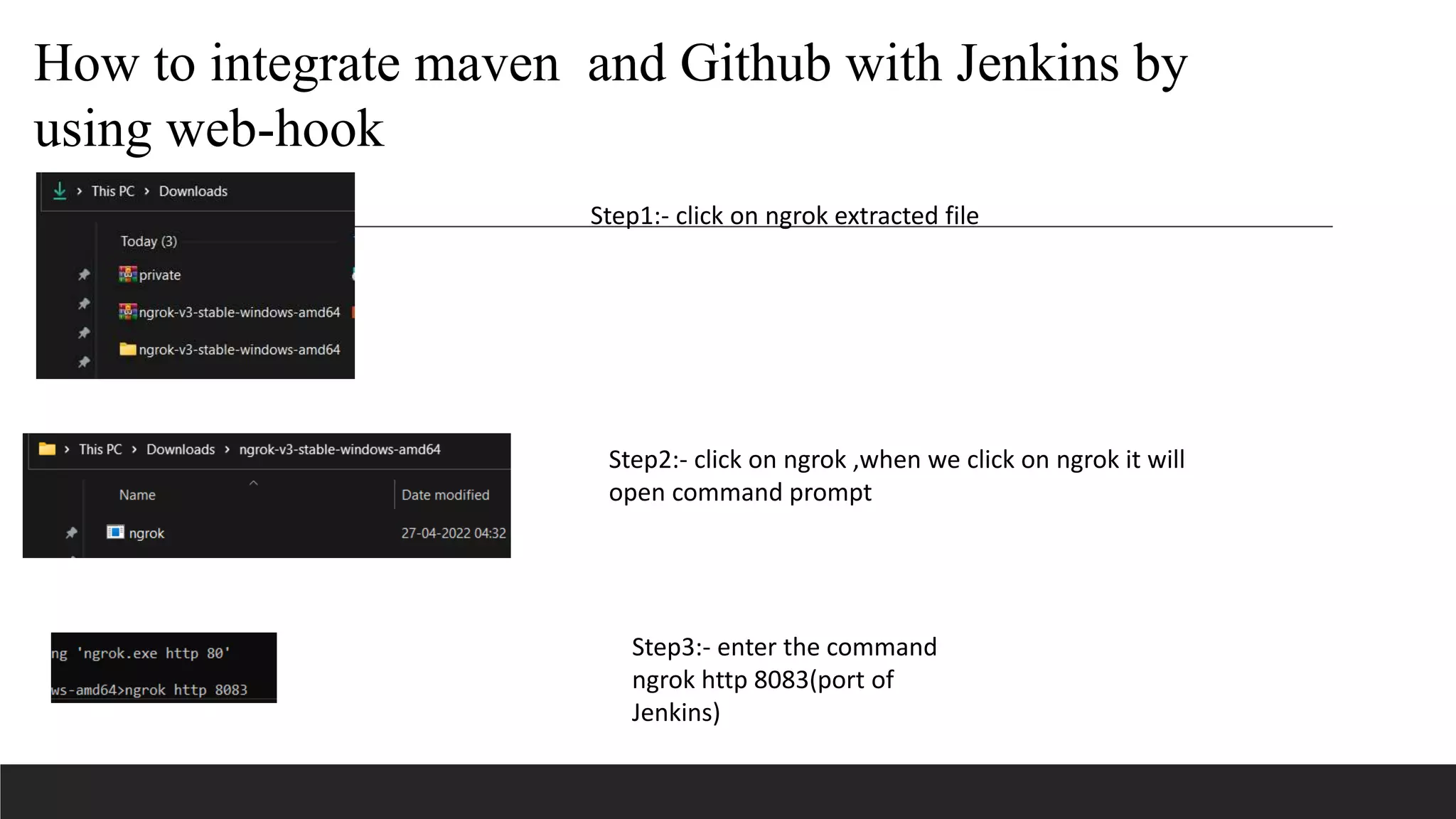
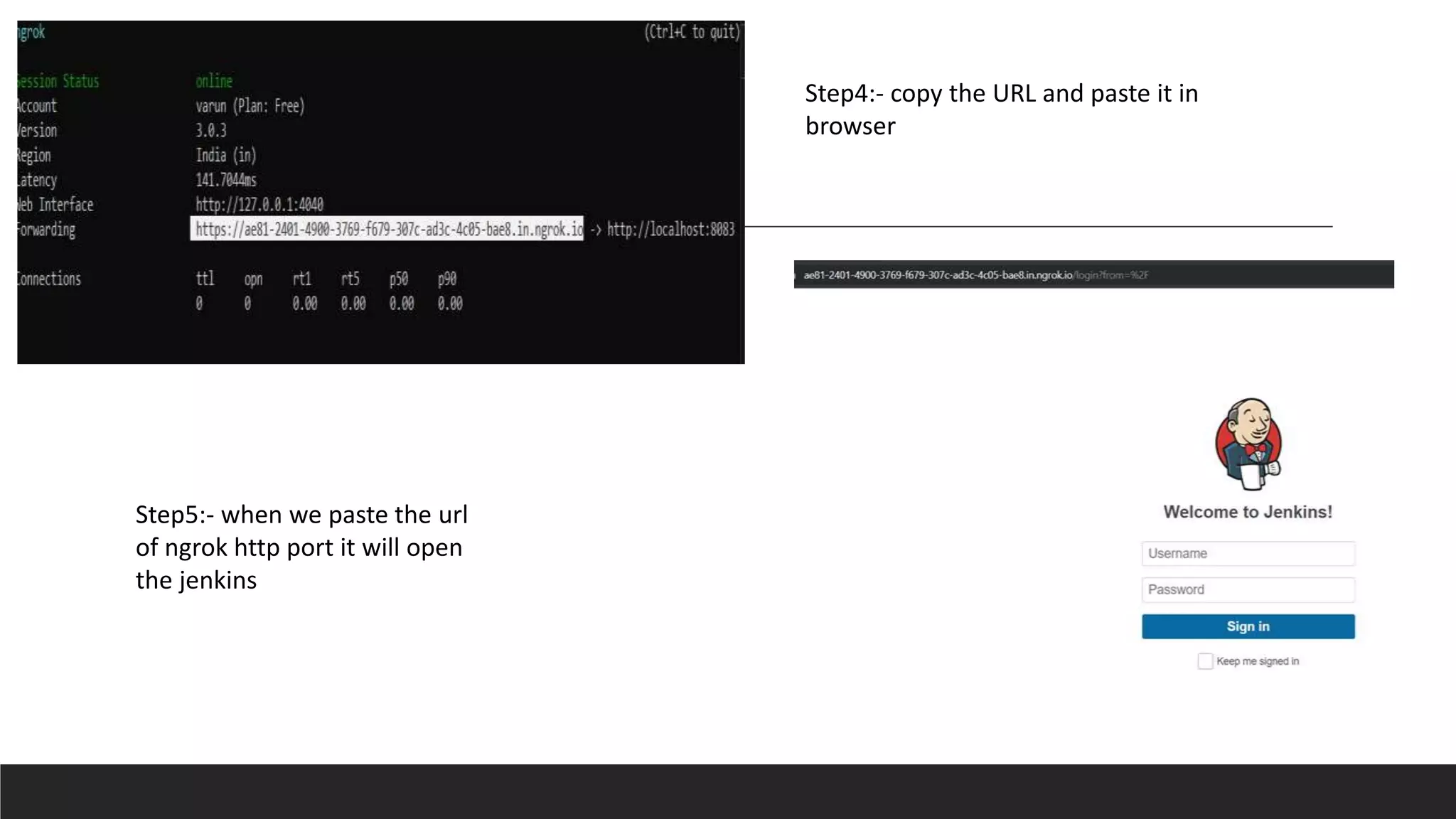
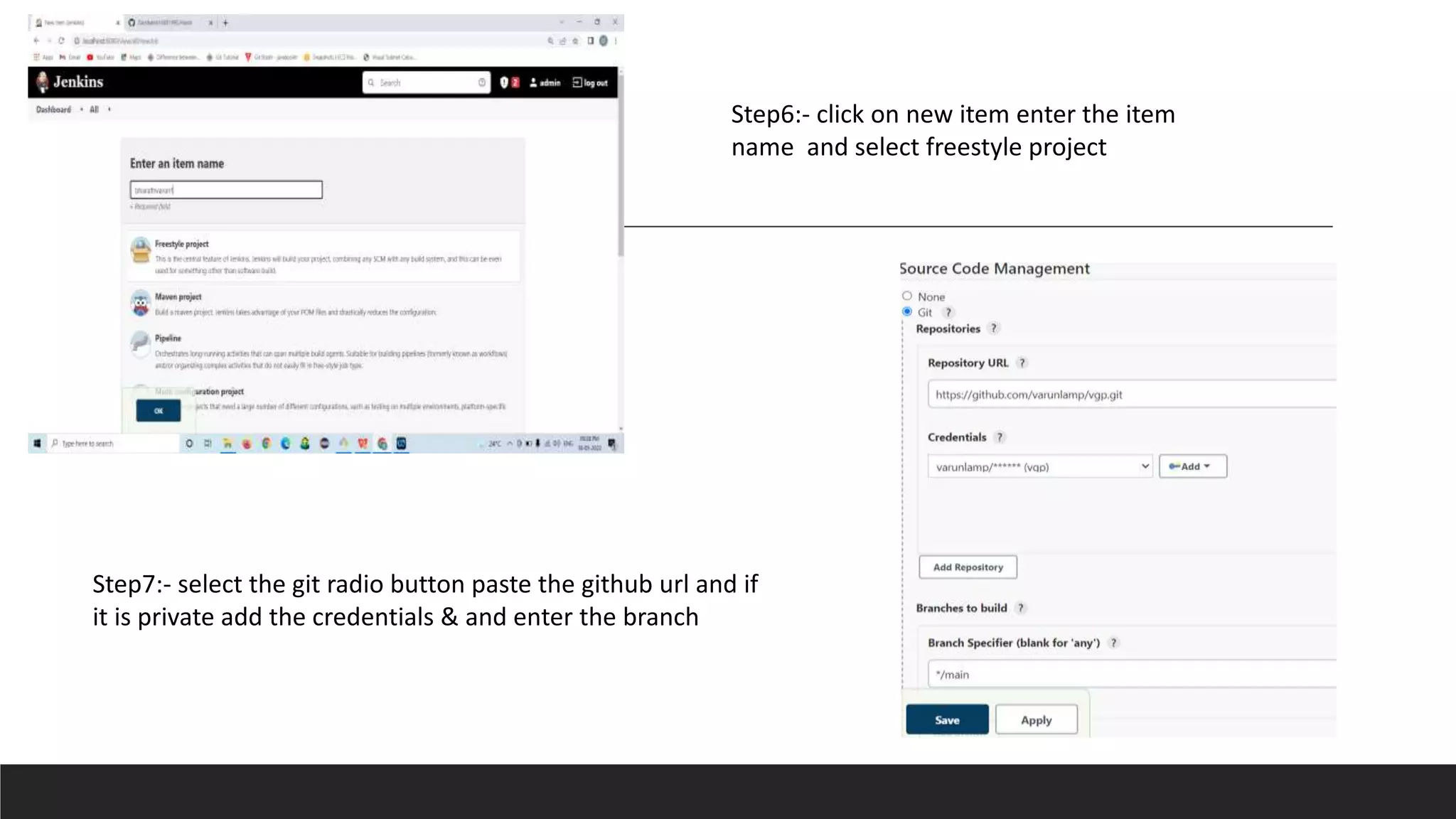
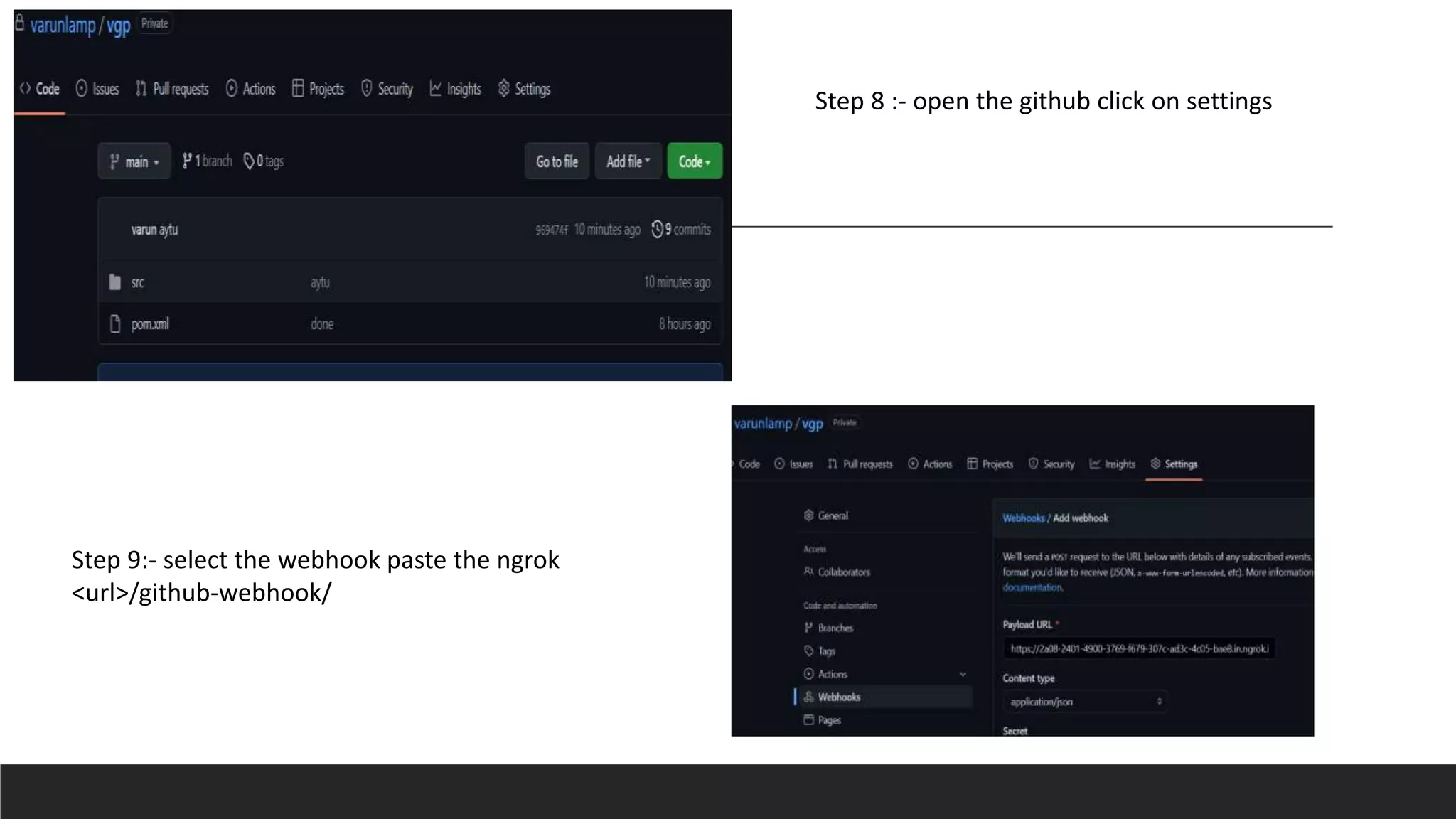
