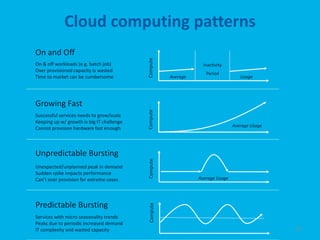
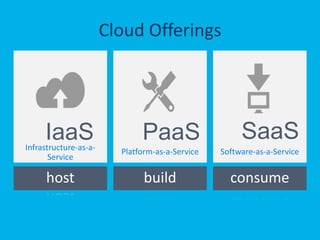
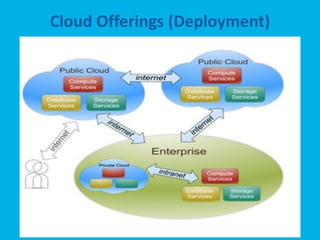
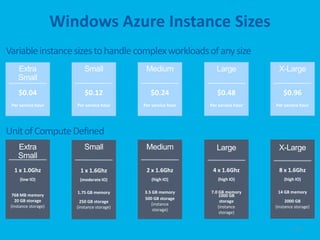
The document provides an overview of Microsoft's cloud computing platform, Azure. It defines cloud computing and discusses common scenarios. It then outlines Azure's core services including compute, storage, SQL database, caching, and access control. Azure provides scalable infrastructure across Microsoft's global data centers and supports building apps using virtual machines, web apps, and managed services with a pay-as-you-go model.