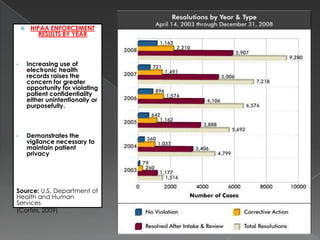
The document discusses key components of a Clinical Information System (CIS) including the Electronic Health Record (EHR). It describes the 8 components of an EHR, how clinical decision making systems work, considerations for safety, cost, and education. Clinical decision making systems use evidence-based practices and hierarchical approaches to determine diagnoses and treatment plans. Safety involves backing up data, protecting files from threats, and complying with privacy laws like HIPAA. Costs include purchasing, maintenance, training staff, and ongoing security and upgrades. Education of staff is important both initially and continuously as systems evolve.