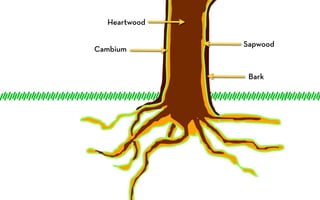
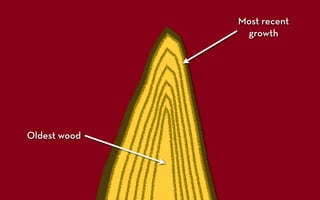
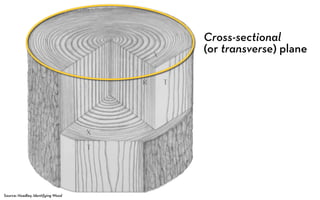
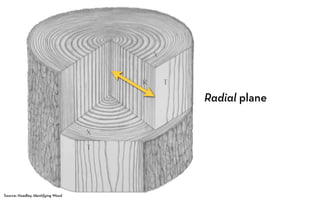
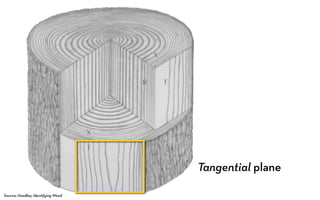
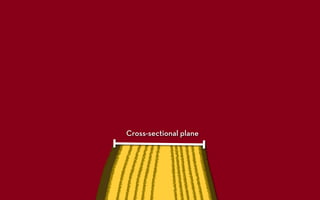
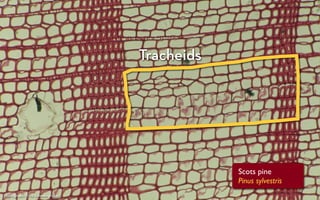
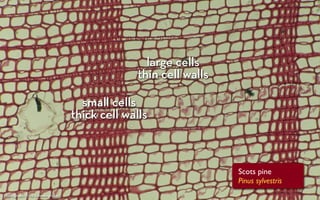
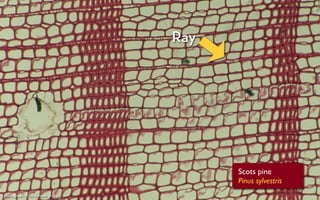
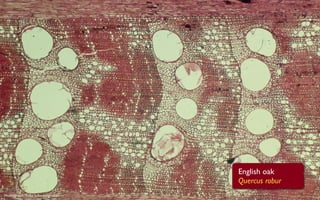
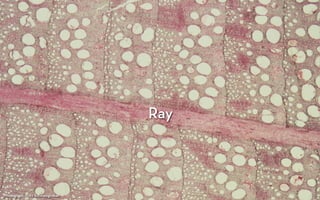
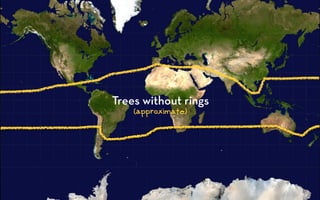
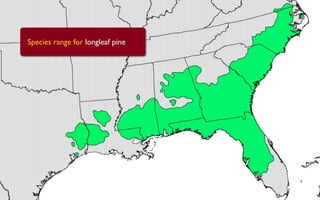
Tree rings are growth rings visible in the cross-section of tree trunks and branches. They result from the tree's growth pattern, which is influenced by environmental factors. The document defines trees and their basic anatomy, including key tissues like heartwood, sapwood, cambium and bark. It describes tree ring patterns in conifers like pine and hemlock versus hardwoods like oak, and key cell types seen in rings. Some trees like mangroves may not exhibit clear annual growth rings.