This document discusses Continuous Integration (CI), including its definition, workflow, popular tools, requirements, principles, functionalities, and Jenkins configuration. CI is a software development practice where team members frequently integrate their work and have it automatically tested. The workflow involves integrating code changes, building, testing, archiving, and deploying. Popular CI tools include Jenkins, TravisCI, TeamCity, BuildBot, and Bamboo. Jenkins can be installed via packages or by running its WAR file. The advantages of CI include easier configuration, detecting integration issues early, and keeping the codebase bug-free. Initial setup and developing tests can be disadvantages.



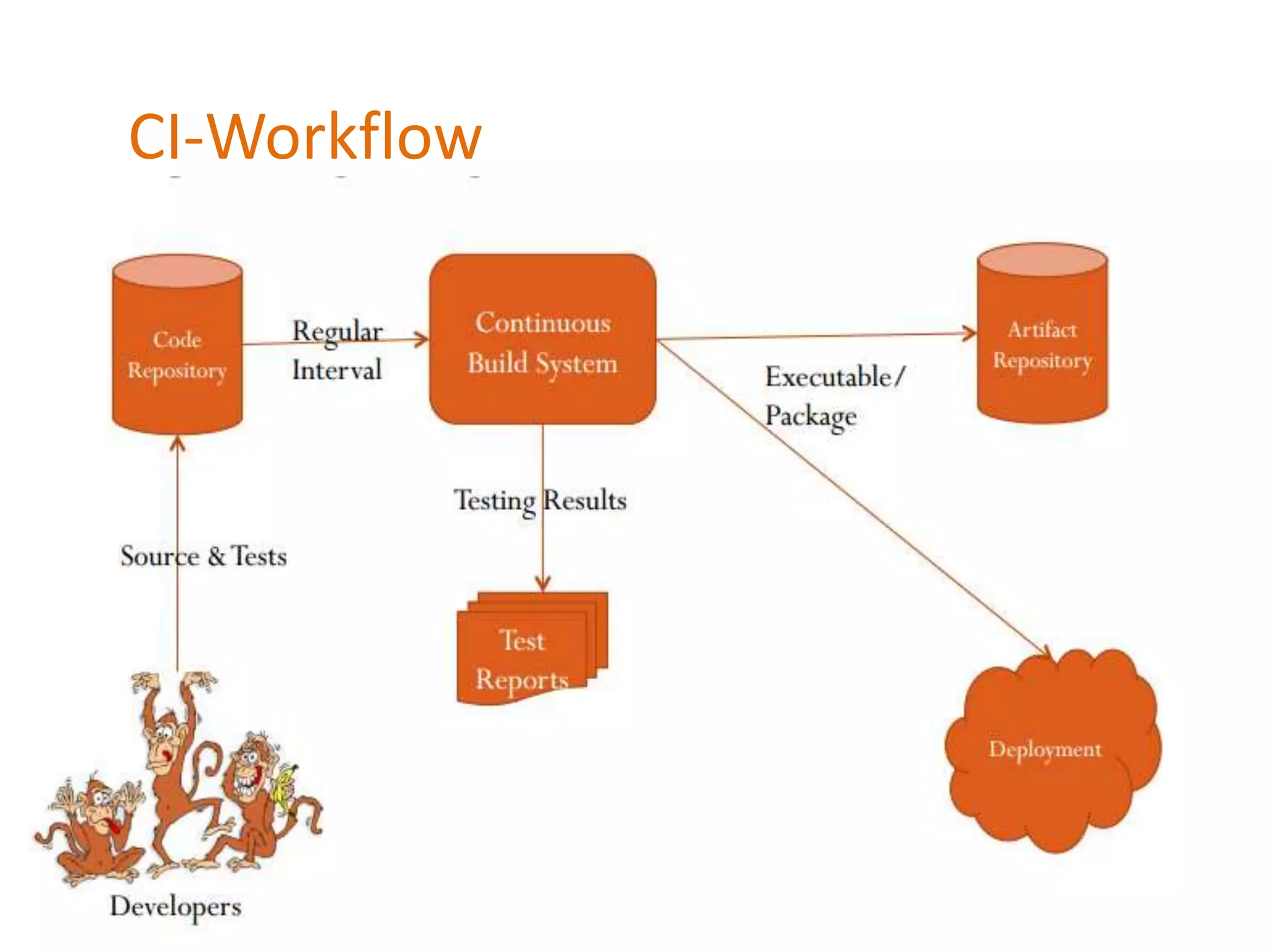
![Workflow contains following steps:
• Integrated
All changes up until some point are combined into the project.
• Built
The code is compiled into a executable or package
• Tested
Automated test suites are run
• Archived
Versioned and stored
• Deployed
Loaded onto the system[server] where developers can interact with it.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/contineousintegration-140326230034-phpapp01/75/Contineous-integration-5-2048.jpg)





![Jenkins configuration
We can install Jenkins in following ways:
Installing Jenkins on Ubuntu
Jenkins provides Debian/Ubuntu packages which
install Jenkins and register Jenkins as start
service[/etc/init.d/jenkins]
Using the .war file of Jenkins
start Jenkins directly via the command line with
java -jar jenkins*.war.
Then jenkins running under the following URL:
http://localhost:8080/jenkins](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/contineousintegration-140326230034-phpapp01/75/Contineous-integration-11-2048.jpg)



![Useful links
• http://jenkins-ci.org/ [To download .war]
• http://www.blackbuild.com/15-must-have-plugins-
for-jenkins/ [Plugins]
• http://thefutureofdeployment.com/set-database-
continuous-integration-automated-deployment-
jenkins-lunch/ [To run database scripts]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/contineousintegration-140326230034-phpapp01/75/Contineous-integration-15-2048.jpg)