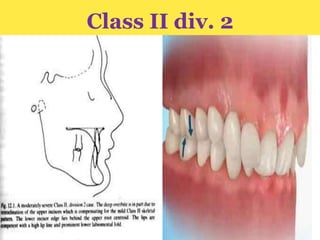
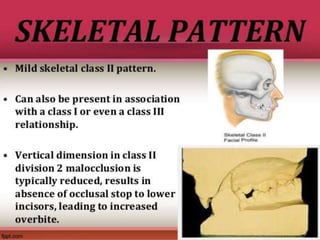
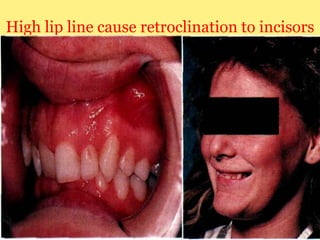
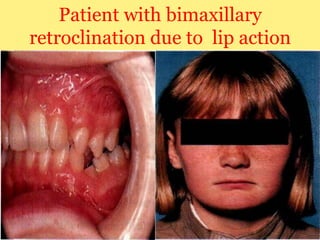
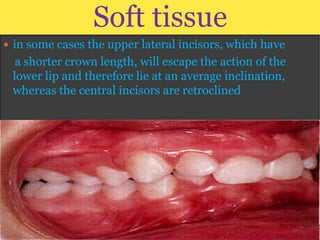
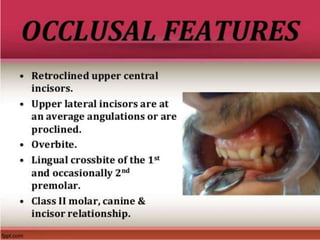
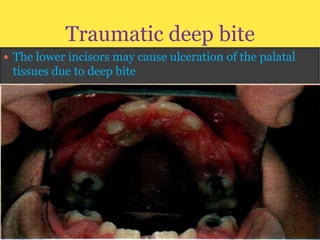
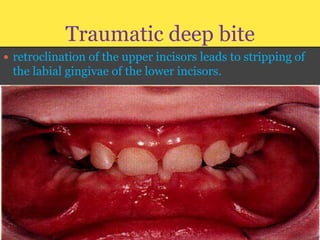
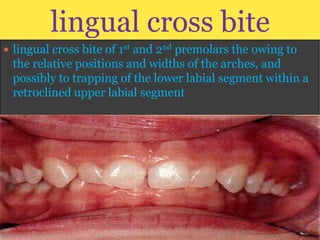
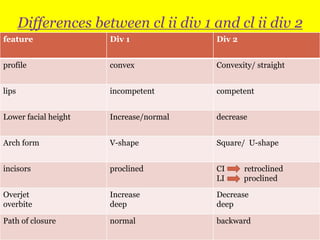
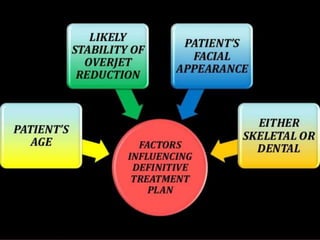
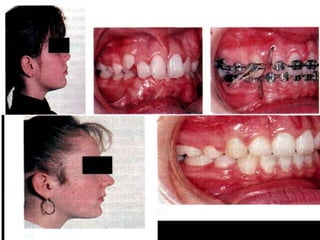
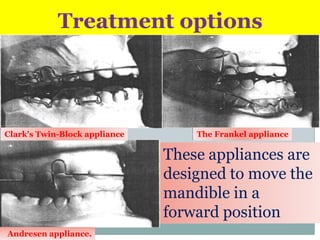
Class II division 2 malocclusion is characterized by retroclined upper incisors with minimal overjet and deep overbite. It has a prevalence of 10% in Caucasian populations. There are three types based on spatial conditions in the maxilla. Treatment aims to improve aesthetics, function, relieve crowding, and reduce overbite. Options include no treatment, removable appliances, single/twin fixed appliances, functional appliances, and orthognathic surgery. Stability can be an issue after treatment, especially for lateral incisor alignment and overbite correction.