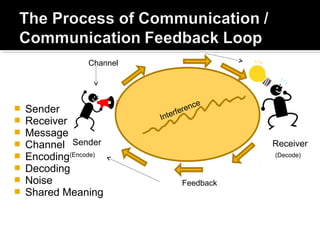
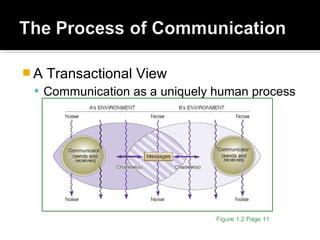
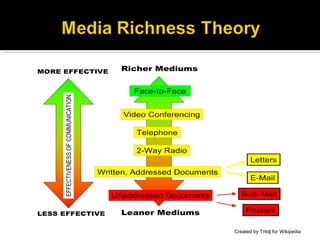
This document summarizes key concepts from a textbook about small group communication. It discusses definitions of groups, primary and secondary groups, types of groups like problem-solving and decision-making groups, and virtual small group communication using technology. It also outlines components of the communication process, characteristics of effective teams, challenges groups face, and qualities of competent group communicators.