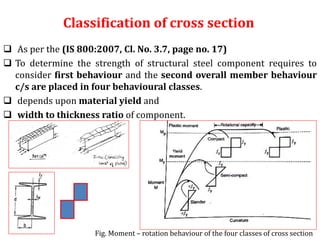
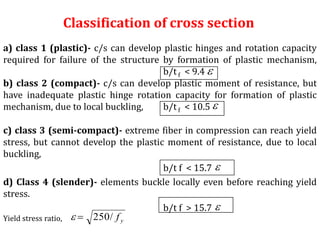
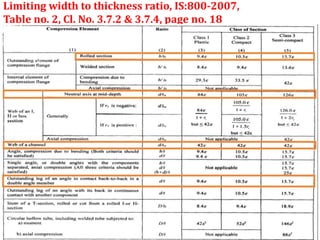
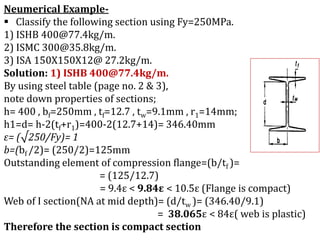
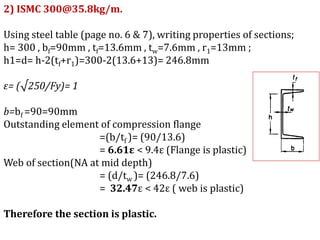
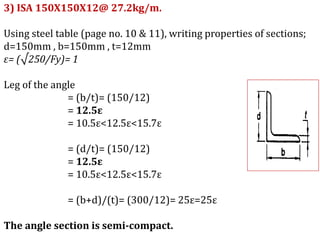
This document discusses the classification of steel cross sections according to Indian Standard IS 800:2007. It explains that cross sections are classified into four classes - plastic, compact, semi-compact, and slender - based on their width-thickness ratio and ability to develop plastic hinges and plastic moment capacity. Formulas and limiting ratios for each class are provided. Three example cross sections are then classified - a ISHB 400 section is compact, a ISMC 300 section is plastic, and a ISA 150X150X12 angle section is semi-compact.