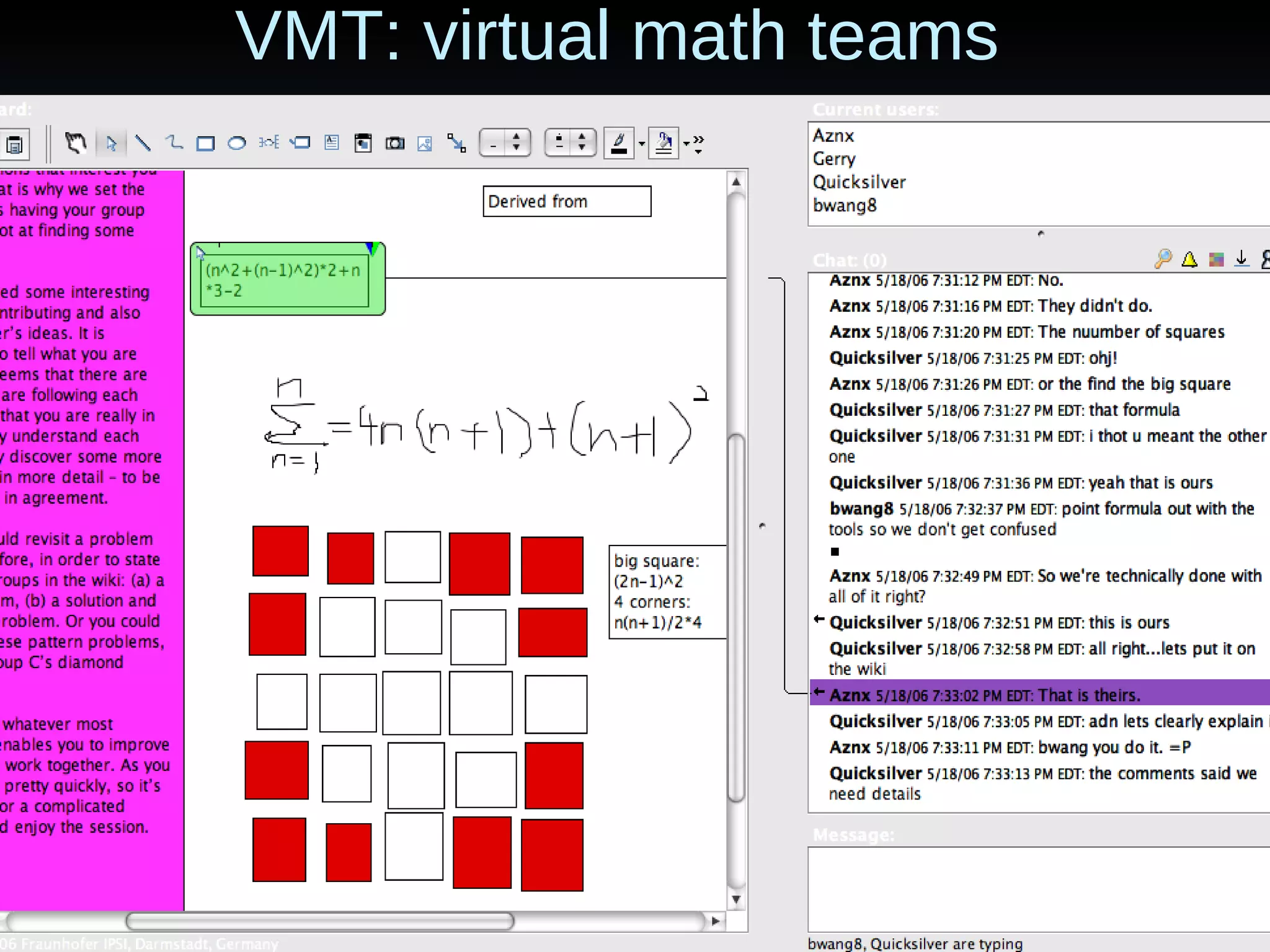
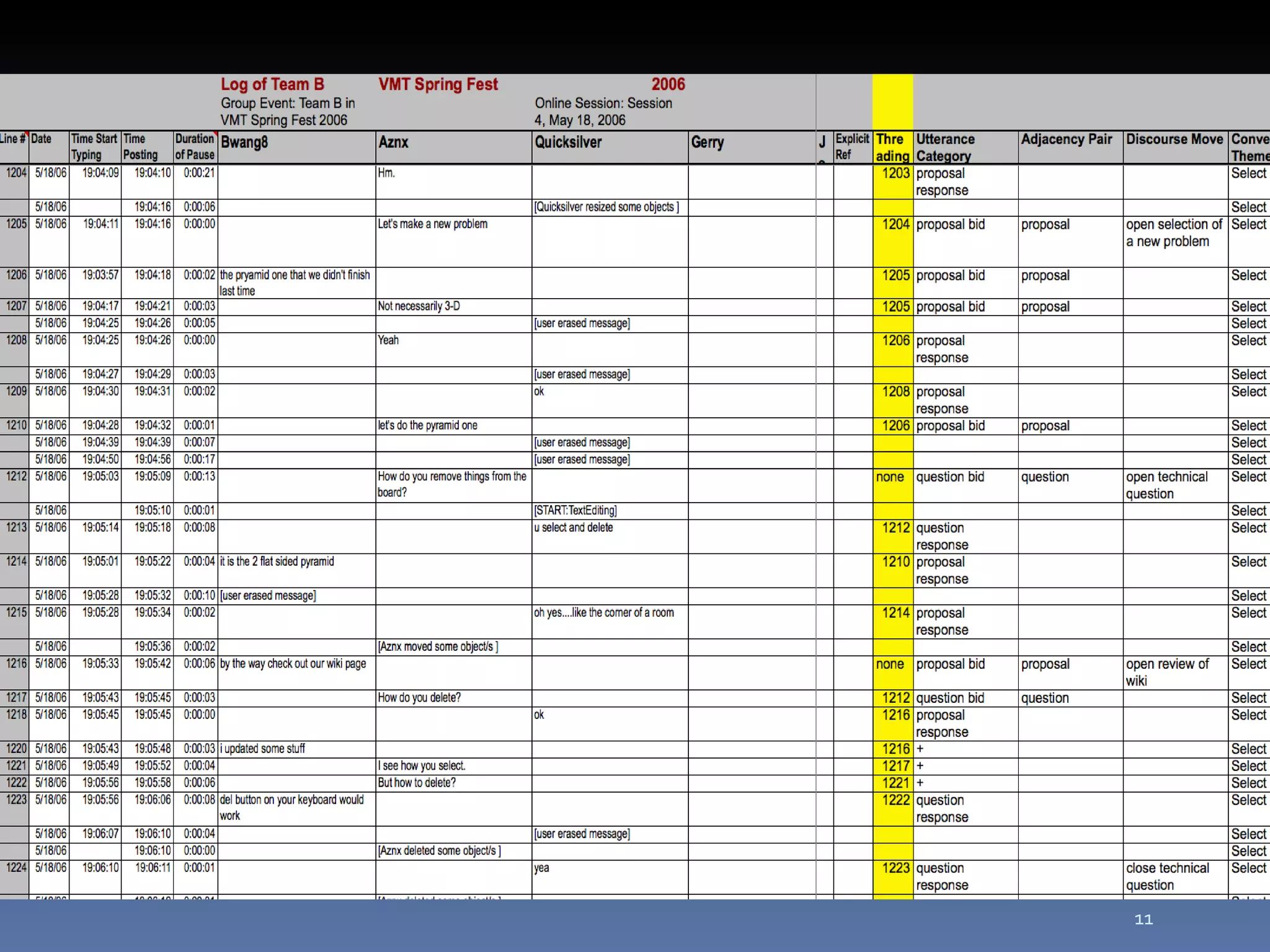
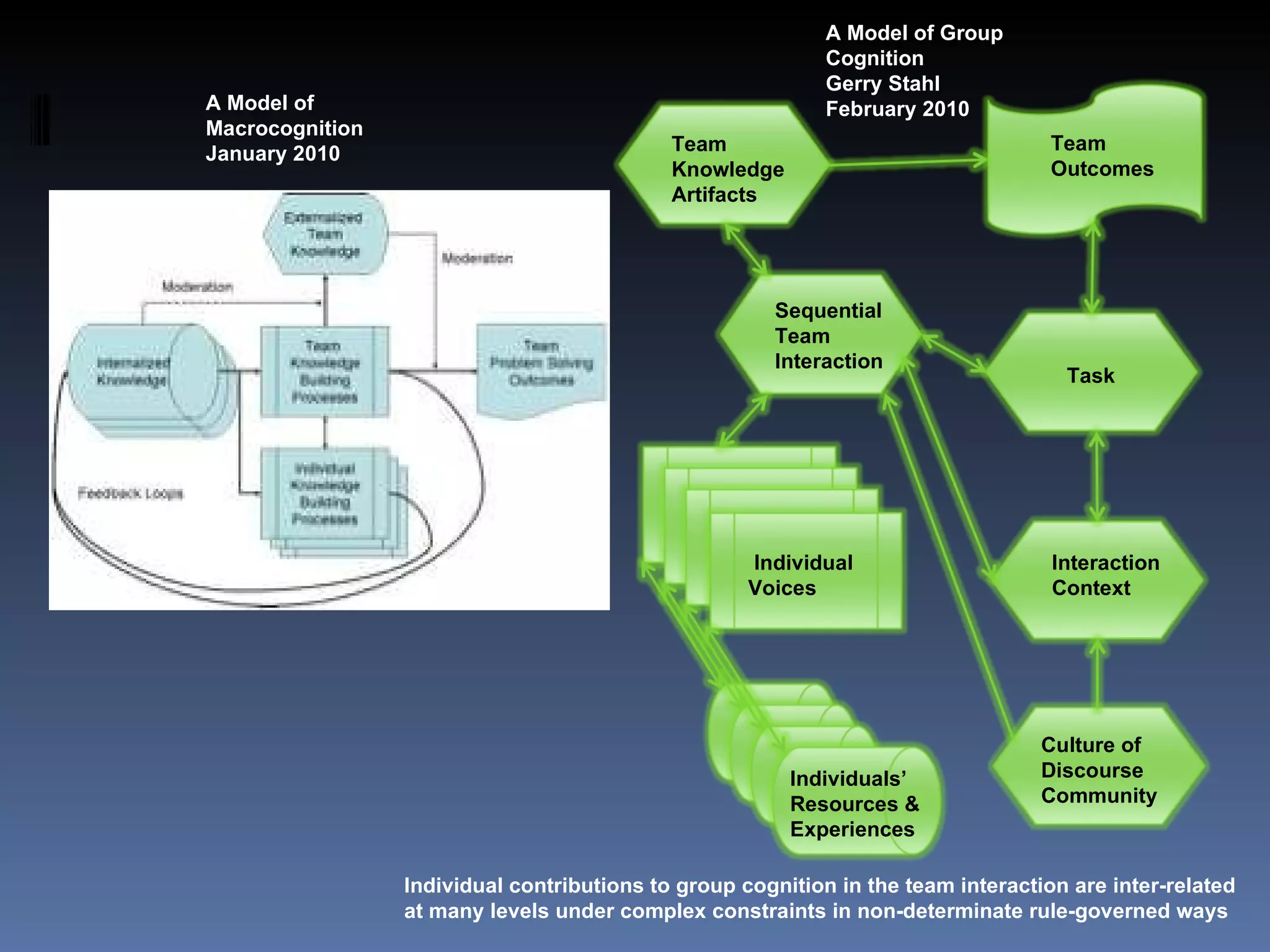
The document discusses computer-supported collaborative learning (CSCL) and virtual math teams (VMT) as contexts for studying group cognition and communication. It examines how small groups solve problems and build knowledge together online. The author analyzes VMT group interactions to understand how cognition occurs at the group level through communication sequences. The analysis focuses on how groups coordinate tasks, construct meaning jointly, and produce shared artifacts and understanding.











![For Further Information Slides: http://www.slideshare.net/Gerry.Stahl Website: http://GerryStahl.net Email: [email_address] Group Cognition (2006, MIT Press) Studying Virtual Math Teams (2009, Springer)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ckiworkshop-100208185649-phpapp02/75/Computer-Supported-Collaborative-Learning-CSCL-Virtual-Math-Teams-VMT-and-Group-Cognition-16-2048.jpg)