The document defines and describes various types of disabilities:
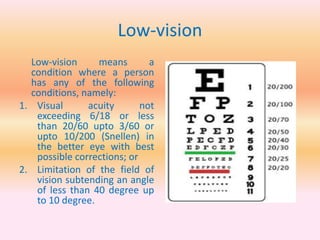
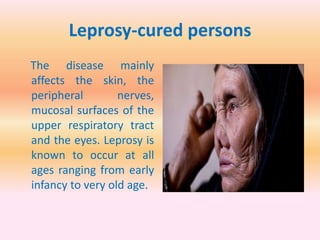
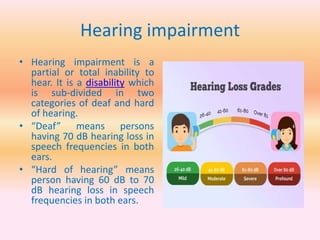
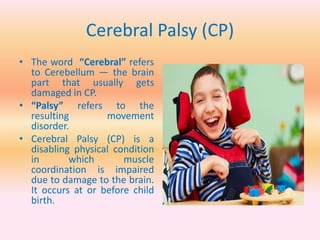
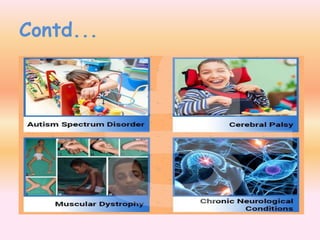
- Physical disabilities include blindness, low vision, leprosy, hearing and speech impairments, locomotor disabilities, dwarfism, cerebral palsy, muscular dystrophy, and others.
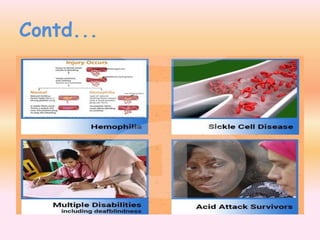
- Developmental and learning disabilities include intellectual disability, autism spectrum disorder, specific learning disabilities, and multiple disabilities.
- Neurological disabilities include mental illness, epilepsy, multiple sclerosis, Alzheimer's, dystonia, ALS, Huntington's disease, and others.
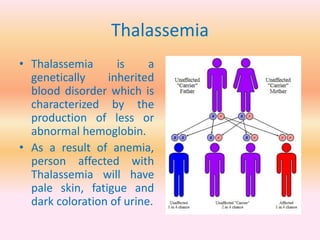
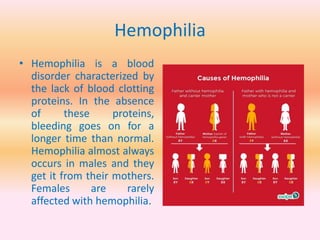
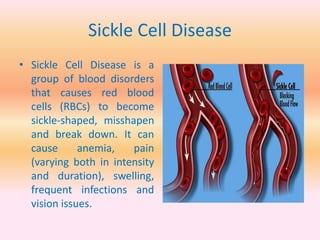
- Blood disorders include thalassemia, hemophilia, and sickle cell disease.
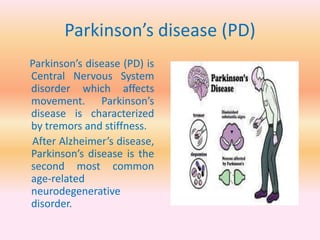
- The document also mentions acid attack survivors, Parkinson's disease, and provides an overview of the