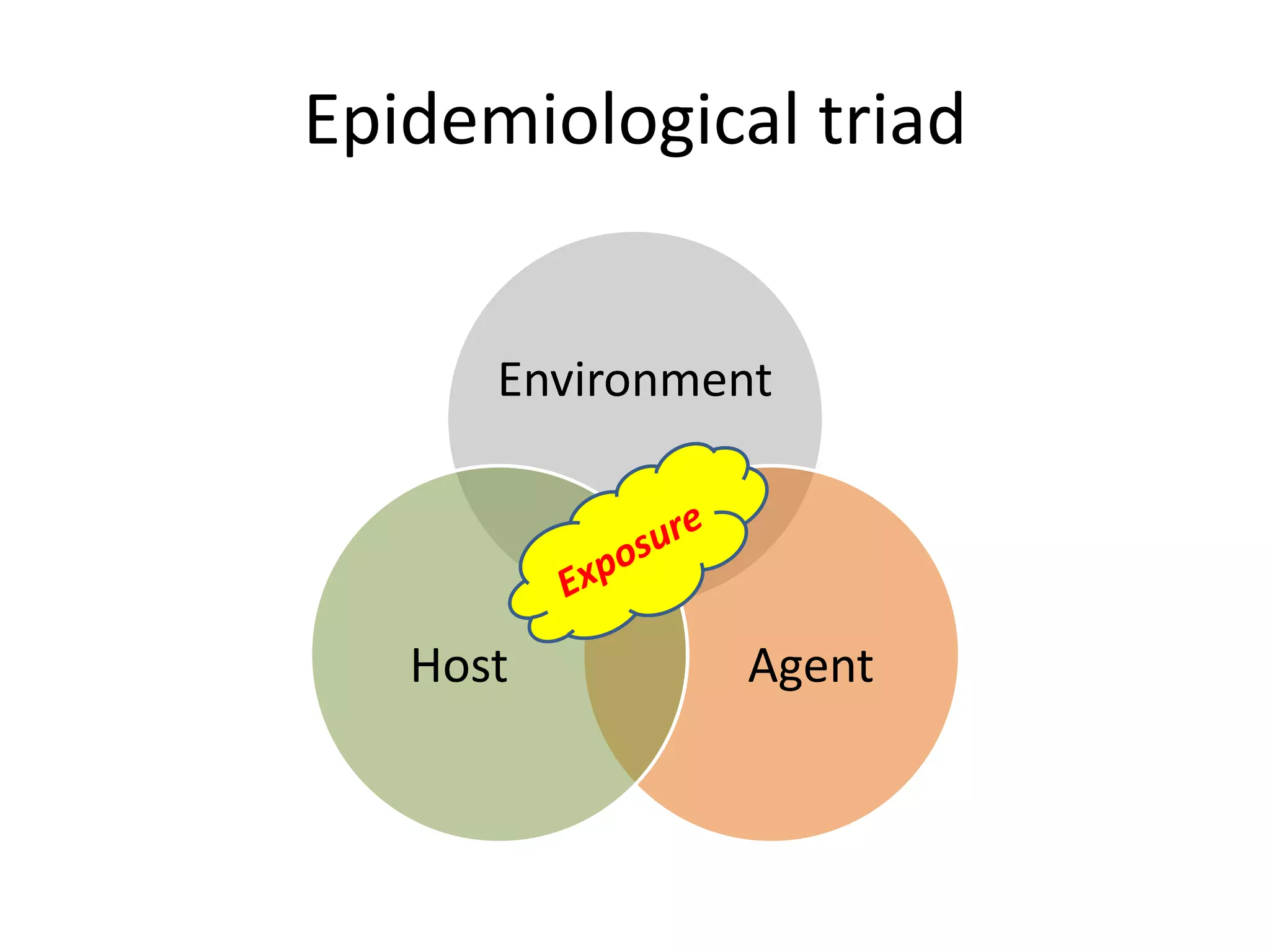
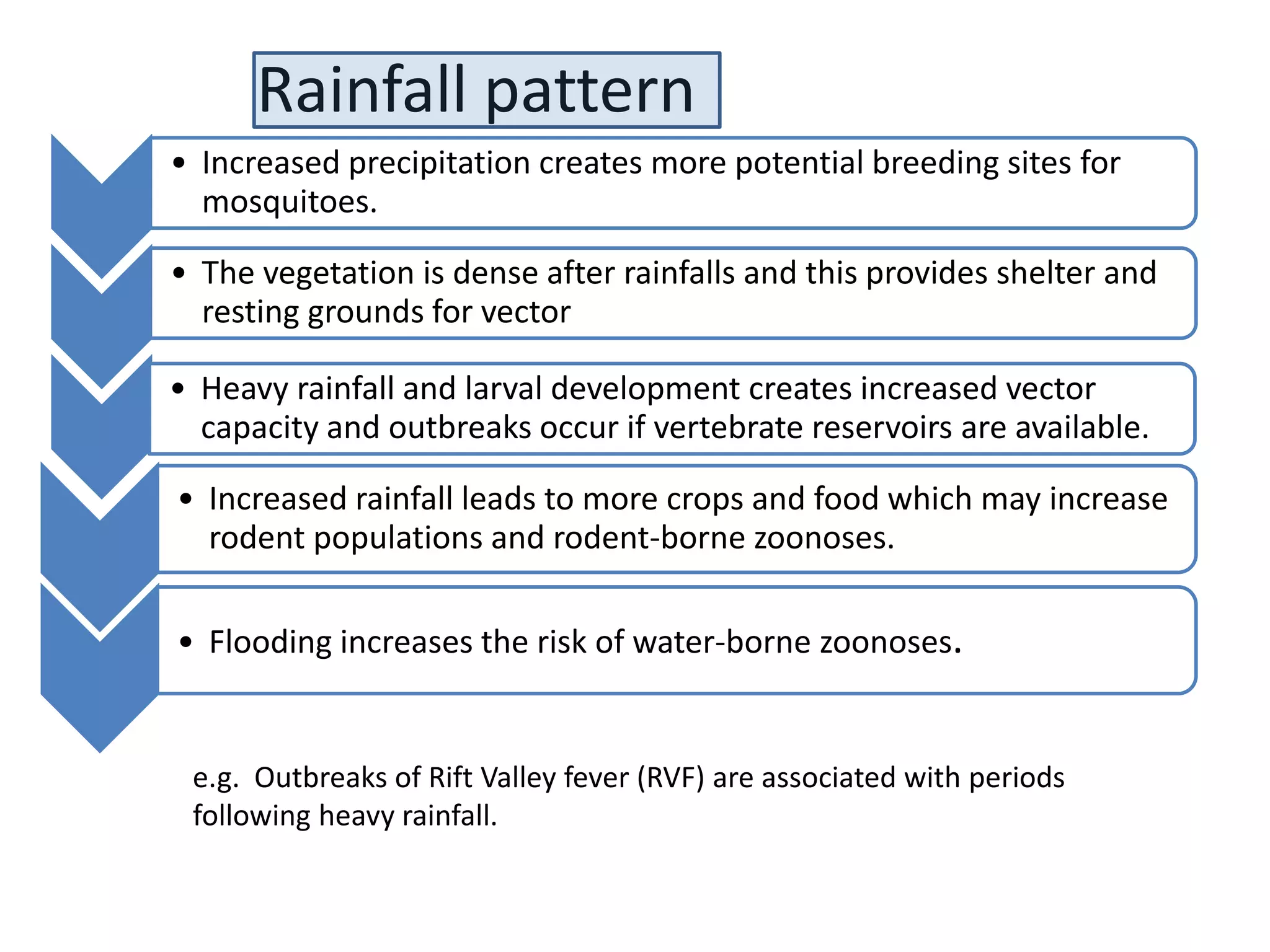
Climate change can impact the transmission of zoonotic diseases in several ways. Warmer temperatures allow vectors like mosquitoes and ticks to survive in new areas, increasing transmission of diseases. Increased rainfall can create more breeding sites for mosquitoes and flooding events, raising risks of water-borne diseases. Changes in animal migration patterns and environments from climate change can spread zoonotic pathogens over longer distances. A variety of zoonotic diseases may see changed prevalence and transmission under climate change conditions through these types of environmental and ecological impacts.