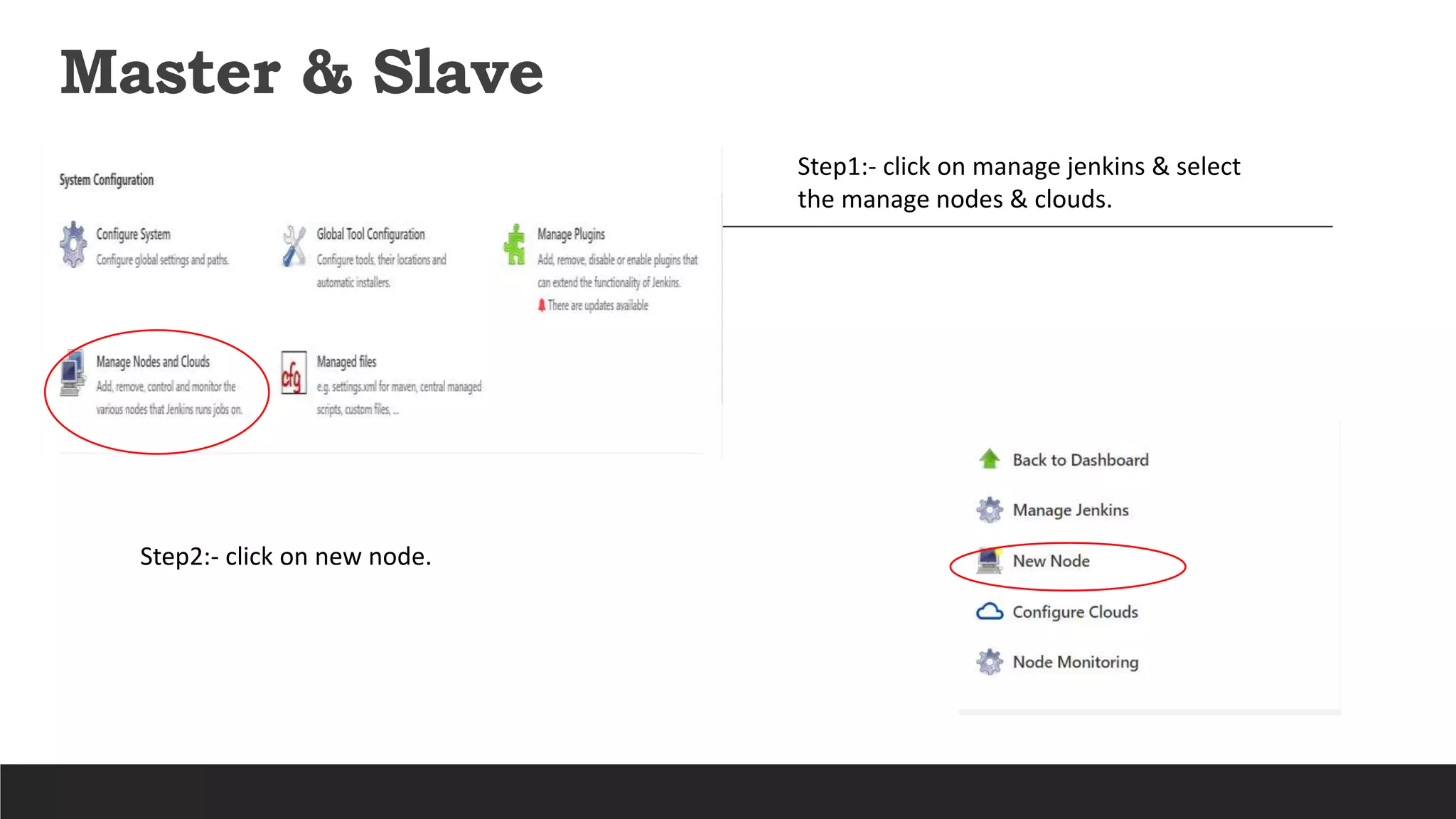
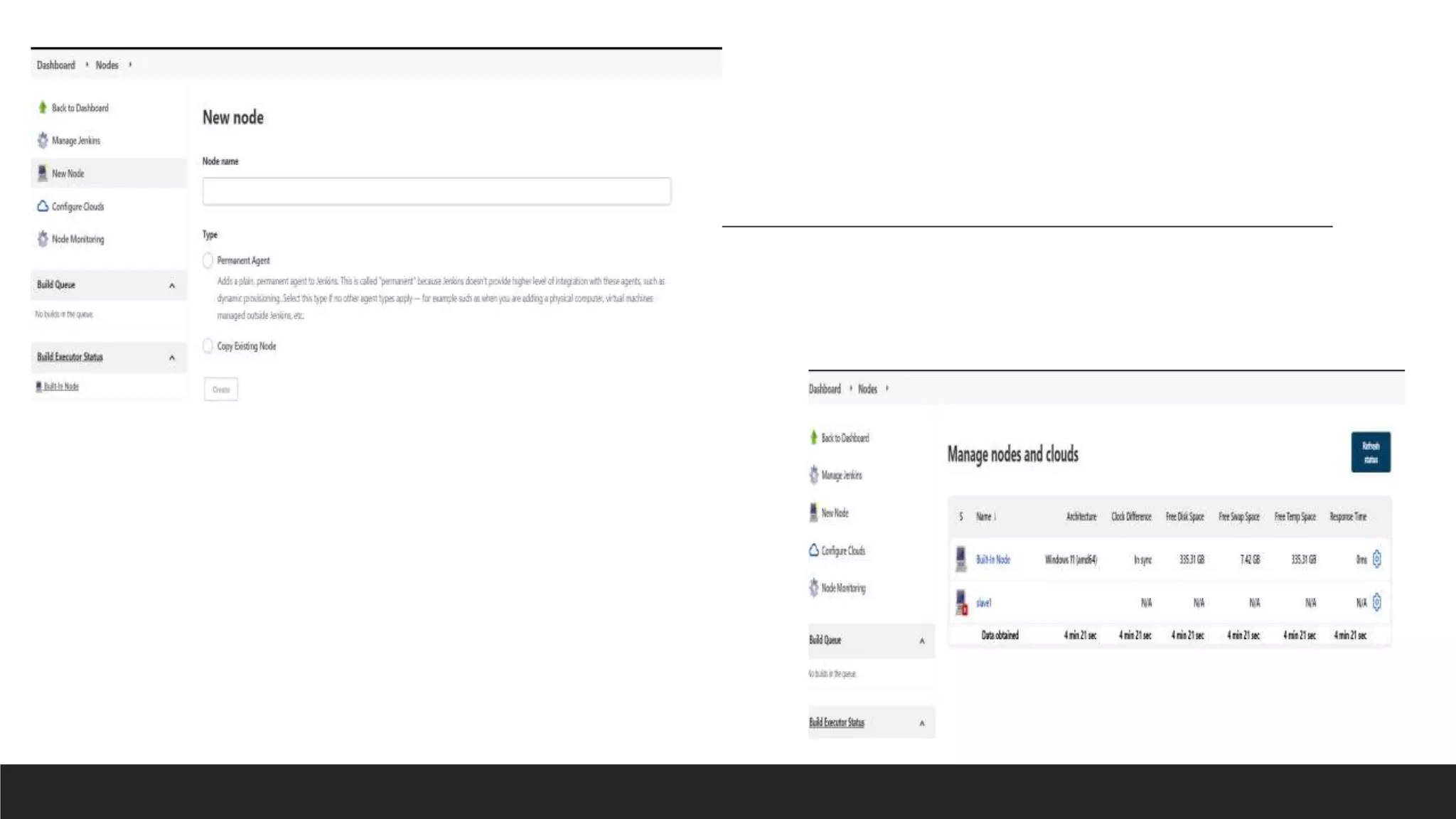
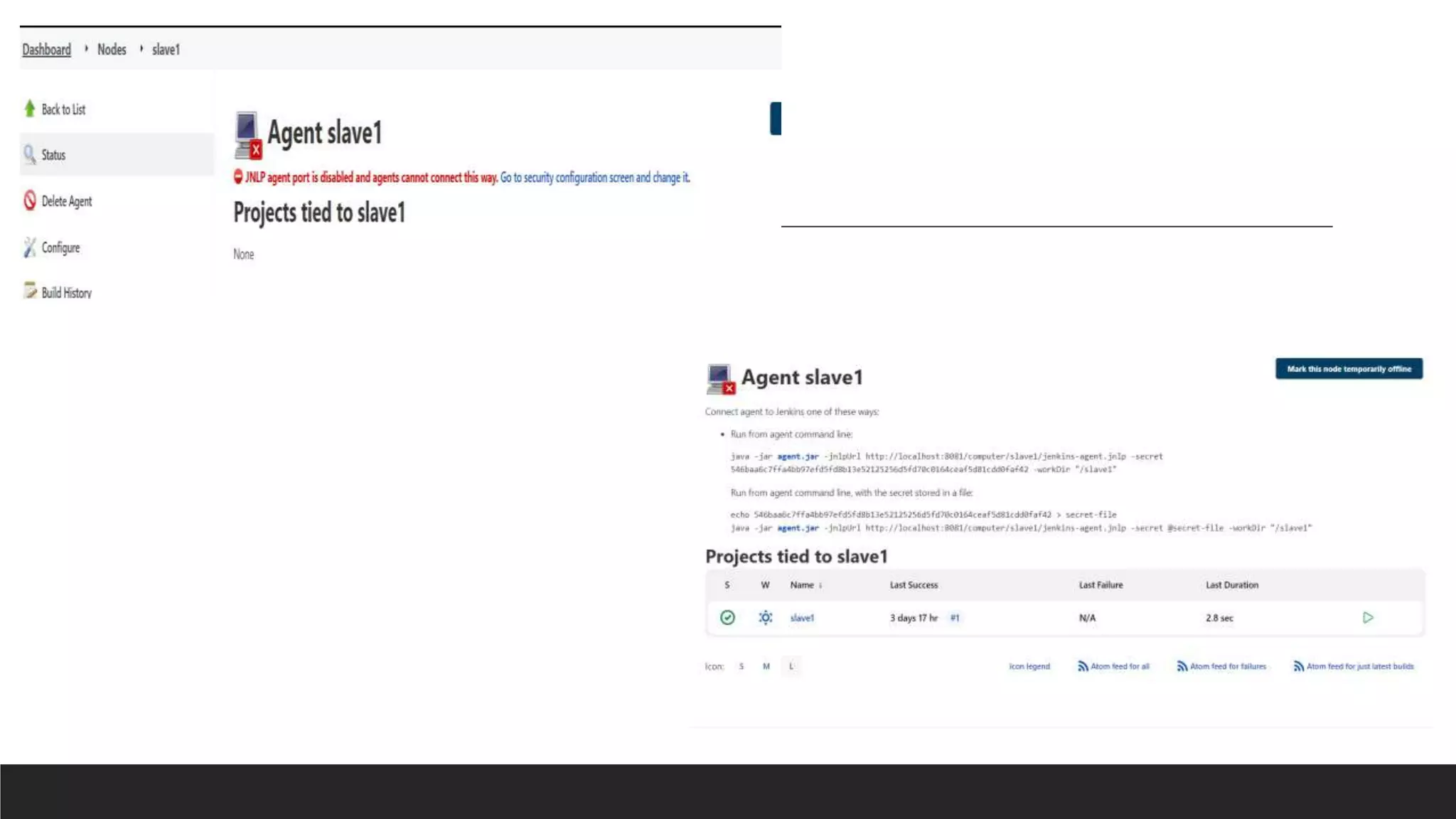
