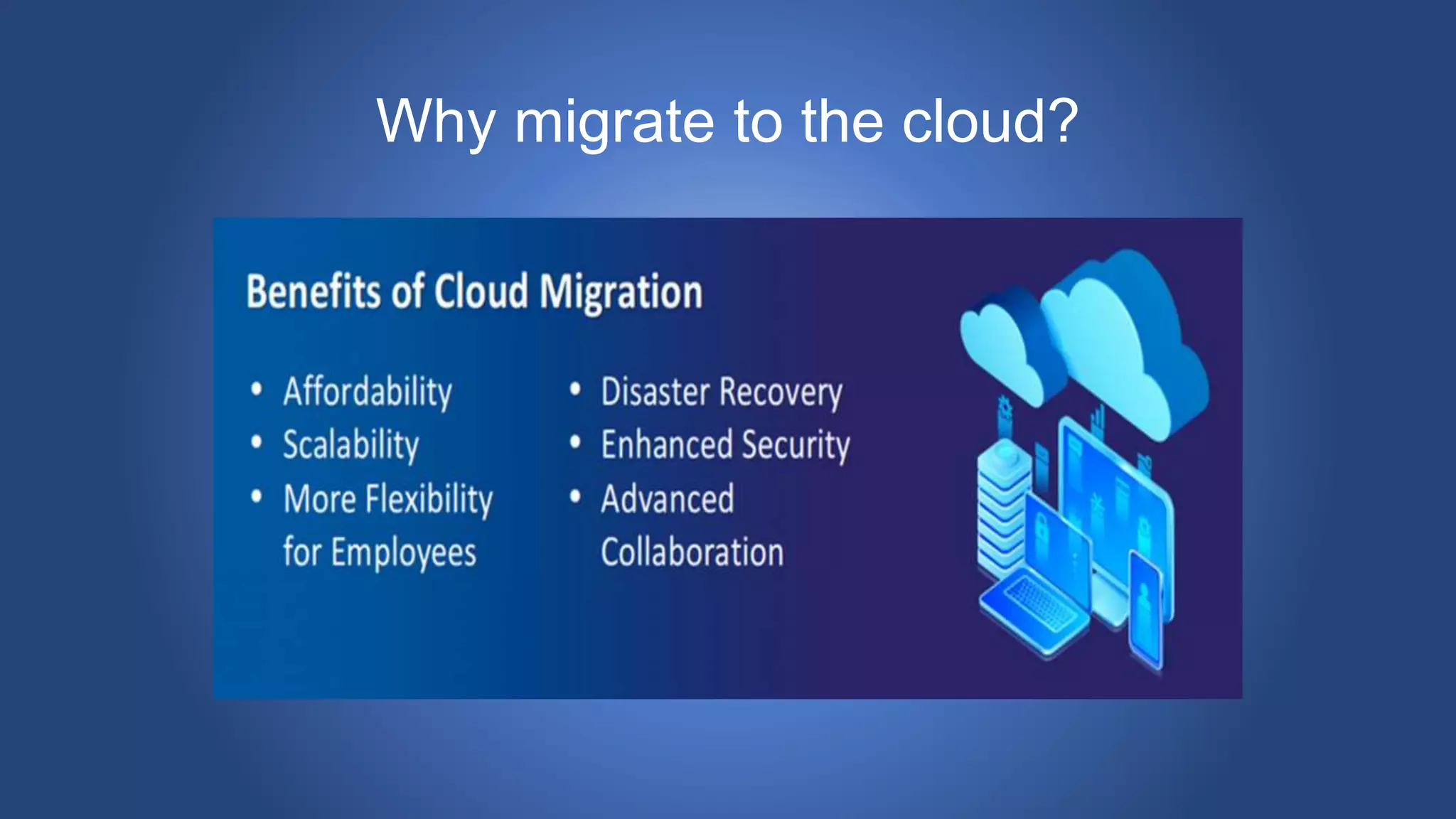
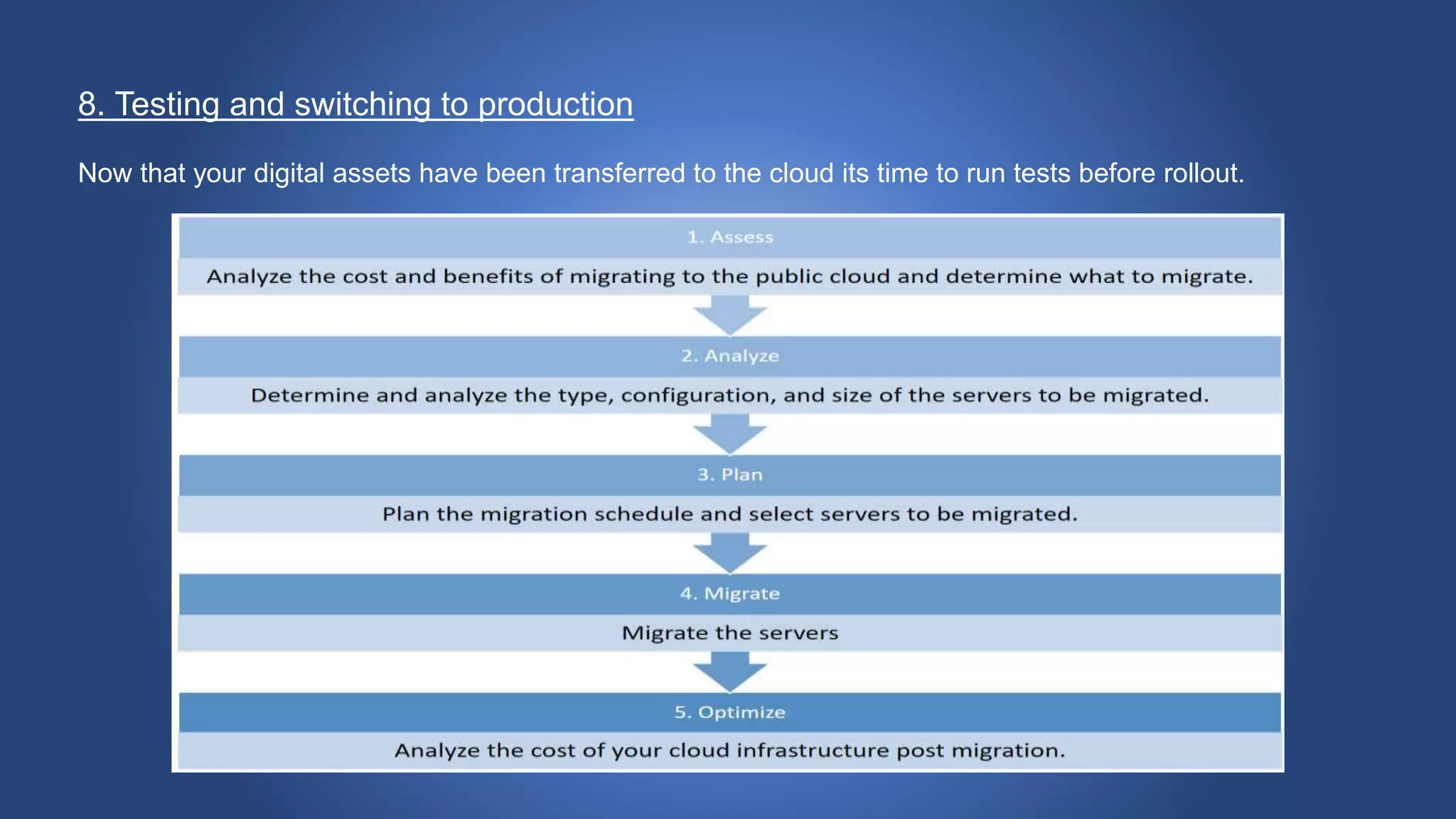
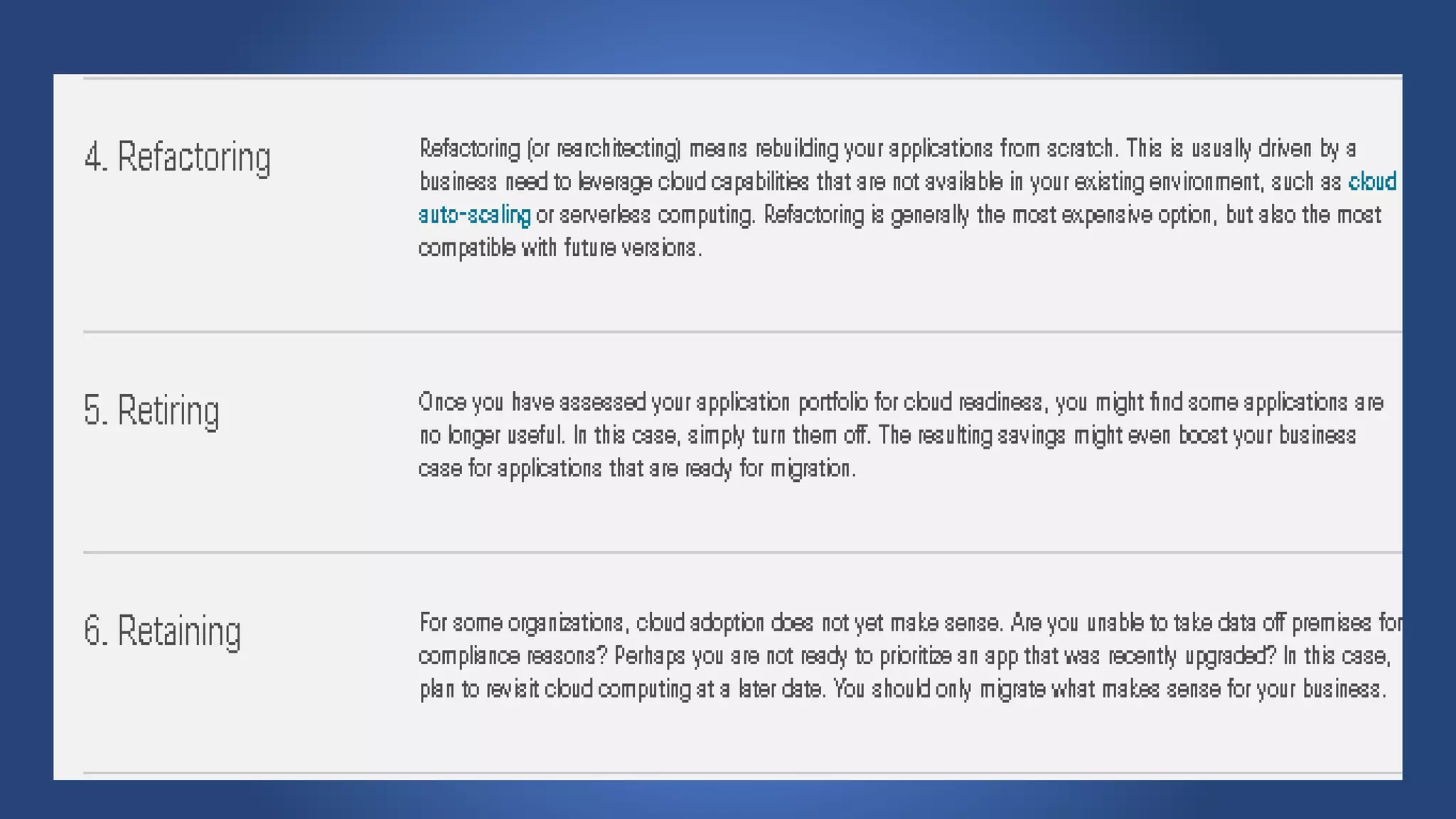
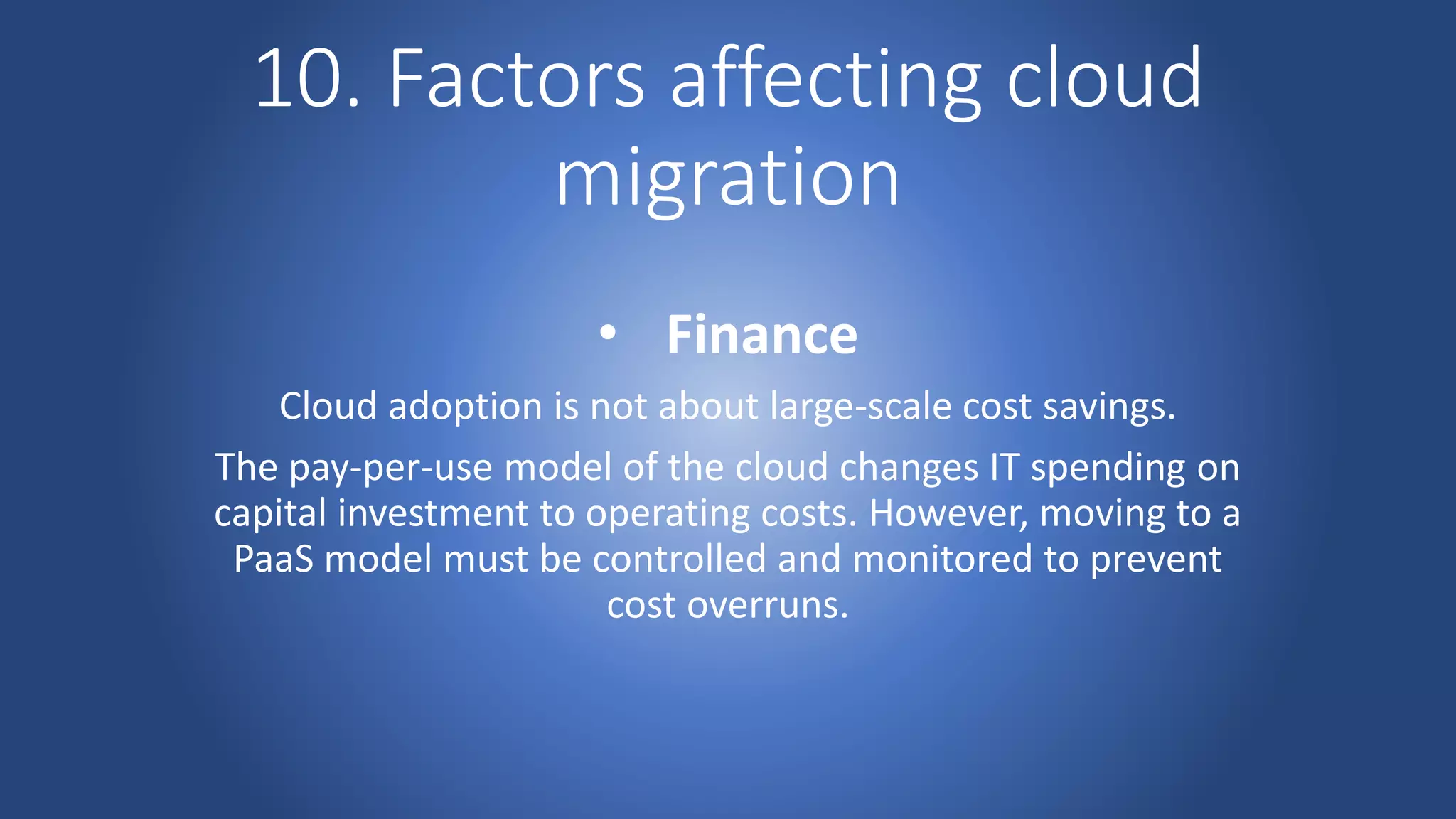
Cloud migration involves moving digital assets like applications and databases from a company's on-premise infrastructure to cloud infrastructure. There are several steps to a successful cloud migration including forming a migration team, assessing organizational readiness, choosing a cloud vendor and designing the cloud environment, creating a roadmap, choosing a migration strategy, migrating data, testing, and switching to production. Key risks of cloud migration include cost, loss of control, vendor lock-in, and potential performance issues. People, finances, and legal/compliance issues are also important factors to consider.