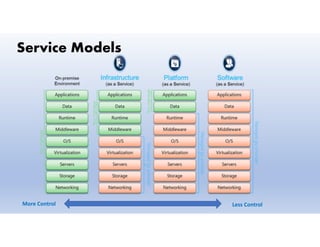
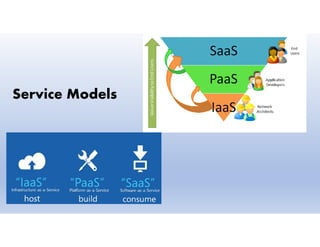
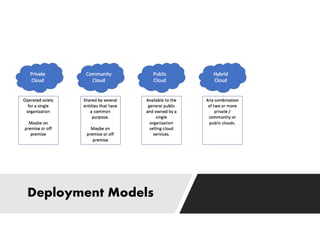
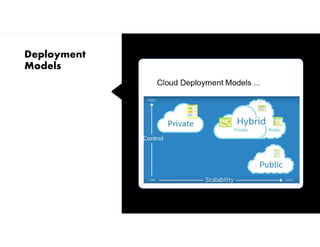
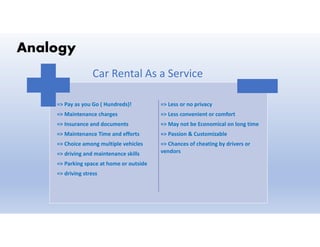
This document provides definitions and explanations of key concepts related to cloud computing. It defines cloud computing as the on-demand delivery of computing resources like servers, storage, databases, and applications via the internet, with a pay-as-you-go pricing model. The document then discusses the history of major cloud companies and offerings, characteristics of cloud computing, common service and deployment models, and analogies and terminology used in cloud computing.