This document provides information on Jenkins, including:
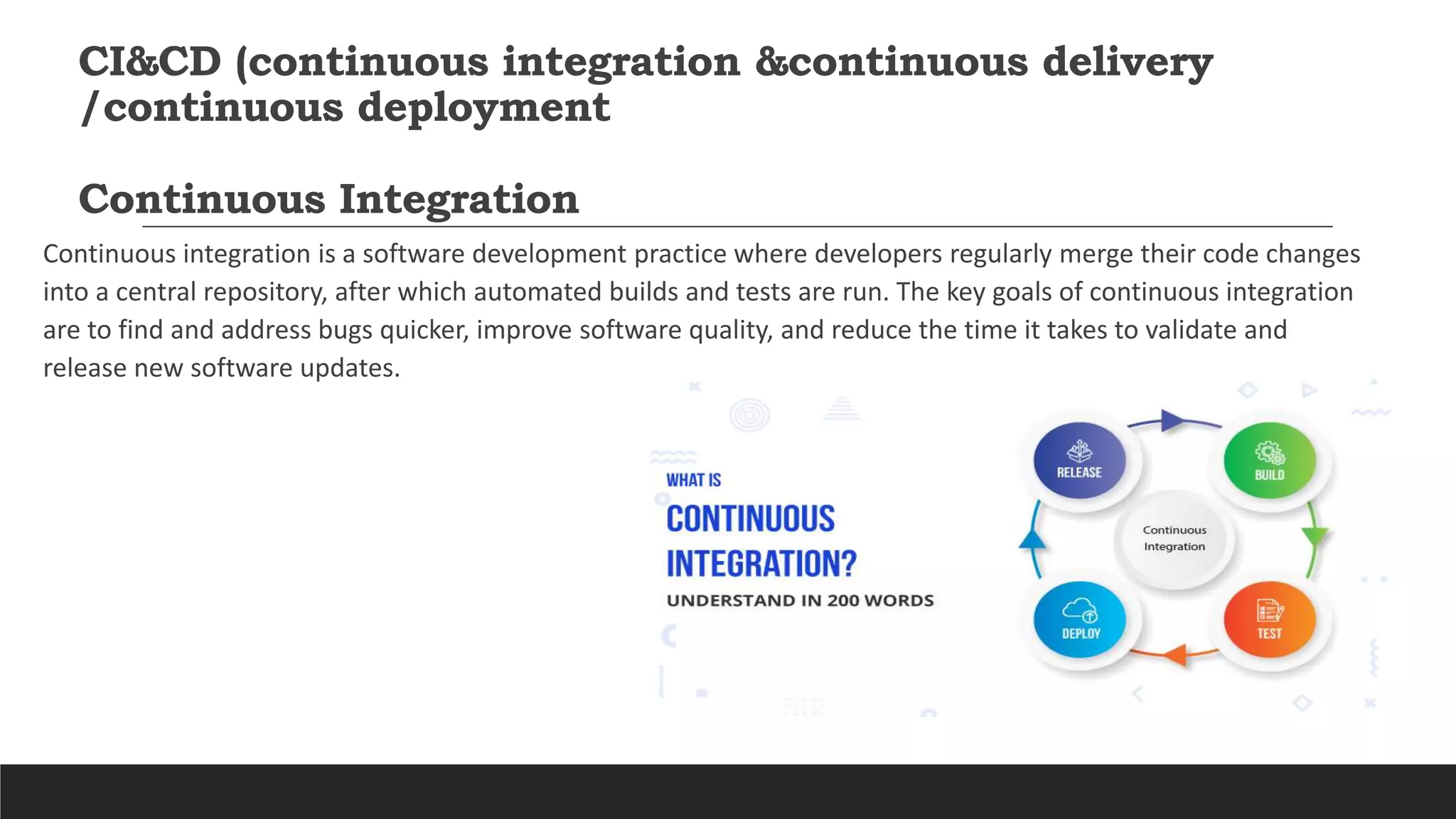
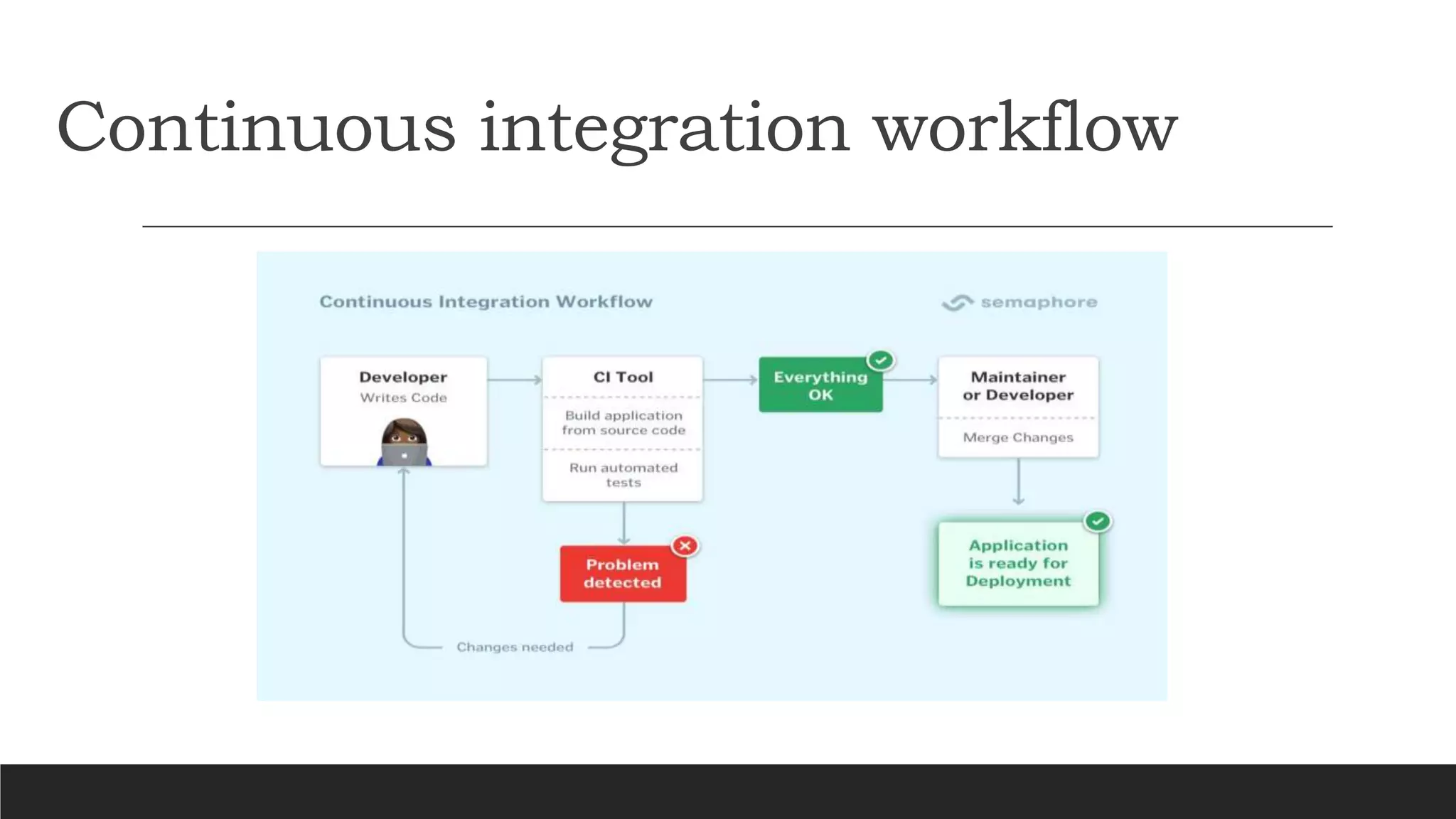
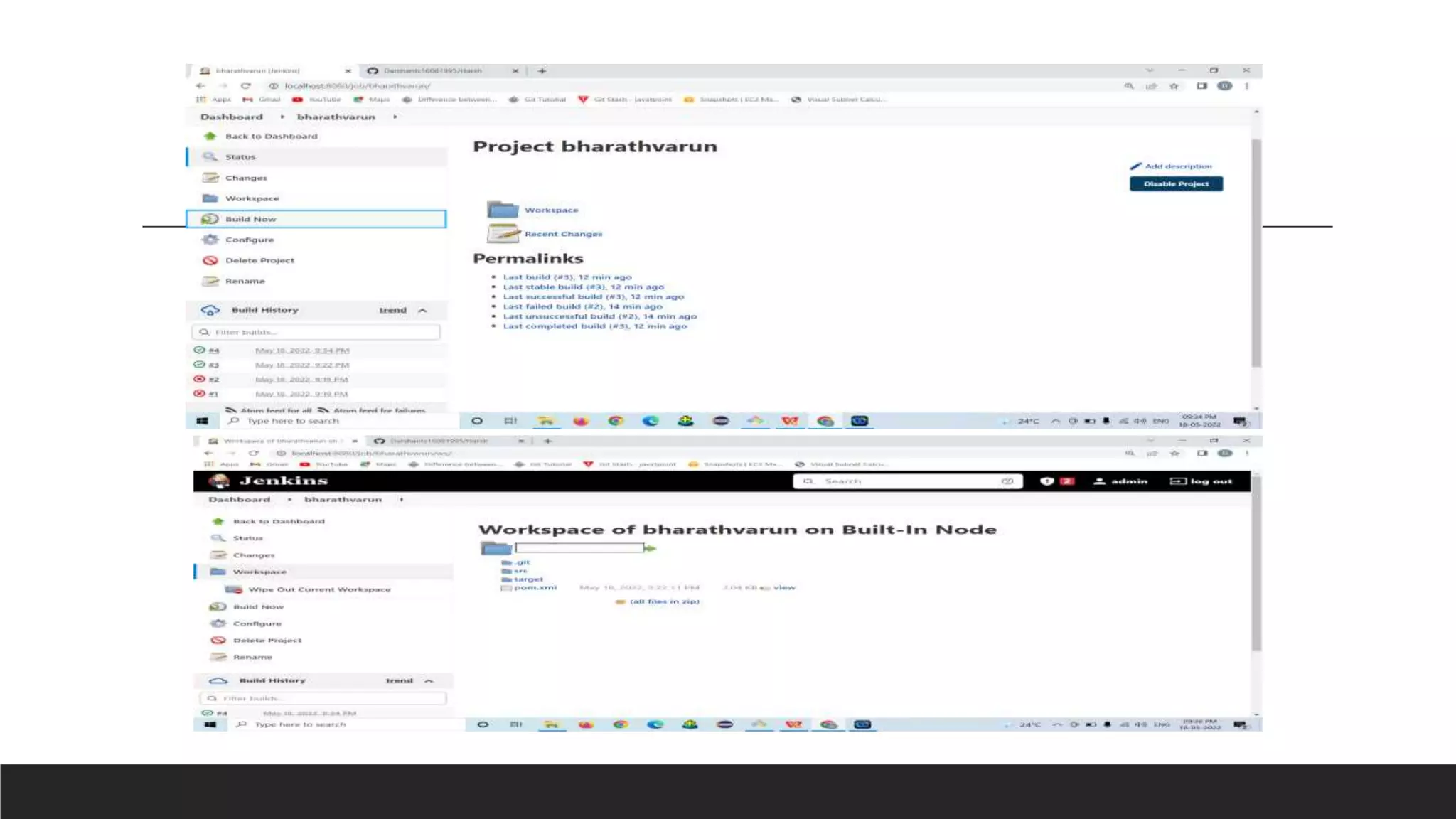
