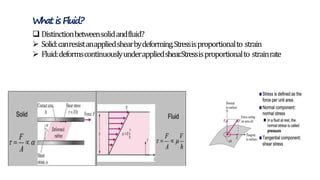
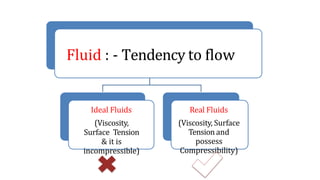
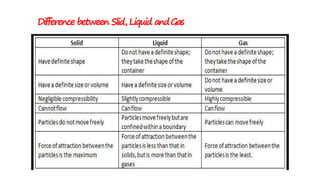
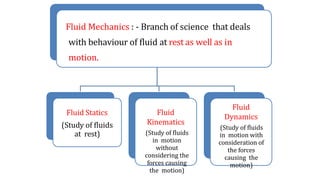
This document provides an introduction to fluid mechanics for a civil engineering course. It defines a fluid as a substance that continuously deforms under the application of shear stress, regardless of the magnitude of stress. Fluids are classified as liquids or gases depending on their molecular spacing. The document outlines the key differences between solids and fluids, noting that solids can resist shear stress while fluids deform continuously. It also introduces some fundamental fluid mechanics concepts like fluid statics, kinematics, and dynamics, which study fluids at rest, in motion without forces, and in motion with forces, respectively. The overall document serves as an introductory overview of fluid properties and the basic study of fluids.