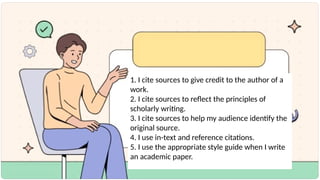
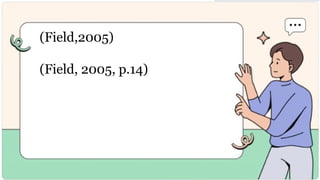
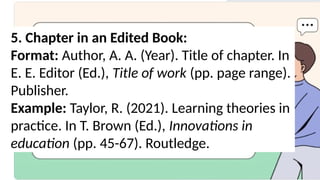
The document outlines the importance of citing sources in academic writing, highlighting purposes such as giving credit to original authors and promoting scholarly writing. It discusses the significance of effective communication, digital literacy, cultural awareness, and critical thinking, supported by various citations. It also provides guidelines for APA and MLA citation styles, including examples and formatting rules.