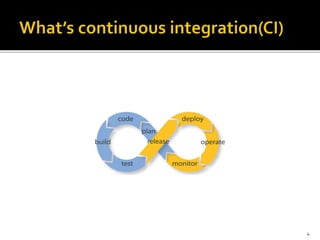
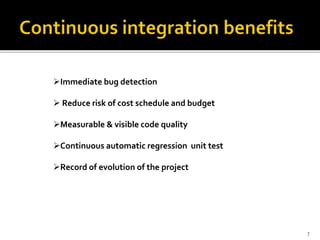
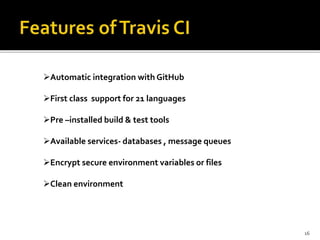
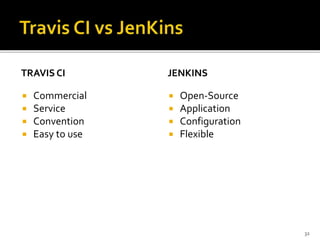
This document provides an overview of continuous integration and compares two popular tools: Travis CI and Jenkins. Continuous integration involves regularly integrating code changes into a shared repository. Martin Fowler's definition is provided. The challenges of integration are discussed. Key aspects of continuous integration like building, testing, and archiving are outlined. Benefits like early bug detection are noted. Travis CI and Jenkins are introduced as popular CI tools. Travis CI is a hosted service that integrates with GitHub, while Jenkins is an open-source application. Their features, uses cases, and examples of companies using each tool are summarized.



























![http://www.uqasar.eu/review-saas-continuous-integration-tools-series/
Continuous Integration (Jenkins/Hudson) - SlideShare
[PPT]CI-201110.ppt
[PDF]Jenkins Continuous Build System
http://www.slideshare.net/bsiggelkow/travis-ci
http://www.slideshare.net/gabevanslv/travis-ci-23997525?related=1
https://docs.travis-ci.com/user/getting-started/
34](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/new-160121120311/85/Continuous-integration-34-320.jpg)
