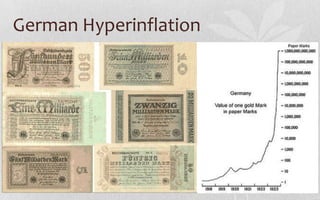
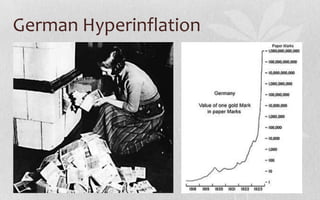
After World War I, the US economy experienced a recession from 1919-1921 as veterans returned home and an influenza pandemic hit. The 1920s saw social and cultural changes like women's suffrage and Prohibition, but also violence like the Sacco and Vanzetti case and Wall Street bombing. The stock market crashed in 1929, plunging the US into the Great Depression. President Hoover initially responded through public works projects and urging cooperation from business leaders, but unemployment rose sharply. By 1932, Hoover had lost public support and Franklin D. Roosevelt was elected promising a new approach.