- Jenkins is an open source automation tool that allows continuous integration and delivery of software projects. It builds, tests, and prepares code changes for release.
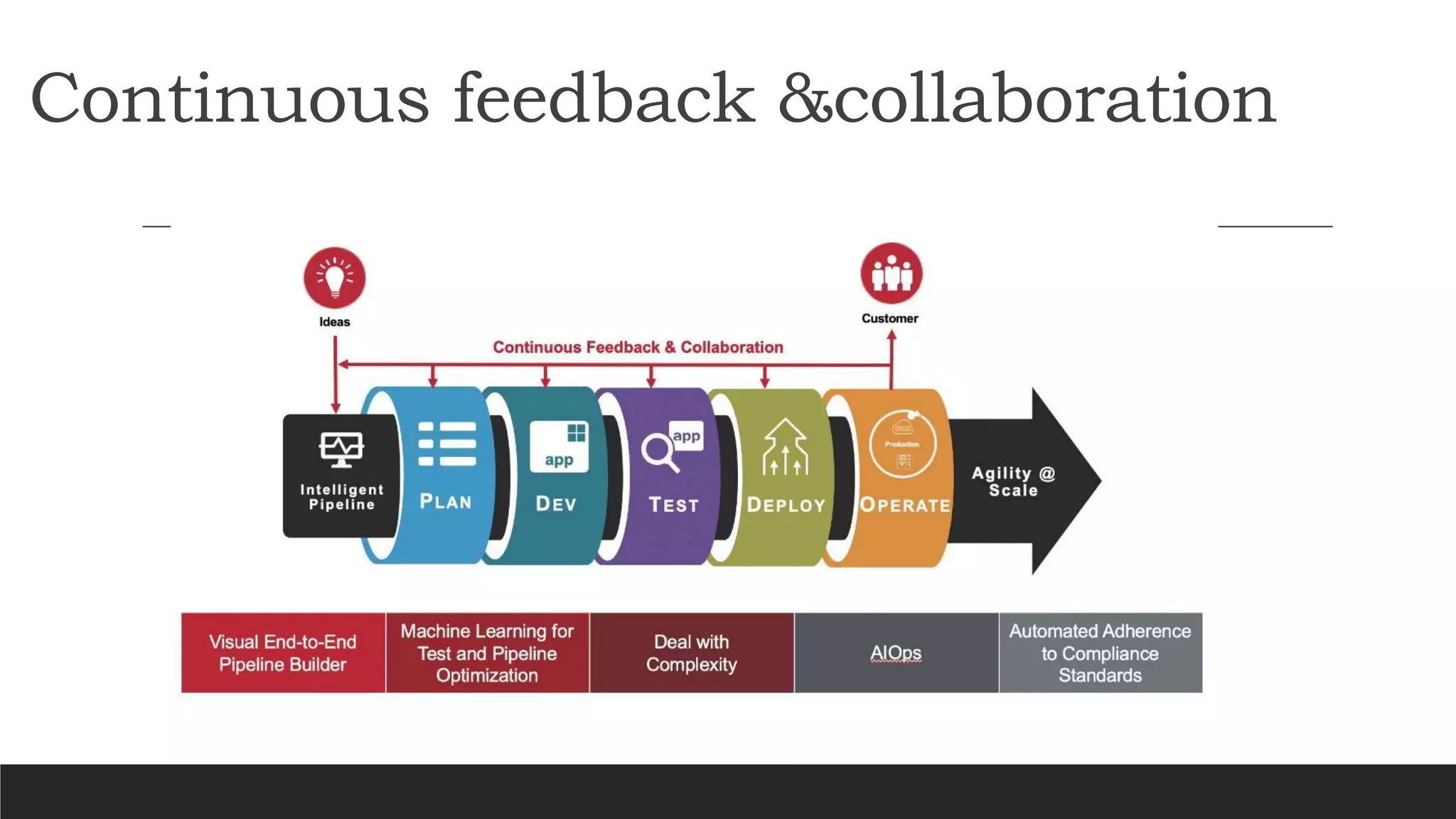
- Key benefits of Jenkins include speeding up the software development process through automation, integrating with many testing and deployment technologies, and making it easier for developers to integrate changes and users to obtain fresh builds.
