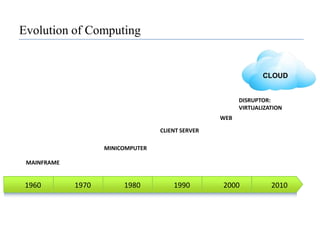
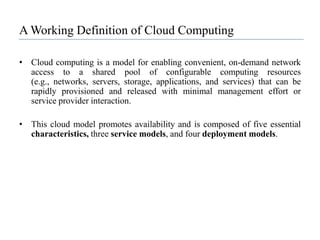
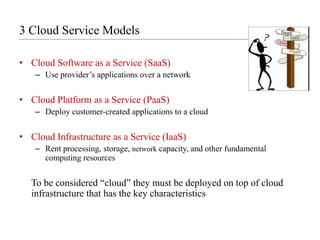
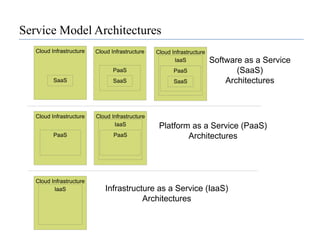
This document provides an overview of cloud computing, including its evolution, definitions, characteristics, service models, deployment models, benefits, challenges, and case studies. It discusses the key technologies that enable cloud computing such as virtualization, web services, and software as a service. Several real-world examples of organizations using cloud computing are presented, including Google, Amazon, Facebook, IBM, Microsoft, Salesforce.com, and government agencies. The document also examines the economics of cloud computing and traditional data centers.









![A “sunny” vision of the futureSun Microsystems CTO Greg PapadopoulosUsers will “trust” service providers with their data like they trust banks with their money“Hosting providers [will] bring ‘brutal efficiency’ for utilization, power, security, service levels, and idea-to-deploy time” –CNET articleBecoming cost ineffective to build data centersOrganizations will rent computing resources Envisions grid of 6 cloud infrastructure providers linked to 100 regional providers](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cloudcomputinganoverview-111017224639-phpapp02/85/Cloud-computing-An-Overview-18-320.jpg)





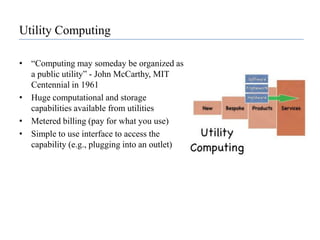

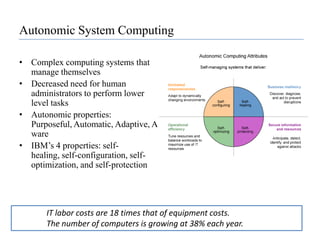
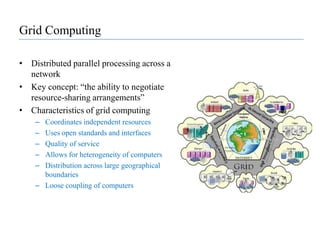

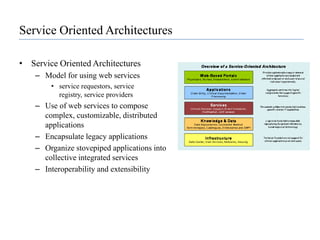

![Software as a Service (SaaS)SaaS is hosting applications on the Internet as a service (both consumer and enterprise)Jon Williams, CTO of Kaplan Test Prep on SaaS“I love the fact that I don't need to deal with servers, staging, version maintenance, security, performance”Eric Knorr with Computerworld says that “[there is an] increasing desperation on the part of IT to minimize application deployment and maintenance hassles”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cloudcomputinganoverview-111017224639-phpapp02/85/Cloud-computing-An-Overview-37-320.jpg)



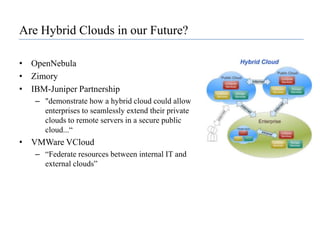


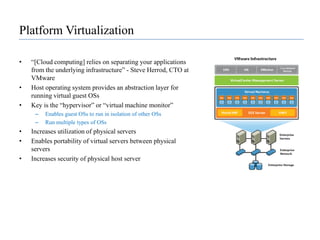
![Platform Virtualization“[Cloud computing] relies on separating your applications from the underlying infrastructure” - Steve Herrod, CTO at VMwareHost operating system provides an abstraction layer for running virtual guest OSsKey is the “hypervisor” or “virtual machine monitor”Enables guest OSs to run in isolation of other OSsRun multiple types of OSsIncreases utilization of physical serversEnables portability of virtual servers between physical serversIncreases security of physical host server](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cloudcomputinganoverview-111017224639-phpapp02/85/Cloud-computing-An-Overview-44-320.jpg)