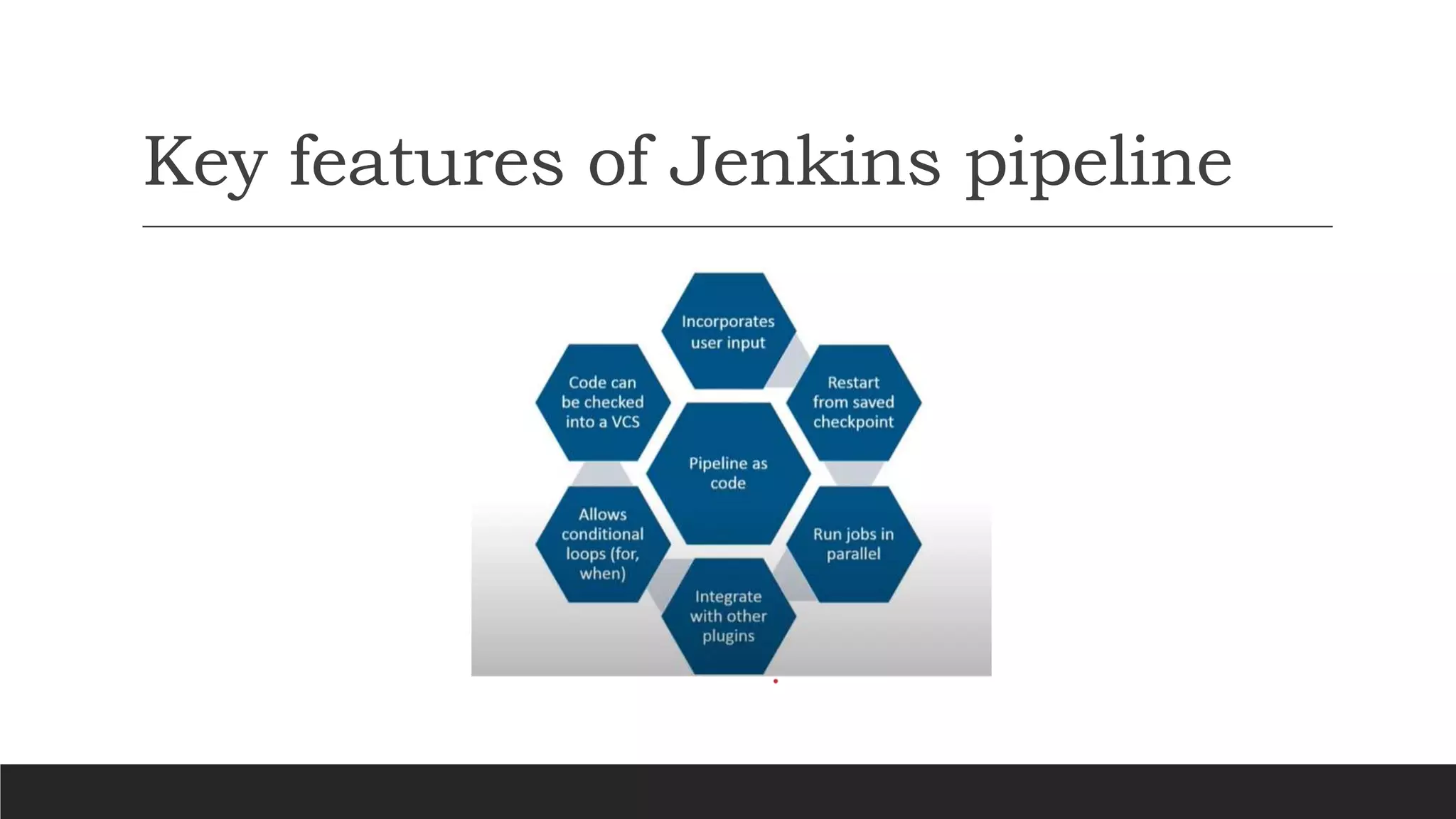
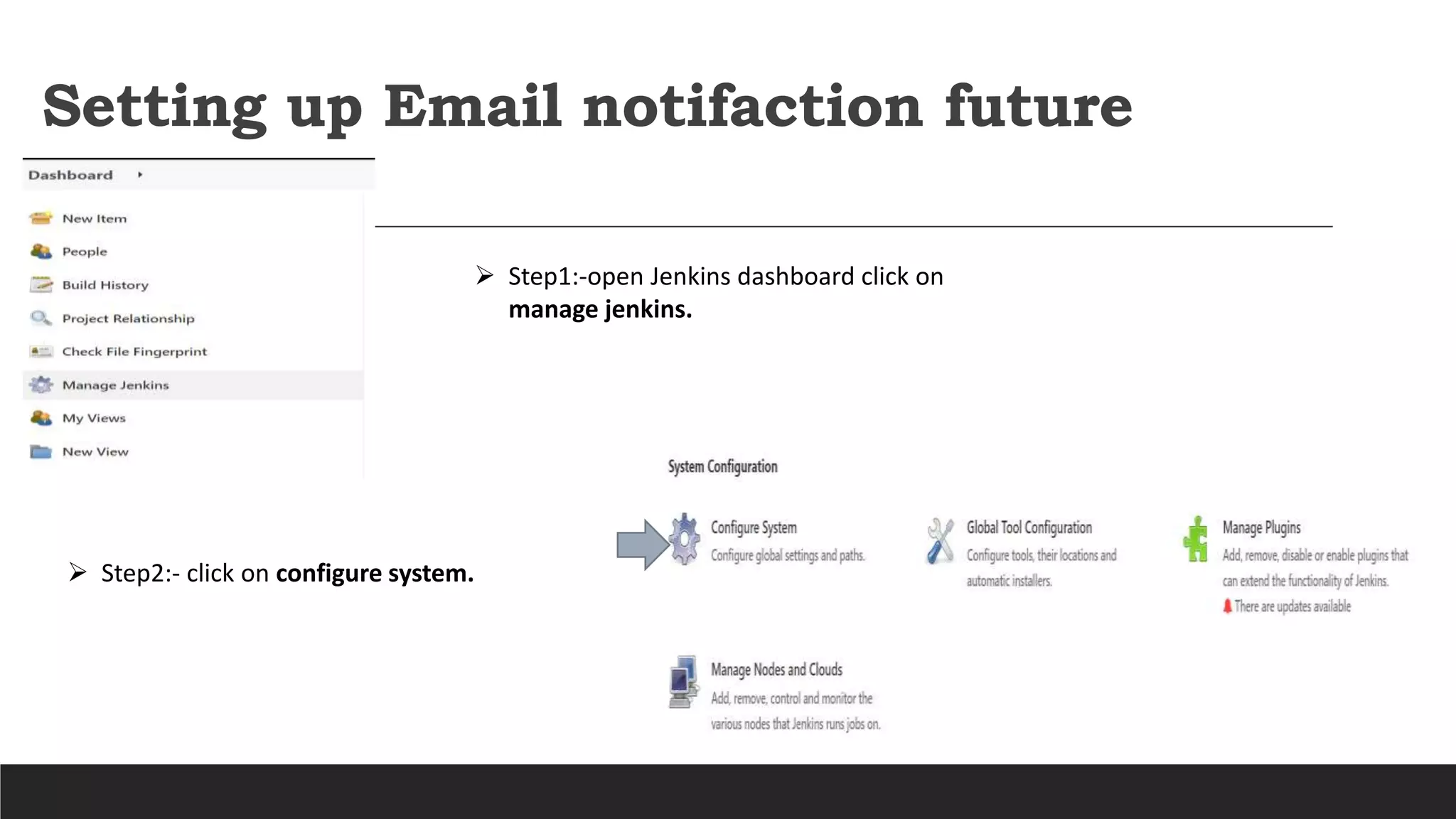
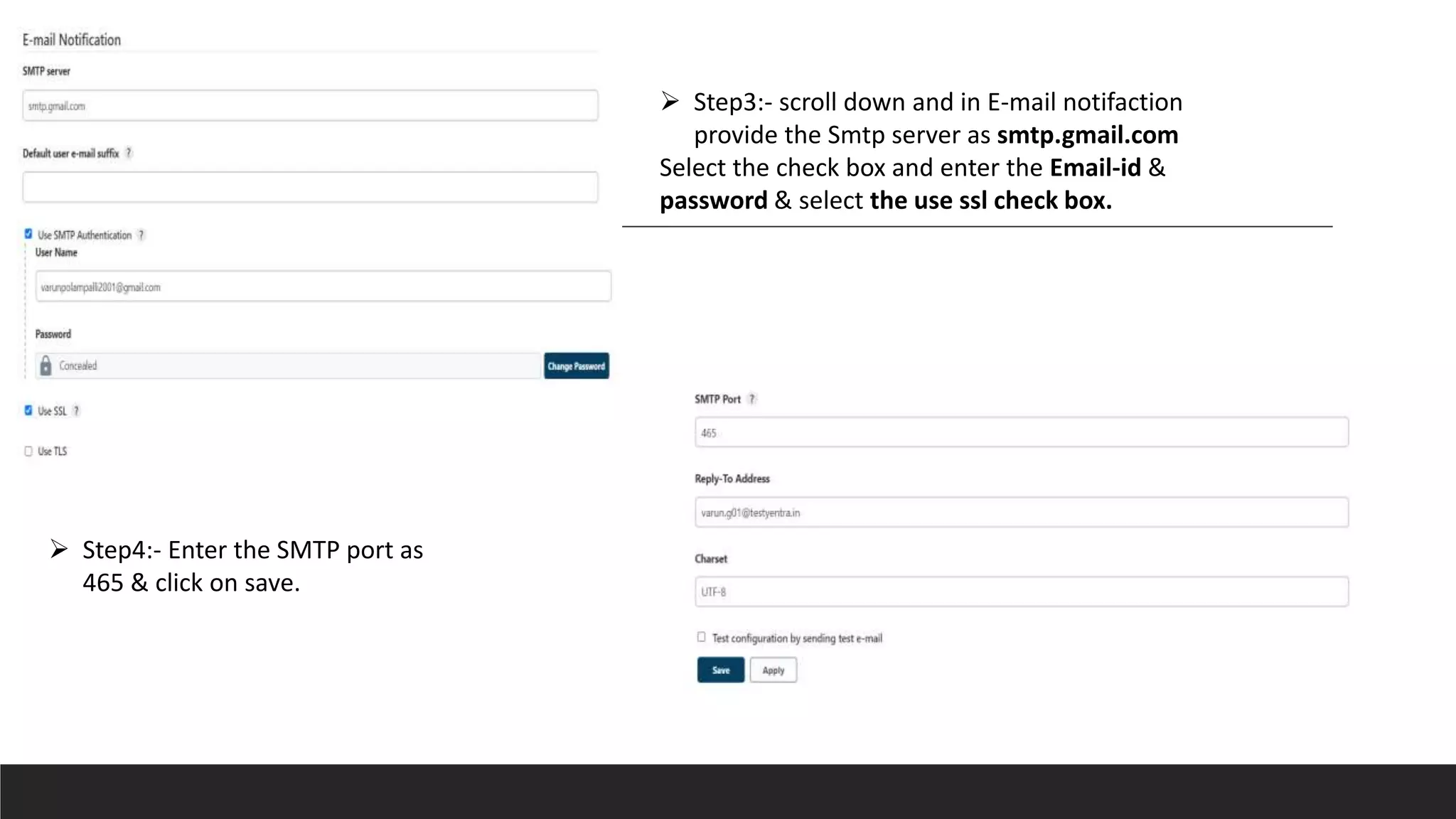
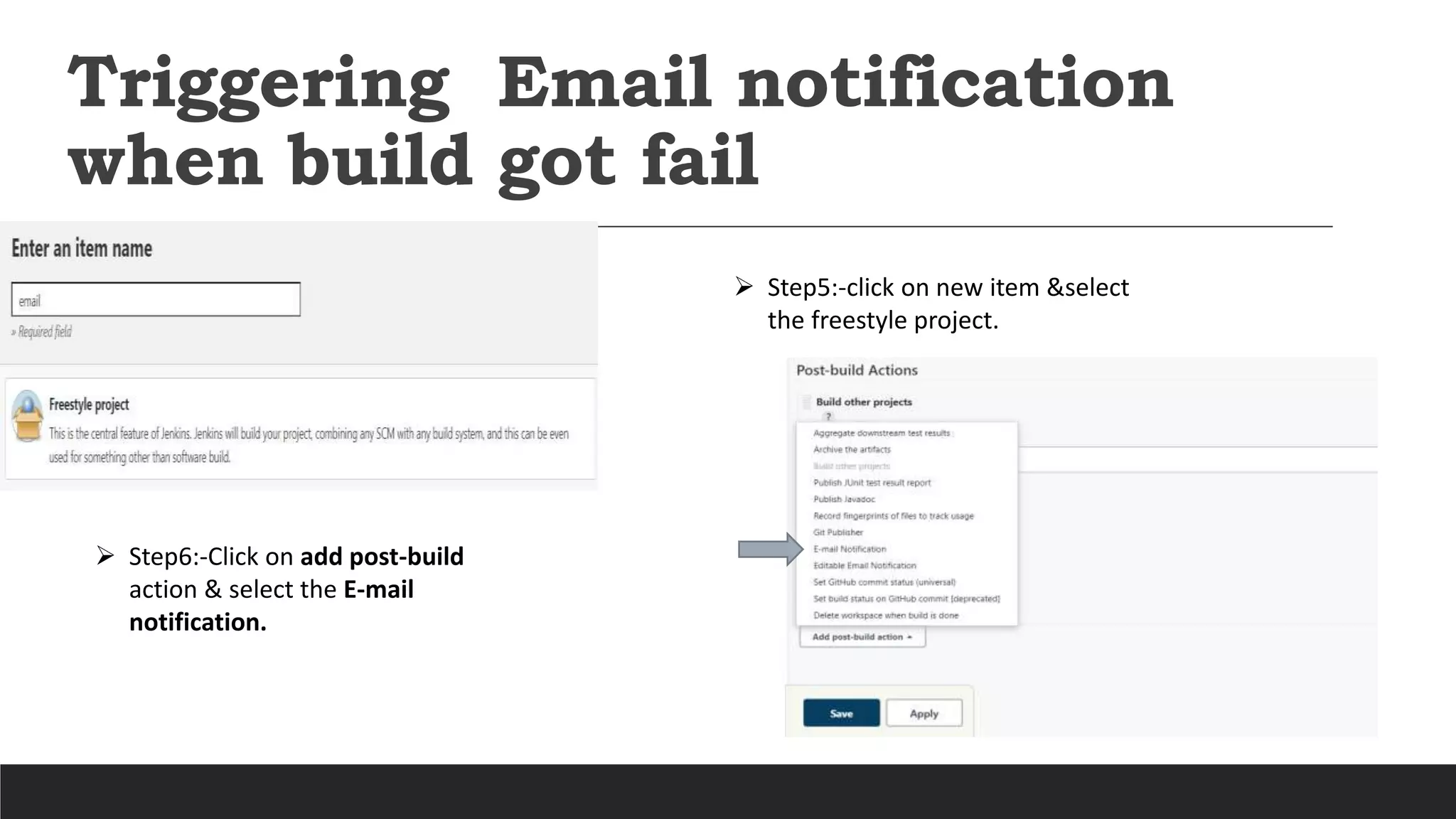
- Jenkins uses plugins to integrate various DevOps stages like build, test, package, deploy, etc. It supports pipelines to automate development tasks.